AzorubinCAS# 3567-69-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 3567-69-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 19118.0 | Appearance | Powder |
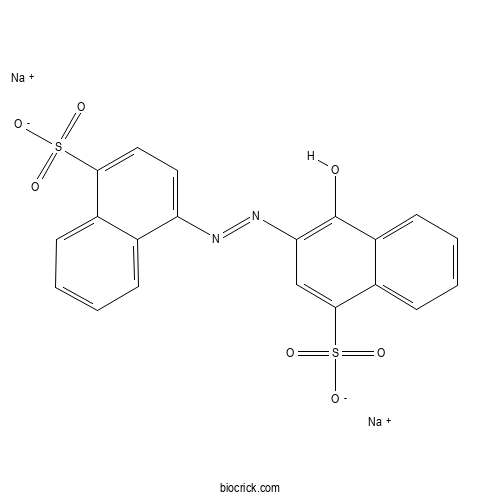
| Formula | C20H12N2Na2O7S2 | M.Wt | 502.43 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | disodium;4-hydroxy-3-[(4-sulfonatonaphthalen-1-yl)diazenyl]naphthalene-1-sulfonate | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C2C(=C1)C(=CC=C2S(=O)(=O)[O-])N=NC3=C(C4=CC=CC=C4C(=C3)S(=O)(=O)[O-])O.[Na+].[Na+] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YSVBPNGJESBVRM-UHFFFAOYSA-L | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H14N2O7S2.2Na/c23-20-15-8-4-3-7-14(15)19(31(27,28)29)11-17(20)22-21-16-9-10-18(30(24,25)26)13-6-2-1-5-12(13)16;;/h1-11,23H,(H,24,25,26)(H,27,28,29);;/q;2*+1/p-2 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Azorubin Dilution Calculator

Azorubin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9903 mL | 9.9516 mL | 19.9033 mL | 39.8065 mL | 49.7582 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3981 mL | 1.9903 mL | 3.9807 mL | 7.9613 mL | 9.9516 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.199 mL | 0.9952 mL | 1.9903 mL | 3.9807 mL | 4.9758 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0398 mL | 0.199 mL | 0.3981 mL | 0.7961 mL | 0.9952 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0199 mL | 0.0995 mL | 0.199 mL | 0.3981 mL | 0.4976 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Filbertone
Catalog No.:BCX0660
CAS No.:81925-81-7
- 6'-O-galloylalbiflorin
Catalog No.:BCX0659
CAS No.:929042-36-4
- 3-O-Coumaroylquinic acid
Catalog No.:BCX0658
CAS No.:87099-71-6
- Acid Red 73
Catalog No.:BCX0657
CAS No.:5413-75-2
- Glycyroside
Catalog No.:BCX0656
CAS No.:125310-04-5
- 4-O-galloylalbiflorin
Catalog No.:BCX0655
CAS No.:1201580-97-3
- 8,9-epoxy-3-isobutyryloxy-10-(2-methylbutanoyl)thymol
Catalog No.:BCX0654
CAS No.:22518-07-6
- 3-Indoleacetamide
Catalog No.:BCX0653
CAS No.:879-37-8
- Coumalic acid
Catalog No.:BCX0652
CAS No.:500-05-0
- Dehydrosulphurenic acid
Catalog No.:BCX0651
CAS No.:175615-56-2
- 4-Ethoxybenzyl alcohol
Catalog No.:BCX0650
CAS No.:6214-44-4
- D-Tartaric acid
Catalog No.:BCX0649
CAS No.:147-71-7
- Ophiopogonside A
Catalog No.:BCX0662
CAS No.:2423917-90-0
- 6''-O-apiosyl-Visammioside
Catalog No.:BCX0663
CAS No.:2254096-97-2
- Isotoosendanin
Catalog No.:BCX0664
CAS No.:97871-44-8
- N-benzylpentadecanamide
Catalog No.:BCX0665
CAS No.:1572037-13-8
- Safranal
Catalog No.:BCX0666
CAS No.:116-26-7
- Apigenin-7-diglucuronide
Catalog No.:BCX0667
CAS No.:74696-01-8
- Trans-Emodin bianthrone
Catalog No.:BCX0668
CAS No.:61281-20-7
- Bigelovin
Catalog No.:BCX0669
CAS No.:3668-14-2
- Ankaflavin
Catalog No.:BCX0670
CAS No.:50980-32-0
- Ergolide
Catalog No.:BCX0671
CAS No.:54999-07-4
- Sorbitol
Catalog No.:BCX0672
CAS No.:50-70-4
- Urolithin A
Catalog No.:BCX0673
CAS No.:1143-70-0
Templating agent-mediated Cobalt oxide encapsulated in Mesoporous silica as an efficient oxone activator for elimination of toxic anionic azo dye in water: Mechanistic and DFT-assisted investigations.[Pubmed:36574575]
Chemosphere. 2023 Feb;313:137309.
While Azorubin S (AZRS) is extensively used as a reddish anionic azo dye for textiles and an alimentary colorant in food, AZRS is mutagenic/carcinogenic, and it shall be removed from dye-containing wastewaters. In view of advantages of SO(4)(*-)-related chemical oxidation technology, oxone (KHSO(5)) would an ideal source of SO(4)(*-) for degrading AZRS, and heterogeneous Co(3)O(4)-based catalysts is required and shall be developed for activating oxone. Herein, a facile protocol is proposed for fabricating mesoporous silica (MS)-confined Co(3)O(4) by a templating agent-mediated dry-grinding procedure. As the templating agent retained inside the ordered pores of MS (before calcination) would facilitate insertion and dispersion of Co ions into pores, the resulting Co(3)O(4) nanoparticles (NPs) would be grown and confined within the pores of MS after calcination, affording Co@MS. On the contrary, another analogue, Co/MS, is also prepared using the similar protocol without the templating agent-mediated introduction of Co, but Co(3)O(4) NPs seriously aggregate as clusters on MS. Therefore, Co@MS outperforms Co/MS for activating oxone to eliminate AZRS. Co@MS shows a noticeably lower activation energy of AZRS elimination than the existing catalysts, revealing its advantage over the reported catalysts. Moreover, the mechanistic investigation of AZRS elimination by Co@MS-activated oxone has been also elucidated for identifying the presence of SO(4)(*‒), (*)OH, and (1)O(2) in AZRS degradation using scavengers, electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy, and semi-quantification. The AZRS decomposition pathway is also investigated and unveiled in details via the DFT calculation. These results validate that Co@MS appears as a superior catalyst of oxone activation for AZRS degradation.
Synthesis of a molecularly imprinted polymer for the selective recognition of carmoisine (Azorubin E122) from pomegranate juice.[Pubmed:27928889]
J Sep Sci. 2017 Feb;40(4):962-970.
Since natural pigments are lost during the processing of beverages such as pomegranate juice, carmoisine, as an adulterant, is often added into the pure juice to improve color characteristics. In this study, molecularly imprinted polymers, as an adsorbent of carmoisine, were synthesized using acrylamide, methacrylic acid, and 4-vinylpyridine as functional monomers and then they were evaluated in terms of the separation and detection of carmoisine. Experiments on the batch adsorption of carmoisine 10 ppm stock solution revealed a better binding capacity for the 4-vinylpyridine-based polymer in comparison to methacrylic acid and acrylamide polymers. The complexation of carmoisine with the 4-vinylpyridine-based polymer was confirmed by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The synthesized polymer exerted a high thermal degradation point and average diameter of polymer particles were obtained to be 0.2 mum by dynamic light scattering analysis. This work showed that detection of pomegranate juice adulteration with carmoisine is not necessarily difficult, time consuming or expensive with selective separation techniques such as molecularly imprinted polymers.
Determination of vanadium in groundwater samples with an improved kinetic spectrophotometric method.[Pubmed:24701912]
Environ Technol. 2014 May-Jun;35(9-12):1165-74.
A kinetic catalytic method has been developed for the determination of vanadium based on its catalytic effect on the redox reaction of Azorubin S and bromate in the presence of a sulphuric and nitric acid mixture. The reaction is monitored spectrophotometrically by measuring the decrease in absorbance of the reaction mixture at 515 nm. The fixed-time method was used for 0.5-5 min. Optimization of the reaction conditions regarding concentrations of acids, dye, oxidant, masking agent, etc. was investigated. The rate of decrease in absorbance of Azorubin S was proportional to the concentration of vanadium in the range of 2.0-1.05 x 10(3) ng mL(-1). 3Sb/m was 0.0129 ng mL(-1) and 10 Sb/m was 0.0432 ng mL(-1). The catalytic method based on the oxidation reaction of Azorubin S and bromate shows a good selectivity for vanadium over a wide variety of interference cations and anions. The proposed method was successfully applied to the determination of vanadium in groundwater samples and spiked-water samples.
Effects of maternally exposed coloring food additives on receptor expressions related to learning and memory in rats.[Pubmed:23429044]
Food Chem Toxicol. 2013 Jun;56:145-8.
Exposure to artificial food colors and additives (AFCAs) has been implicated in the induction and severity of some childhood behavioral and learning disabilities. N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) and nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nACHRs) are thought to be effective in the learning and memory-generating process. In this study, we investigated the effects of intrauterine exposure to AFCAs on subunit concentrations of NMDARs and nAChRs isoforms in rats. We administered a mixture of AFCAs (Eritrosin, Ponceau 4R, Allura Red AC, Sunset Yellow FCF, Tartrazin, Amaranth, Brilliant Blue, Azorubin and Indigotin) to female rats before and during gestation. The concentration of NR2A and NR2B subunits and nAChR alpha7, alpha4beta2 isoforms in their offspring's hippocampi were measured by Western Blotting. Expressions of NR2B and nAChR beta2 were significantly increased (17% and 6.70%, respectively), whereas expression of nAChR alpha4 was significantly decreased (5.67%) in male experimental group compared to the male control group (p<0.05). In the female experimental group, AFCAs caused a 14% decrease in NR2B expression when compared to the female control group (p<0.05). Our results indicate that exposure to AFCAs during the fetal period may lead to alterations in expressions of NMDARs and nAChRs in adulthood. These alterations were different between male and female genders.
Applicability and robustness of the hen's egg test for analysis of micronucleus induction (HET-MN): results from an inter-laboratory trial.[Pubmed:22580102]
Mutat Res. 2012 Aug 30;747(1):118-134.
The hen's egg test for analysis of micronucleus formation (HET-MN) was developed several years ago to provide an alternative test system to the in vivo micronucleus test. In order to assess its applicability and robustness, a study was carried out at the University of Osnabrueck (lab A) and at the laboratories of Henkel AG & Co. KGaA (lab B). Following transfer of the method to lab B, a range of test substances that had been pre-tested at lab A, were tested at Henkel: the genotoxins cyclophosphamide, dimethylbenz(a)anthracene, methotrexate, acrylamide, Azorubin, N-nitroso-dimethylamine and the non-genotoxins, orange G and isopropyl myristate. In a second phase, additional compounds with known in vivo properties were examined in both labs: the non-genotoxin, ampicillin, the "irrelevant" positives, isophorone and 2,4-dichlorophenol ("irrelevant" means positive in standard in vitro tests, but negative in vivo), the clastogen p-chloroaniline, and the aneugens carbendazim and vinorelbine. All substances were correctly predicted in both labs with respect to their in vivo genotoxic properties, indicating that the HET-MN may have an improved predictivity compared with current standard in vitro test systems. The results support the promising role of the HET-MN assay as a supplement to existing test batteries.
Effects of maternally exposed colouring food additives on cognitive performance in rats.[Pubmed:22323474]
Toxicol Ind Health. 2013 Aug;29(7):616-23.
Artificial food colourings and additives (AFCAs) have long been suggested to adversely affect the learning and behaviour in children. In this study, we aimed to provide additional data to clarify the possible side effects of colouring additives on behaviour and memory. We administered acceptable daily intake values of AFCAs as a mixture (Eritrosin, Ponceau 4R, Allura Red AC, Sunset Yellow FCF, Tartrazin, Amaranth, Brilliant Blue, Azorubin and Indigotin) to female rats before and during gestation and then tested their effects on behaviour and on spatial working memory in their offspring. Effects on spatial learning and memory were evaluated by Morris water maze, behavioural effects were evaluated by open-field test and forced swim test. Our results showed that commonly used artificial food colourings have no adverse effects on spatial working memory and did not create a depressive behaviour in offspring. But they showed a few significant effects on locomotor activity as AFCAs increased some parameters of locomotor activity.
Identification and simultaneous determination of Azorubin, Allura red and Ponceau 4R by differential pulse polarography: application to soft drinks.[Pubmed:18968486]
Talanta. 2002 Jan 4;56(1):115-22.
Azorubin (E 122), Ponceau 4R (E 124) and Allura red (E 129), are the most used red dyes in soft drinks manufacturing, and in some cases two dyes are present. The aim of this work is to show that using differential pulse polarography, it was possible to distinguish these synthetic dyes from the natural dyes providing from fruits. In addition, in an appropriate supporting electrolyte, identification and quantitative analysis of these three red dyes were possible, even when they were mixed. Various electrolytes were tested such as potassium chloride, which is a classical supporting electrolyte, citric acid which is one of the components of the soft beverages, sodium citrate and a phosphate buffer. It was shown that the peak intensities and potentials, and consequently their resolution, depend greatly on the pH values. In potassium chloride and sodium citrate the peaks of Azorubin, Allura red and Ponceau 4R were well separated and dyes were identified without ambiguity. Buffer solutions with pH close to 8 and 9 appeared to be appropriate, as the potentials and the intensities of the peaks were slightly changed when small amounts of soft drinks, usually at pH close to 3, were introduced in the cell. A procedure using the standard addition technique was developed, tested with model syrups and then applied to commercial syrups, soda and non-alcoholic bitters.
The hen's egg test for micronucleus induction (HET-MN): novel analyses with a series of well-characterized substances support the further evaluation of the test system.[Pubmed:18201925]
Mutat Res. 2008 Feb 29;650(2):150-64.
The hen's egg test for micronucleus induction (HET-MN) combines the use of the commonly accepted genetic endpoint "formation of micronuclei" with the well-characterized and complex model of the incubated hen's egg, which enables metabolic activation, elimination and excretion of xenobiotics -- including those that are mutagens or promutagens. This assay procedure is in line with demands for animal protection. In three previous publications we presented the scientific rationale and methodological aspects for this assay as well as results for some well-characterized mutagens and promutagens. Here we present the results of new experiments involving further genotoxic and non-genotoxic model substances. Making a comparison with published data we have to date not found any false negatives or false positives in the experiments presented here and in trials published before, thus demonstrating a promising predictivity of genotoxic effects with this assay. We could confirm relevant genotoxicity for the following substances in the HET-MN: acetylamino-fluorene (2-AAF), acrylamide (ACM), cytarabine (AraC), methotrexate (MTX), cadmium chloride (CD), dipotassium monochromate (DPC), and epirubicine (EPI). Negative results were obtained for Azorubin (E122), orange G (OG) and starch (STRC). The micronucleus frequencies (MNE II) of the concurrent negative controls were in agreement with the values of the historical negative control (0.87 per thousand+/-0.87; average+/-s.d.). This value is based upon the scoring of 556,500 erythrocytes from 445 eggs. In historical positive controls the administration of 0.05mg cyclophosphamide/egg at d8 resulted in an MNE II-frequency of 12.4 per thousand+/-6.8 (average+/-s.d.) at d 10.5. This value is based upon the scoring of 249,250 erythrocytes from 223 eggs.
Sulphonylurea sensitivity and enriched expression implicate inward rectifier K+ channels in Drosophila melanogaster renal function.[Pubmed:16169954]
J Exp Biol. 2005 Oct;208(Pt 19):3771-83.
Insect Malpighian (renal) tubules are capable of transporting fluid at remarkable rates. Secondary active transport of potassium at the apical surface of the principal cell must be matched by a high-capacity basolateral potassium entry route. A recent microarray analysis of Drosophila tubule identified three extremely abundant and enriched K(+) channel genes encoding the three inward rectifier channels of Drosophila: ir, irk2 and irk3. Enriched expression of inward rectifier channels in tubule was verified by quantitative RT-PCR, and all three IRKs localised to principal cells of the main segment (and ir and irk3 to the lower tubule) by in situ hybridisation, suggesting roles both in primary secretion and reabsorption. A new splice form of irk2 was also identified. The role of inward rectifiers in fluid secretion was assessed with a panel of selective inhibitors of inward rectifier channels, the antidiabetic sulphonylureas. All completely inhibited fluid secretion, with IC(50)s of 0.78 mmol l(-1) for glibenclamide and approximately 5 mmol l(-1) for tolbutamide, 0.01 mmol l(-1) for minoxidil and 0.1 mmol l(-1) for diazoxide. This pharmacology is consistent with a lower-affinity class of inward rectifier channel that does not form an obligate multimer with the sulphonylurea receptor (SUR), although effects on non-IRK targets cannot be excluded. Glibenclamide inhibited fluid secretion similarly to basolateral K(+)-free saline. Radiolabelled glibenclamide is both potently transported and metabolised by tubule. Furthermore, glibenclamide is capable of blocking transport of the organic dye amaranth (Azorubin S), at concentrations of glibenclamide much lower than required to impact on fluid secretion. Glibenclamide thus interacts with tubule in three separate ways; as a potent inhibitor of fluid secretion, as an inhibitor (possibly competitive) of an organic solute transporter and as a substrate for excretion and metabolism.
[Food additives as a cause of medical symptoms: relationship shown between sulfites and asthma and anaphylaxis; results of a literature review].[Pubmed:11020839]
Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2000 Sep 16;144(38):1836-9.
OBJECTIVE: To determine if a causal connection exists between food additives and various medical complaints. DESIGN: Literature study. METHOD: Medline over the period January 1966-January 1999 was searched for articles on the following substances not containing protein and lactose: monosodium glutamate (MSG), sulfites, azo-dyes (tartrazine, sunset yellow, Azorubin, amarant, cochineal red), benzoates, sorbates, butylated hydroxyanisole/butylated hydroxytoluene (BHA/BHT), parabens, cinnamon and vanilla, in combination with key words regarding food and side effects. Of those studies purporting to demonstrate an effect, only double-blind randomized placebo-controlled studies with oral challenge were assessed further, unless the complaint was anaphylaxis. Of studies not demonstrating an effect the design was assessed. RESULTS: Only for sulfites as causative agents of asthma and anaphylaxis, methodologically adequate studies demonstrating a causal connection could be found. For azo-dyes, benzoates, MSG, sorbates and BHA/BHT, no link with medical symptoms was demonstrable. For parabens, cinnamon and vanilla there were insufficient or inadequate data to justify a conclusion.
[Use of computers for processing thin-layer chromatograms based on an example of red food dyes].[Pubmed:10943012]
Vopr Pitan. 2000;69(1-2):63-5.
On an example of definition of the forbidden red dye amaranth E123 in a mix with other red food dyes (Azorubin E122 and ponso 4R E124) the method of quantitative processing think level chromatograms was developed. The method includes transfer of chromatogram in a digital kind by scanning and processing of the received image with the help of the program Adobe Photoshop 5.0. The average values of detection of dyes on the developed method make for Azorubin, amaranth and ponso 4R accordingly 95.6, 97.1 and 99.4% with correlation coefficients 0.98, 0.98 and 0.99.
[Analysis of cytogenetic activity of food dyes].[Pubmed:8553630]
Vopr Med Khim. 1995 Sep-Oct;41(5):50-3.
The cytogenetic activity of food dyes was examined in the experiments on male C57B1/6 mice which were orally given during 5 days the following daily doses: Tartrasine (E102), 0.5 and 5.0 mg/kg; Indigo carmine (E132), 1.4 and 14 mg/kg; Canset yellow (E110), 0.17 and 1.7 mg/kg; Cochenillerot A (E124), 0.63 and 6.3mg/kg; Azorubin (E122), 1 and 10 mg/kg and Patentblau V (E131), 0.08 and 0.8 mg/kg. Five hundred metaphase slides each were analyzed in the control and experimental test series. The findings may conclude that the dyes tested within the above dose ranges do not induce any increase in the level of cells with chromosomal damages in the inbred animals.
Microbiological research on soft drinks: discolouring of natural-flavoured products.[Pubmed:1509827]
Zentralbl Mikrobiol. 1992;147(1-2):51-60.
The results of experiments testing the effects of yeasts, sunlight, and temperature on the food dyes tartrazine, ponceau 4R, indigotin and Azorubin (used for colouring ginger soft drink) are reported. Light was found to exert a greater influence than heat, and yeasts growth hastened colour degradation. Yeasts assimilated to varying extent the colouring compounds and, when failing to do it, showed a certain power of adsorption by the no longer viable cells.
[Spectral characteristics of dyes--the ultraviolet and visible bands].[Pubmed:3441460]
Probl Khig. 1987;12:115-26.
A spectral characteristic of 7 dyes: Azorubin, amaranth-5, erythrosin, indigotin ponso-4R, tetrasin and chinolin yellow is made. It includes the visual and ultraviolet field (from 200 to 850 nm) of water dye solutions. Besides absorption spectra area-made derivative spectra: I and IInd derivative of the absorption. The maximums and minimums of the absorptions and the minimums of the derivatives are determined. Suitable maximums and minimums for qualitative and quantitative characteristics of the dyes are chosen. A spectrophotometric system "Spectronic-2000" - "Baush and Lomb" is used. For quantitative determination of dyes are given the conditions of work in the derivative variant and the measures of length in intervals from 5 to 50 micrograms/cm3 (in water solution). When there is no spectral characteristic in the infrared field the given spectra could serve for evaluation of the dyes quality and quantity for sanitary and hygiene control.


