Azilsartan MedoxomilAngiotensin II receptor type 1 antagonist CAS# 863031-21-4 |
- AST-1306 TsOH
Catalog No.:BCC4043
CAS No.:1050500-29-2
- Compound 56
Catalog No.:BCC3615
CAS No.:171745-13-4
- AEE788 (NVP-AEE788)
Catalog No.:BCC2520
CAS No.:497839-62-0
- AST-1306
Catalog No.:BCC3727
CAS No.:897383-62-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 863031-21-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11238823 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C30H24N4O8 | M.Wt | 568.53 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 125 mg/mL (219.87 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
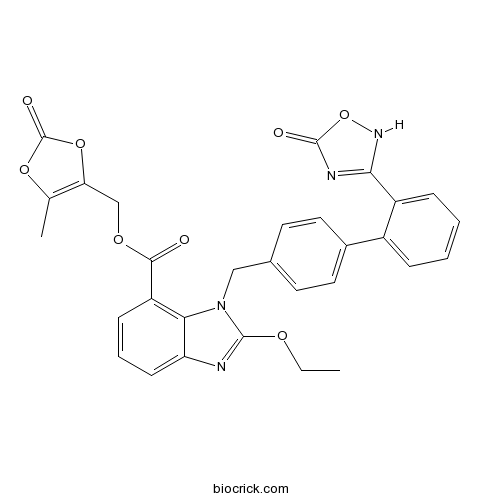
| Chemical Name | (5-methyl-2-oxo-1,3-dioxol-4-yl)methyl 2-ethoxy-3-[[4-[2-(5-oxo-2H-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)phenyl]phenyl]methyl]benzimidazole-4-carboxylate | ||
| SMILES | CCOC1=NC2=CC=CC(=C2N1CC3=CC=C(C=C3)C4=CC=CC=C4C5=NC(=O)ON5)C(=O)OCC6=C(OC(=O)O6)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QJFSABGVXDWMIW-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C30H24N4O8/c1-3-38-28-31-23-10-6-9-22(27(35)39-16-24-17(2)40-30(37)41-24)25(23)34(28)15-18-11-13-19(14-12-18)20-7-4-5-8-21(20)26-32-29(36)42-33-26/h4-14H,3,15-16H2,1-2H3,(H,32,33,36) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Azilsartan Medoxomil Dilution Calculator

Azilsartan Medoxomil Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7589 mL | 8.7946 mL | 17.5892 mL | 35.1784 mL | 43.9731 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3518 mL | 1.7589 mL | 3.5178 mL | 7.0357 mL | 8.7946 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1759 mL | 0.8795 mL | 1.7589 mL | 3.5178 mL | 4.3973 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0352 mL | 0.1759 mL | 0.3518 mL | 0.7036 mL | 0.8795 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0176 mL | 0.0879 mL | 0.1759 mL | 0.3518 mL | 0.4397 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Azilsartan medoxomil(TAK 491) is an orally administered angiotensin II receptor type 1 antagonist with IC50 of 0.62 nM, which used in the treatment of adults with essential hypertension.
- alpha-Amyrin acetate
Catalog No.:BCN4410
CAS No.:863-76-3
- 10-Hydroxycanthin-6-one
Catalog No.:BCN3906
CAS No.:86293-41-6
- Isoiridogermanal
Catalog No.:BCN7613
CAS No.:86293-25-6
- Ganoderic acid TR
Catalog No.:BCN3207
CAS No.:862893-75-2
- Salvianan
Catalog No.:BCN3545
CAS No.:862832-46-0
- IKK-3 Inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1643
CAS No.:862812-98-4
- LY2228820
Catalog No.:BCC2528
CAS No.:862507-23-1
- Imatinib hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1644
CAS No.:862366-25-4
- RA VII
Catalog No.:BCN3512
CAS No.:86229-97-2
- Valeriotriate B
Catalog No.:BCN6751
CAS No.:862255-64-9
- Mirodenafil
Catalog No.:BCC5254
CAS No.:862189-95-5
- Nandrolone undecylate
Catalog No.:BCC9090
CAS No.:862-89-5
- Azilsartan medoxomil monopotassium
Catalog No.:BCC4089
CAS No.:863031-24-7
- Impurity C of Calcitriol
Catalog No.:BCC5384
CAS No.:86307-44-0
- Dasatinib monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCN2177
CAS No.:863127-77-9
- 8-epi-Chlorajapolide F
Catalog No.:BCN6426
CAS No.:863301-69-3
- PSI-6206
Catalog No.:BCC3609
CAS No.:863329-66-2
- Medetomidine
Catalog No.:BCC1736
CAS No.:86347-14-0
- Medetomidine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4351
CAS No.:86347-15-1
- Cebranopadol
Catalog No.:BCC1467
CAS No.:863513-91-1
- Gnetol
Catalog No.:BCN3382
CAS No.:86361-55-9
- 6-Epiharpagide
Catalog No.:BCN4563
CAS No.:86362-16-5
- 5,8-Epidioxyergosta-6,9(11),22-trien-3-ol
Catalog No.:BCN1327
CAS No.:86363-50-0
- Ganoderic acid Y
Catalog No.:BCN2439
CAS No.:86377-52-8
Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling of the antihypertensive interaction between azilsartan medoxomil and chlorthalidone in spontaneously hypertensive rats.[Pubmed:28190245]
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2017 May;390(5):457-470.
A pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic (PK-PD) model was developed to describe the time course of blood pressure following oral administration of Azilsartan Medoxomil (AZM) and/or chlorthalidone (CLT) in spontaneously hypertensive (SH) rats. The drug concentration and pharmacological effects, including systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) were measured by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and tail-cuff manometry, respectively. Sequential PK-PD analysis was performed, wherein the plasma concentration-time data was modeled by one compartmental analysis. Subsequently PD parameters were calculated to describe the time-concentration-response relationship using indirect response (IDR) PK-PD model. The combination of AZ and CLT had greater BP lowering effect compared to AZ or CLT alone, despite of no pharmacokinetic interaction between two drugs. These findings suggest synergistic antihypertensive pharmacodynamic interaction between AZ and CLT noncompetitively, which was simulated by inhibitory function of AZ and stimulatory function of CLT after concomitant administration of the two drugs. The present model was able to capture the turnover of blood pressure adequately at different time points at two different dose levels. The current PK-PD model was successfully utilized in the simulation of PD effect at a dose combination of 0.5 and 2.5 mg/kg for AZ and CLT, respectively. The developed preclinical PK-PD model may provide guidance in the optimization of dose ratio of individual drugs in the combined pharmacotherapy of AZ and CLT at clinical situations.
[Azilsartan Medoxomil Capabilities in Arterial Hypertension and Obesity].[Pubmed:28290827]
Kardiologiia. 2016 Dec;56(11):108-112.
Arterial hypertension (AH) is one of the most common cardiovascular disease. Angiotensin II (AT II), the hormone of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, realizes its negative effects through AT 1 receptors - application point of angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB). Due to different dissociation AT 1 receptors properties some ARBs are more effective than others. Multiply multicenter randomized and observational studies approve the effectiveness and safety of Azilsartan Medoxomil in patients with AH 1-2 grade. Several preclinical studies have shown the additional properties of azilsartan, including increase of insulin sensitivity, cardio- and nephron protection in obesity. In our clinical case we showed the positive influence of Azilsartan Medoxomil on clinic and ambulatory blood pressure, 24-hour aortic stiffness parameters, longitudinal left ventricular strain in patient with AH and obesity.
The Impact of Azilsartan Medoxomil Treatment (Capsule Formulation) at Doses Ranging From 10 to 80 mg: Significant, Rapid Reductions in Clinic Diastolic and Systolic Blood Pressure.[Pubmed:27558280]
J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 2017 Mar;19(3):312-321.
In this phase 2, multicenter, parallel-group, double-blind, dose-ranging study, hypertensive adults (n=449) were randomized to receive one of five doses of a capsule formulation of Azilsartan Medoxomil (AZL-M; 5, 10, 20, 40, 80 mg), olmesartan medoxomil (OLM) 20 mg, or placebo once daily. The primary endpoint was change in trough clinic diastolic blood pressure (DBP) at week 8. AZL-M provided rapid statistically and clinically significant reductions in DBP and systolic blood pressure (SBP) vs placebo at all doses except 5 mg. Placebo-subtracted changes were greatest with the 40 mg dose (DBP, -5.7 mm Hg; SBP, -12.3 mm Hg). Clinic changes with AZL-M (all doses) were statistically indistinguishable vs OLM, although there were greater reductions with AZL-M 40 mg using 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure. Adverse event frequency was similar in the AZL-M and placebo groups. Based on these and other findings, subsequent trials investigated the commercial AZL-M tablet in the dose range of 20 to 80 mg/d.
[Hronotherapy Aspects of Efficiency Azilsartan Medoxomil in Combination Therapy in Patients With Hypertension and Metabolic Syndrome].[Pubmed:28290893]
Kardiologiia. 2016 Oct;56(10):35-40.
OBJECTIVE: Determination of the effectiveness and safety of different dosing regimens during the day (in the morning or at bedtime) combination therapy including Azilsartan Medoxomil in patients with essential hypertension and metabolic syndrome (MS). DESIGN AND METHODS: The study included 60 patients with uncontrolled hypertension and MS (age median - 59 (54-65) years). Patients were randomized in two groups: group 1 (n=30) received Azilsartan Medoxomil 40 mg/day, and indapamide retard 1,5 mg/day in the morning; group 2 (n=30)- azilsartan medoxomoil 40 mg at bedtime and indapamide retard 1,5 mg in the morning. All patients at baseline, and after 4 and 12weeks assessed levels of office blood pressure (BP), heart rate (HR); at baseline and after 12 weeks was conducted ambulatory BPmonitoring (ABPM). Evaluated the main indicators of circadian blood pressure profile, as well as the central aortic pressure (CAP) and the rigidity of the vascular wall: systolic, diastolic, and mean arterial pressure in the aorta, aortic augmentation index, pulse wave velocity in the aorta, the augmentation index. Study results were processed using the program Statistica 6.1 by methods nonparametric statistics. RESULTS: Regardless of the regimen used azilsartan destination as part of combination therapy after 4 weeks showed a significant (p<0.05) reduction in SBP and DBP. After 12 weeks of observation target blood pressure was recorded 27 (90%) patients of group 1 and 29 (96.7%)- group2. As a result of ABPM after 12 weeks of treatment in both groups showed a statistically significant (p<0.05) improvement in all parameters investigated. However, positive changes such indicators as an index time of hypertension in the day and night hours, SBP, DBP, and BP variability during the night, the morning rise of systolic as well as the speed of morning rise in SBP and DBP were more pronounced in the appointment Azilsartan Medoxomil at bedtime compared to morning reception. The use of both treatment regimens provided significant (p<0.05) increase frequency registration profile dippear and reduction - non-dipper. Importantly, irrespective of the time of taking the drugs in both groups occurred significant (p <0.05), and a comparable improvement in rigidity and CAP vascular wall. CONCLUSION: When combined with essential hypertension and MS azilsartana use of combination drug therapy provided achievement of the target values of blood pressure in the majority of patients, a significant improvement in the main indicators of ABPM, CAP, and the rigidity of the vascular wall, as well as the normalization of daily profile of blood pressure in the majority of patients, regardless of dosing regimen during the day. However, the combination of indapamide retard morning - Azilsartan Medoxomil at bedtime accompanied by a significantly greater positive changes most ABPM parameters, especially at night.


