AmlodipineCalcium channel blocker CAS# 88150-42-9 |
- Azelnidipine
Catalog No.:BCC4400
CAS No.:123524-52-7
- Verapamil HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4747
CAS No.:152-11-4
- Gabapentin HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4502
CAS No.:60142-95-2
- Zonisamide sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4240
CAS No.:68291-98-5
- Manidipine
Catalog No.:BCC4404
CAS No.:89226-50-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 88150-42-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 2162 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H25ClN2O5 | M.Wt | 408.88 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 30 mg/mL (73.37 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
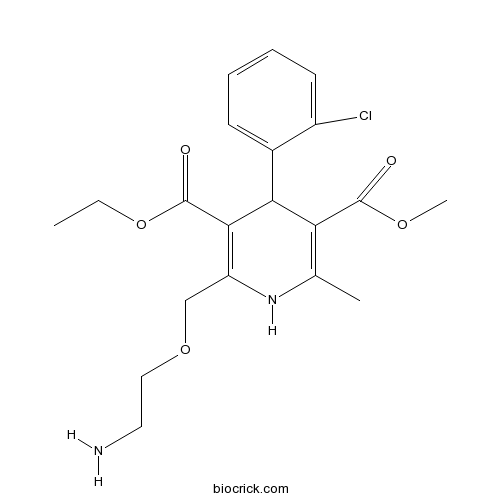
| Chemical Name | 3-O-ethyl 5-O-methyl 2-(2-aminoethoxymethyl)-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-6-methyl-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate | ||
| SMILES | CCOC(=O)C1=C(NC(=C(C1C2=CC=CC=C2Cl)C(=O)OC)C)COCCN | ||
| Standard InChIKey | HTIQEAQVCYTUBX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H25ClN2O5/c1-4-28-20(25)18-15(11-27-10-9-22)23-12(2)16(19(24)26-3)17(18)13-7-5-6-8-14(13)21/h5-8,17,23H,4,9-11,22H2,1-3H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Amlodipine Dilution Calculator

Amlodipine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4457 mL | 12.2285 mL | 24.4571 mL | 48.9141 mL | 61.1426 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4891 mL | 2.4457 mL | 4.8914 mL | 9.7828 mL | 12.2285 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2446 mL | 1.2229 mL | 2.4457 mL | 4.8914 mL | 6.1143 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0489 mL | 0.2446 mL | 0.4891 mL | 0.9783 mL | 1.2229 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0245 mL | 0.1223 mL | 0.2446 mL | 0.4891 mL | 0.6114 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Amlodipine is a long-acting calcium channel blocker.Amlodipine is a dihydropyridine calcium antagonist (calcium ion antagonist or slow-channel blocker) that inhibits the movement of calcium ions into vascular smooth muscle cells and cardiac muscle cells.
- DuP 697
Catalog No.:BCC7064
CAS No.:88149-94-4
- Dauriporphine
Catalog No.:BCN7903
CAS No.:88142-60-3
- 6-Formyllimetin
Catalog No.:BCN3427
CAS No.:88140-31-2
- Daphniyunnine B
Catalog No.:BCN4429
CAS No.:881388-88-1
- Daphniyunnine A
Catalog No.:BCN4428
CAS No.:881388-87-0
- KU-0060648
Catalog No.:BCC1110
CAS No.:881375-00-4
- Notoginsenoside Fc
Catalog No.:BCN3853
CAS No.:88122-52-5
- JNJ-26854165 (Serdemetan)
Catalog No.:BCC2240
CAS No.:881202-45-5
- Valganciclovir
Catalog No.:BCC2026
CAS No.:88110-89-8
- Notoginsenoside Fe
Catalog No.:BCN3852
CAS No.:88105-29-7
- 30-Hydroxygambogic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3081
CAS No.:881027-36-7
- HDS 029
Catalog No.:BCC7441
CAS No.:881001-19-0
- G-1
Catalog No.:BCC6045
CAS No.:881639-98-1
- 26RFa
Catalog No.:BCC6163
CAS No.:881640-56-8
- Levistilide A
Catalog No.:BCN1197
CAS No.:88182-33-6
- 3,5,9-Trihydroxyergosta-7,22-dien-6-one
Catalog No.:BCN1318
CAS No.:88191-14-4
- MDL 28170
Catalog No.:BCC2352
CAS No.:88191-84-8
- iMDK
Catalog No.:BCC6365
CAS No.:881970-80-5
- Clofibric Acid
Catalog No.:BCC4652
CAS No.:882-09-7
- (-)-Chelidonine
Catalog No.:BCN7456
CAS No.:88200-01-5
- Notopterol
Catalog No.:BCN5386
CAS No.:88206-46-6
- H-Leu-OAll.TosOH
Catalog No.:BCC2969
CAS No.:88224-03-7
- H-Ile-OAll.TosOH
Catalog No.:BCC2963
CAS No.:88224-05-9
- P005091
Catalog No.:BCC1287
CAS No.:882257-11-6
[Effects of Amlodipine/Lisinopril Fixed-Dose Combination on Severity of Left Ventricular Hypertrophy and Parameters of Myocardial Stiffness in Patients With Hypertension].[Pubmed:28290816]
Kardiologiia. 2016 Dec;56(11):27-37.
AIM: To assess effects of 12 weeks treatment with the Amlodipine/lisinopril fixed-dose combination (ALFDC) on the left ventricular (LV) mass index (LVMI), parameters of LV and left atrial stiffness. METHODS: At phase 1 of the study we examined 44 healthy subjects (21 men, 23 women, mean age 51.5+/-1.0 years) and 60 untreated patients (31 men, 29 women, mean age 53.6+/-0.8 years) with stage II grade 1-2hypertension. Myocardial stiffness parameters, LVMI were calculated using data of transthoracic echocardiography. 2-D speckle tracking echocardiography was used for determination of LV myocardial global longitudinal peak strain (GLPS). All participants underwent ambulatory blood pressure (BP) monitoring, and office BP measurement. At phase 2 a subgroup of 30 untreated patients (16 men, 14 women; mean age 52.7+/-1.11years) received ALFDC in a start dose of 5 mg/10 mg titrated every 14 days to achieve BP<140/90 mm Hg. Therapy in selected doses was continued for 12 weeks thereafter. RESULTS: In hypertensive patients LV GLPS was significantly lower while LA stiffness index higher compared with controls (17.08+/-0.38 vs. 19.91+/-0.41%, p<0.001, and 0.20+/-0.01 vs. 0.16+/-0.01, p<0.01, respectively). There were no significant differences in the LA tissue Doppler derived strain, LV end-systolic elastance, LA expansion index between hypertensive and control groups. After ALFDC therapy BP was significantly (p<0.001) reduced: systolic (S)BP from 154.4+/-2.7 to 130.6+/-1.2, diastolic (D)BP from 96.5+/-1.3 to 83.0+/-0.5 mm Hg. After therapy LV GLPS, LA expansion index, LV diastolic elastance significantly increased (from 17.10+/-0.57 to 18.29+/-0.35%, p<0.01; from 1.47+/-0.08 to 1.68+/-0.08, p<0.001; from 9.25+/-0.99 [10-2] to 10.88+/-1.0 8 [10-2], p<0.05, respectively) while LVMI, LV end-diastolic stiffness, and LA stiffness index significantly (p<0.001) decreased (from 129.4+/-4.5 to 111.8+/-3.3 g/m2, from 0.16+/-0.01 to 0.12+/-0.01 mm Hg/ml, from 0.21+/-0.02 to 0.15+/-0.01, respectively). Change in the LA tissue Doppler derived strain correlated with the change in dynamics of nighttime SBP (r=-0.410, p<0.05). There was direct relationship between change in LV diastolic elastance and nighttime DBP (r=0.424; p<0.05); and an inverse correlation between changes in LV end-diastolic stiffness and dynamics of the daytime SBP and DBP (r=-0.404; p<0.05 and r=-0.364; p<0.05, respectively). Change of LVMI after ALFDC treatment correlated with dynamics of 24-hour, daytime SBP, and daytime pulse pressure (r=0.382, p<0.05, r=0.478, p<0.01, and r=0.364, p<0.05, respectively). CONCLUSION: In untreated patients with stage II, 1-2 degree hypertension 12-week therapy with ALFDC allowed to achieve target BP levels, reduced severity of LV hypertrophy and improved stiffness parameters of the myocardium.
Development, validation and comparison of near infrared and Raman spectroscopic methods for fast characterization of tablets with amlodipine and valsartan.[Pubmed:28340729]
Talanta. 2017 May 15;167:333-343.
The objective of this study was to develop, validate and compare NIR and Raman spectroscopic methods for fast characterization in terms of API content and tensile strength of fixed-dose combination tablets containing Amlodipine and valsartan. For the APIs assay NIR-transmittance and Raman-reflectance methods were considered, whereas for the tensile strength assay Raman spectra were recorded in reflectance configuration and NIR spectra were recorded in both reflectance and transmittance. Multivariate calibration models (PLS) were built by applying different pre-processing methods (SNV, MSC, SD+SNV) on certain spectral regions. Correlating pre-processed spectral data with tablet properties resulted in highly predictive models except in the case of NIR-transmittance spectra for tensile strength estimation. The best models selected by cross-validation were further validated on independent samples in terms of linearity, trueness, accuracy and precision. Using Bland and Altman analysis the analytical performance of the NIR and Raman methods were compared, demonstrating their similarity considering the investigated applications. The two spectroscopic methods can be used in association to confirm each others results for at-line characterization of the pharmaceutical product.
Blood pressure-lowering efficacy and safety of perindopril/indapamide/amlodipine single-pill combination in patients with uncontrolled essential hypertension: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, controlled trial.[Pubmed:28306636]
J Hypertens. 2017 Jul;35(7):1481-1495.
OBJECTIVES: This 4-month, double-blind, randomized, controlled trial was designed to demonstrate the superiority of perindopril/indapamide/Amlodipine single pill over perindopril/indapamide after 1 month and to determine further up-titration efficacy and safety in patients with mild-to-moderate hypertension. METHODS: After a 1-month run-in period on perindopril/indapamide 5/1.25 mg, patients with SBP/DBP at least 150/95 mmHg and no diabetes or renal insufficiency received perindopril/indapamide/Amlodipine 5/1.25/5 mg single pill or continued on the same treatment. At 1, 2, and 3 months, patients with uncontrolled blood pressure (SBP/DBP >/= 140/90 mmHg) were gradually up-titrated with a higher dose of the triple therapy up to perindopril/indapamide/Amlodipine 10/2.5/10 mg in both groups. Efficacy was assessed on office supine SBP (main criterion) and DBP, blood pressure control, and response rates. Treatment effect on ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) and home blood pressure monitoring (HBPM) parameters was also assessed in two subpopulations of 276 and 263 patients, respectively. RESULTS: A total of 454 hypertensive patients (diabetes and renal insufficiency excluded) were randomized, 227 to each group (56% were men, mean age was 55 years, blood pressure 162.3/101.1 mmHg). After 1 month, superior SBP (-3.1 mmHg, P = 0.02) and DBP (-2.8 mmHg, P < 0.001) reductions were observed with perindopril/indapamide/Amlodipine, which were even more pronounced after excluding white-coat effect in the sustained hypertension population (-5.3/-3.7 mmHg). Similar results were observed in terms of blood pressure response (72 vs. 53%, P < 0.0001) and control rates (32 vs. 25%, P = 0.005). Up-titration was effective at each visit in both treatment arms (P < 0.001). Both ABPM and HBPM results confirmed the superiority of the triple therapy at 1 month on ASBP/ADBP and HSBP/HDBP: -4.5/-2.0 mmHg for ABPM (P < 0.001/P = 0.04), and -4.9/-3.1 mmHg for HBPM (both, P < 0.001). Up-titration steps resulted in further significant decreases in both ABPM and HBPM. Both treatment regimens were well tolerated regarding adverse events or laboratory testing. In particular, peripheral edema known to be Amlodipine dose dependent, appeared in only a few cases, none with the highest dose. Hypotension, orthostatic hypotension, and cough whatever the dose were infrequent. There were no treatment-related serious adverse events. CONCLUSION: Perindopril/indapamide/Amlodipine in a single pill produces superior reductions in blood pressure compared with dual therapy. Triple therapy up-titration was well tolerated and effective leading to BP control rates of over 80%. Analysis of 24-h ABPM and HBPM results corroborated these findings.
[Efficacy and Safety of a Fixed Combination of Perindopril Arginine and Amlodipine in Patients With Hypertension Uncontrolled by Treatment With Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers in Real Clinical Practice. Results of the PREVOSHODSTVO (SUPERIORITY) Program].[Pubmed:28290831]
Kardiologiia. 2017 Jan;(1):30-36.
The article presents preliminary results of a subanalysis of PREVOSHODSTVO (SUPERIORITY) phase IV study. Aim of this subanalysis was to assess efficacy and tolerability of a fixed-dose perindopril/Amlodipine combination (FDPAC) in patients with arterial hypertension (AP) uncontrolled on previous treatment with angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs). MATERIAL AND METHODS: We included in this analysis 125 patients (70.4% women, mean age 57.2+/-10.0 years), final analysis of efficacy was performed on 124 patients. Before inclusion in the study 47 patients received ARB either as monotherapy (n=47), or components of free-dose (n=49) and fixed-dose (n=28) dual combinations with other antihypertensive drugs. Dose. of FDPAC was determined by physician. Duration of observation period was 24 weeks. RESULTS: After 2weeks significant reduction of blood pressure (BP) (from 159.9+/-8.8/93.8+/-6.8 to 143.9+/-10.7/86.4+/-6.5 mm Hg, p<0.001) was noted. At final visit mean BP was 125.1+/-7.1/78.1+/-4.7 mm Hg. Number of patients with target BP (< 140/90 mm Hg) was 24, 75 and 97% after 1, 3, and 6 months, respectively. Visit-to-visit systolic BP variability by the end of the observation period decreased to 3.8+/-2.3 mm Hg. CONCLUSION: In patients, whose hypertension was not controlled by treatment with ARBs the fixed-dose combination of perindopril/Amlodipine provided high percentage of achievement of target BP and reduction of long-term BP variability.


