BigelovinCAS# 3668-14-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 3668-14-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3080597.0 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C17H20O5 | M.Wt | 304.34 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
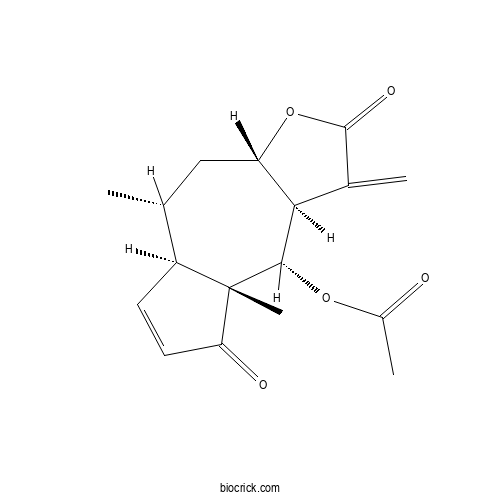
| Chemical Name | [(3aS,5R,5aR,8aR,9S,9aR)-5,8a-dimethyl-1-methylidene-2,8-dioxo-3a,4,5,5a,9,9a-hexahydroazuleno[6,5-b]furan-9-yl] acetate | ||
| SMILES | CC1CC2C(C(C3(C1C=CC3=O)C)OC(=O)C)C(=C)C(=O)O2 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DCNRYQODUSSOKC-MMLVVLEOSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C17H20O5/c1-8-7-12-14(9(2)16(20)22-12)15(21-10(3)18)17(4)11(8)5-6-13(17)19/h5-6,8,11-12,14-15H,2,7H2,1,3-4H3/t8-,11+,12+,14-,15+,17+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Bigelovin Dilution Calculator

Bigelovin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.2858 mL | 16.429 mL | 32.858 mL | 65.716 mL | 82.145 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6572 mL | 3.2858 mL | 6.5716 mL | 13.1432 mL | 16.429 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3286 mL | 1.6429 mL | 3.2858 mL | 6.5716 mL | 8.2145 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0657 mL | 0.3286 mL | 0.6572 mL | 1.3143 mL | 1.6429 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0329 mL | 0.1643 mL | 0.3286 mL | 0.6572 mL | 0.8214 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Trans-Emodin bianthrone
Catalog No.:BCX0668
CAS No.:61281-20-7
- Apigenin-7-diglucuronide
Catalog No.:BCX0667
CAS No.:74696-01-8
- Safranal
Catalog No.:BCX0666
CAS No.:116-26-7
- N-benzylpentadecanamide
Catalog No.:BCX0665
CAS No.:1572037-13-8
- Isotoosendanin
Catalog No.:BCX0664
CAS No.:97871-44-8
- 6''-O-apiosyl-Visammioside
Catalog No.:BCX0663
CAS No.:2254096-97-2
- Ophiopogonside A
Catalog No.:BCX0662
CAS No.:2423917-90-0
- Azorubin
Catalog No.:BCX0661
CAS No.:3567-69-9
- Filbertone
Catalog No.:BCX0660
CAS No.:81925-81-7
- 6'-O-galloylalbiflorin
Catalog No.:BCX0659
CAS No.:929042-36-4
- 3-O-Coumaroylquinic acid
Catalog No.:BCX0658
CAS No.:87099-71-6
- Acid Red 73
Catalog No.:BCX0657
CAS No.:5413-75-2
- Ankaflavin
Catalog No.:BCX0670
CAS No.:50980-32-0
- Ergolide
Catalog No.:BCX0671
CAS No.:54999-07-4
- Sorbitol
Catalog No.:BCX0672
CAS No.:50-70-4
- Urolithin A
Catalog No.:BCX0673
CAS No.:1143-70-0
- 5,7-Dihydroxycoumarin
Catalog No.:BCX0674
CAS No.:2732-18-5
- Dendronobilin B
Catalog No.:BCX0675
CAS No.:1002717-96-5
- Polyporusterone A
Catalog No.:BCX0676
CAS No.:141360-88-5
- Cis-Emodin bianthrone
Catalog No.:BCX0677
CAS No.:61281-19-4
- Anhydrosafflor yellow B
Catalog No.:BCX0678
CAS No.:184840-84-4
- Emodin anthrone
Catalog No.:BCX0679
CAS No.:491-60-1
- Polyporusterone B
Catalog No.:BCX0680
CAS No.:141360-89-6
- 1-Methyl Emodin
Catalog No.:BCX0681
CAS No.:3775-08-4
Bigelovin inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth and metastasis by regulating the MAPT-mediated Fas/FasL pathway.[Pubmed:36812233]
Neoplasma. 2023 Apr;70(2):208-215.
Bigelovin (BigV), as traditional Chinese medicine, has been shown to inhibit the malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This study aimed to investigate whether BigV affects the development of HCC by targeting the MAPT and Fas/FasL pathway. Human HCC cell lines HepG2 and SMMC-7721 were used for this study. Cells were treated with BigV, sh-MAPT, and MAPT. The viability, migration, and apoptosis of HCC cells were detected by CCK-8, Transwell, and flow cytometry assays, respectively. Immunofluorescence and immunoprecipitation were used to verify the relationship between MAPT and Fas. Subcutaneous xenograft tumor and tail vein-injected lung metastases mouse models were constructed for histological observation. Hematoxylin-eosin staining was used to assess lung metastases in HCC. Western blotting was used to measure the expression of migration, apoptosis, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) marker proteins, as well as Fas/FasL pathway-related proteins. BigV treatment inhibited the proliferation, migration, and EMT of HCC cells, whereas enhanced cell apoptosis. Moreover, BigV downregulated MAPT expression. The negative effects of sh-MAPT on HCC cell proliferation, migration, and EMT were enhanced by BigV treatment. Conversely, BigV addition attenuated the positive effects of MAPT overexpression on the malignant progression of HCC. In vivo experiments showed that BigV and/or sh-MAPT reduced tumor growth and lung metastasis while promoting tumor cell apoptosis. Furthermore, MAPT could act with Fas and inhibit its expression. sh-MAPT upregulated the expression of Fas/FasL pathway-associated proteins, which were enhanced by BigV administration. BigV suppressed the malignant progression of HCC via activating the MAPT-mediated Fas/FasL pathway.
Molecular docking study of britannin binding to PD-L1 and related anticancer pseudoguaianolide sesquiterpene lactones.[Pubmed:34789056]
J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2022 Oct;42(5):454-461.
The pseudoguaianolide-type sesquiterpene lactone (SL) britannin (BRT), found in different Inula species, has been characterized as a potent anticancer agent acting via modulation of the transcription factor NFkB and the Nrf2-Keap1 signaling pathway. In addition, a BRT-induced down-regulation of the immune checkpoint PD-L1 (programmed cell death ligand 1) expressed on cancer cells has been evidenced. Here we have performed a docking analysis of the direct binding of BRT to the PD-L1 protein, both in its monomeric and dimeric state. BRT appears to form stable complexes with PD-L1, with a preference for the dimeric form, binding at the interface of the two monomers. The calculated empirical energy of interaction (DeltaE) value reaches -63.1 kcal/mol for the BRT-PD-L1 dimer complex, not far from the value calculated with the reference PD-L1 ligand BMS-202 (DeltaE = -73.4 kcal/mol) under identical conditions. We also studied the potential PD-L1 dimer binding of 15 pseudoguaianolide sesquiterpene lactones analogues to BRT, including helenalin, gaillardin, Bigelovin, coronopilin, and others. The docking analysis predicted that the SL chamissonolide (CHM) can also form equally stable complexes with PD-L1 dimer (DeltaE = -64.8 kcal/mol). Preliminary compound structure-PD-L1 binding relationships have been delineated. This computational study supports the proposed interaction of BRT with PD-L1 and provides a guidance to the design of novel PD-L1 binders incorporating a SL-like tricyclic core unit.
Anticancer Targets and Signaling Pathways Activated by Britannin and Related Pseudoguaianolide Sesquiterpene Lactones.[Pubmed:34680439]
Biomedicines. 2021 Sep 26;9(10):1325.
Sesquiterpene lactones (SLs) are abundant in plants and display a large spectrum of bioactivities. The compound britannin (BRT), found in different Inula species, is a pseudoguaianolide-type SL equipped with a typical and highly reactive alpha-methylene-gamma-lactone moiety. The bioproperties of BRT and related pseudoguaianolide SLs, including helenalin, gaillardin, Bigelovin and others, have been reviewed. Marked anticancer activities of BRT have been evidenced in vitro and in vivo with different tumor models. Three main mechanisms are implicated: (i) interference with the NFkappaB/ROS pathway, a mechanism common to many other SL monomers and dimers; (ii) blockade of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway, with a covalent binding to a cysteine residue of Keap1 via the reactive alpha-methylene unit of BRT; (iii) a modulation of the c-Myc/HIF-1alpha signaling axis leading to a downregulation of the PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint and activation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. The non-specific reactivity of the alpha-methylene-gamma-lactone moiety with the sulfhydryl groups of proteins is discussed. Options to reduce or abolish this reactivity have been proposed. Emphasis is placed on the capacity of BRT to modulate the tumor microenvironment and the immune-modulatory action of the natural product. The present review recapitulates the anticancer effects of BRT, some central concerns with SLs and discusses the implication of the PD1/PD-L1 checkpoint in its antitumor action.
Sesquiterpene lactone Bigelovin induces apoptosis of colon cancer cells through inducing IKK-beta degradation and suppressing nuclear factor kappa B activation.[Pubmed:33929997]
Anticancer Drugs. 2021 Jun 1;32(6):664-673.
Bigelovin, a sesquiterpene lactone extracted from plant Inula helianthus aquatica, exhibited multiple interesting biological activities, including anti-inflammation, antiangiogenesis and cytotoxic action against cancer cells. In the present study, we found that Bigelovin reduced the viability of human colon cancer cells and induced their apoptosis in a time- and dose-dependent manner, with an IC50-5 muM. RNAseq and luciferase reporter analyses revealed that the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) signaling was one of the most significantly inhibited pathways after Bigelovin treatment. Further systemic examination showed that exposure to Bigelovin resulted in ubiquitination and degradation of inhibitor of kappa-B kinase-beta (IKK-beta) and decrease of IkappaB-alpha and p65 phosphorylation, which led to the downregulation of NF-kappaB-regulated genes expression. Moreover, enforced expression of exogenous IKK-beta attenuated Bigelovin-induced NF-kappaB suppression and cell viability reduction. These results indicated that Bigelovin exerts a cytotoxic action against colon cancer cells through the induction of IKK-beta degradation and consequently the inhibition of NF-kappaB signaling. Given the abnormal activation of NF-kappaB signaling in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells and the critical role of chronic inflammation in CRC development, it is conceivable that at least some colorectal cancer cells are addictive to NF-kappaB activation and targeting the pathway is an effective anti-CRC strategy.
Bigelovin, a sesquiterpene lactone, suppresses tumor growth through inducing apoptosis and autophagy via the inhibition of mTOR pathway regulated by ROS generation in liver cancer.[Pubmed:29548826]
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 May 5;499(2):156-163.
Bigelovin (BigV) is a sesquiterpene lactone, isolated from Inula helianthus aquatica, which has been reported to induce apoptosis and show anti-inflammatory and anti-angiogenic activities. Nevertheless, the effects of BigV on liver cancer and the underlying mechanisms have not been investigated. In the study, we found that BigV exhibited potential anti-tumor activities against human liver cancer in vitro and in vivo. BigV reduced the cell proliferation and colony formation. BigV induced apoptosis through improving the cleavage of Caspase-3 and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP-1). The process was along with the activation of autophagy, as proved by the enhanced accumulation of autophagosomes, the microtubule-associated light chain 3B-II (LC3B-II) and Beclin-1, and p62 decrease. Further, the autophagy blockage markedly sensitized BigV-induced cell death, indicating the cytoprotective function of autophagy in liver cancer cell lines. In addition, BigV treatment inactivated the pathway of protein kinase B (AKT)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)/ribosomal protein S6 kinase (p70S6K). Of note, BigV-induced cell death was abolished by over-expressing the phosphorylation of mTOR. Intriguingly, the induction of apoptosis and autophagy were eliminated by the pretreatment of reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenger N-acetyl-l-cysteine (NAC), suggesting that ROS played an important role in the regulation of BigV-induced cell death. Finally, in vivo studies demonstrated that BigV significantly suppressed the growth of HepG2 cancer xenograft tumors through the activation of apoptosis and autophagy in a dose-dependent manner with low systemic toxicity. In conclusion, the results revealed that BigV had significant antitumor effects against human liver cancer and it may potentially be used as a novel antitumor agent for the prevention of liver cancer.
Natural small molecule bigelovin suppresses orthotopic colorectal tumor growth and inhibits colorectal cancer metastasis via IL6/STAT3 pathway.[Pubmed:29454618]
Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Apr;150:191-201.
Bigelovin, a sesquiterpene lactone, has been demonstrated to induce apoptosis, inhibit inflammation and angiogenesis in vitro, but its potential anti-metastatic activity remains unclear. In the present study, two colon cancer mouse models, orthotopic tumor allografts and experimental metastatic models were utilized to investigate the progression and metastatic spread of colorectal cancer after Bigelovin treatments. Results showed that Bigelovin (intravenous injection; 0.3-3 mg/kg) significantly suppressed tumor growth and inhibited liver/lung metastasis with modulation of tumor microenvironment (e.g. increased populations of T lymphocytes and macrophages) in orthotopic colon tumor allograft-bearing mice. Furthermore, the inhibitory activities were also validated in the experimental human colon cancer metastatic mouse model. The underlying mechanisms involved in the anti-metastatic effects of Bigelovin were then revealed in murine colon tumor cells colon 26-M01 and human colon cancer cells HCT116. Results showed that Bigelovin induced cytotoxicity, inhibition of cell proliferation, motility and migration in both cell lines, which were through interfering IL6/STAT3 and cofilin pathways. Alternations of the key molecules including Rock, FAK, RhoA, Rac1/2/3 and N-cadherin, which were detected in Bigelovin-treated cancer cells, were also observed in the tumor allografts of Bigelovin-treated mice. These findings strongly indicated that Bigelovin has potential to be developed as anti-tumor and anti-metastatic agent for colorectal cancer.
Bigelovin triggered apoptosis in colorectal cancer in vitro and in vivo via upregulating death receptor 5 and reactive oxidative species.[Pubmed:28181527]
Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 9;7:42176.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most prevalent cancer and the third highest cancer-related mortality in the United States. Bigelovin, a sesquiterpene lactone isolated from Inula helianthus aquatica, has been proven to induce apoptosis and exhibit anti-inflammatory and anti-angiogenic activities. However, the effects of Bigelovin on CRC and underlying mechanisms have not been explored. The present study demonstrated that Bigelovin exhibited potent anti-tumor activities against CRC in vitro and in vivo. Bigelovin suppressed cell proliferation and colony formation and induced apoptosis in human colorectal cancer HT-29 and HCT 116 cells in vitro. Results also revealed that Bigelovin activated caspases, caused the G2/M cell cycle arrest and induced DNA damage through up-regulation of death receptor (DR) 5 and increase of ROS. In HCT 116 xenograft model, Bigelovin treatment resulted in suppression of tumor growth. Bigelovin at 20 mg/kg showed more significant tumor suppression and less side effects than conventional FOLFOX (containing folinic acid, 5-fluorouracil and oxaliplatin) treatment. In addition, in vivo data confirmed that anti-tumor activity of Bigelovin in CRC was through induction of apoptosis by up-regulating DR5 and increasing ROS. In conclusion, these results strongly suggested that Bigelovin has potential to be developed as therapeutic agent for CRC patients.
Bigelovin inhibits STAT3 signaling by inactivating JAK2 and induces apoptosis in human cancer cells.[Pubmed:25619393]
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015 Apr;36(4):507-16.
AIM: To study the function and mechanism of Bigelovin, a sesquiterpene lactone from the flower of Chinese herb Inula hupehensis, in regulating JAK2/STAT3 signaling and cancer cell growth. METHODS: HepG2 cells stably transfected with the STAT3-responsive firefly luciferase reporter plasmid (HepG2/STAT3 cells), and a panel of human cancer cell lines were used to identify active compounds. Cell viability was measured using MTT assay. Western blotting was used to detect protein expression and phosphorylation. Kinase assays were performed and the reaction between Bigelovin and thiol-containing compounds was analyzed with LC-MS. RESULTS: Bigelovin (1-50 mumol/L) dose-dependently inhibited the IL-6-induced STAT3 activation in HepG2/STAT3 cells (IC50=3.37 mumol/L) and the constitutive STAT3 activation in A549 and MDA-MB-468 cells. Furthermore, Bigelovin dose-dependently inhibited JAK2 phosphorylation in HeLa and MDA-MB-468 cells, as well as the enzymatic activity of JAK2 in vitro (IC50=44.24 mumol/L). Pretreatment of the cells with DTT (500 mumol/L) or GSH (500 mumol/L) eliminated the inhibitory effects of Bigelovin on the IL-6-induced and the constitutive STAT3 activation. The results in LC-MS analysis suggested that Bigelovin might react with cysteine residues of JAK2 leading to inactivation of JAK2. Bigelovin (5 and 20 mumol/L) had no effects on the signaling pathways of growth factors EGF, PDGF or insulin. Finally, Bigelovin suppressed the cell viability and induced apoptosis in 10 different human cancer cell lines, particularly those with constitutively activated STAT3. CONCLUSION: Bigelovin potently inhibits STAT3 signaling by inactivating JAK2, and induces apoptosis of a variety of human cancer cells in vitro.
Small compound bigelovin exerts inhibitory effects and triggers proteolysis of E2F1 in multiple myeloma cells.[Pubmed:24118350]
Cancer Sci. 2013 Dec;104(12):1697-704.
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a currently incurable blood cancer. Here we tested the effects of a small compound Bigelovin on MM cells, and reported that it caused cell cycle arrest and subsequently induced apoptosis. Bigelovin triggered proteolysis of E2F1, which could be inhibited by caspase inhibitor. To investigate the clinical relevance, the expression of E2F1 in MM specimens was tested, and the results showed that E2F1 was overexpressed in 25-57% of MM patients and was associated with higher International Staging System (ISS) stage. These results suggest that E2F1 may be important for MM pathogenesis, and Bigelovin could serve as a lead compound for the development of E2F1 inhibitor.
Anti-angiogenesis and immunomodulatory activities of an anti-tumor sesquiterpene bigelovin isolated from Inula helianthus-aquatica.[Pubmed:23231968]
Eur J Med Chem. 2013 Jan;59:243-52.
Bigelovin is a sesquiterpene lactone isolated from the plant Inula helianthus-aquatica which was traditionally used in cancer treatment in Yunnan, China. The potent apoptotic activities of Bigelovin in human leukemia U937 cells were shown in our previous study. The present study investigated the anti-angiogenic and immunomodulatory effects of Bigelovin using transgenic zebrafish Tg(fli1a:EGFP)y1 with fluorescent blood vessels and human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), respectively. Furthermore, the inhibitory activities of Bigelovin on the human endothelial cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) were also examined. Our results showed that the growth of subintestinal vessels of the Bigelovin-treated zebrafish embryos was significantly inhibited and the gene expressions in angiogenesis signaling pathways (e.g. Ang2 and Tie2) of the zebrafish were down-regulated after Bigelovin treatment. Besides, the proliferation and Th1 cytokines productions (e.g. IFN-gamma, IL-2 and IL-12) were suppressed in Bigelovin-treated PBMCs. On the other hand, Bigelovin was shown to significantly inhibit the human monocyte adhesion to human endothelial cells and the gene expressions of inflammation-related CAMs (e.g. ICAM-1, VCAM-1 and E-selectin) were significantly down-regulated in Bigelovin-treated human endothelial cells. In summary, our data provide the first evidence that Bigelovin possesses anti-angiogenic and immunomodulatory activities, suggesting Bigelovin may exert multi-target functions against cancer in animal models.
[Simultaneous determination of three sesquiterpene lactones in Inula hupehensis by RP-HPLC].[Pubmed:22256758]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2011 Sep;36(18):2520-4.
OBJECTIVE: A RP-HPLC method was developed for simultaneous determination of Bigelovin, ergolide and tomentosin in Inula hupehensis. METHOD: An Agilent C18 column (4.6 mm x 250 mm, 5 microm) was used for separation at 40 degrees C. The mobile phase was acetonitrile-water, and the flow rate was 1.2 mL x min(-1). The detection wavelength was set at 210 nm. RESULT: The method has good linearity in the ranges of 0.01792-0.1792 g x L(-1) (r =0.9999) for Bigelovin, 0.0424-0.4240 g x L(-1) (r =0.9996) for ergolide, and 0.044 8-0.4480 g x L(-1) (r = 0.9996) for tomentosin. The average recoveries of Bigelovin, ergolide, and tomentosin were 98.5%, 98.2%, 98.4%, with the RSD of 1. 3%, 1.3%, 1.7%, respectively. The results demonstrated that there was a significant difference in the contents of three sequterpene lactones among the tested Inulae Flos. CONCLUSION: The results indicated that the present RP-HPLC method is simple, quick and accurate, and can be used for the quality control of I. hupehensis, especially for the authentication of Inulae Flos.
Structure basis of bigelovin as a selective RXR agonist with a distinct binding mode.[Pubmed:21262235]
J Mol Biol. 2011 Mar 18;407(1):13-20.
The nuclear receptor retinoid X receptor (RXR) functions potently in the regulation of homeostasis and cell development, while rexinoids as RXR agonists have proved their therapeutic potential in the treatment of metabolic diseases and cancer. Here, the natural product Bigelovin was identified as a selective RXRalpha agonist. Interestingly, this compound could not transactivate RXRalpha:RXRalpha homodimer but could enhance the transactivation of RXRalpha:peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma heterodimer and repress that of RXRalpha:liver X receptor (LXR) alpha heterodimer, while it had no effects on RXRalpha:farnesoid X receptor heterodimer. Considering that the effective role of LXR response element involved transactivation of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c mediated by RXRalpha:LXRalpha in triglyceride elevation, such LXR response element repressing by Bigelovin has obviously addressed its potency for further research. Moreover, our determined crystal structure of the Bigelovin-activated RXRalpha ligand-binding domain with the coactivator human steroid receptor coactivator-1 peptide revealed that Bigelovin adopted a distinct binding mode. Compared with the known RXR ligands, Bigelovin lacks the acidic moiety in structure, which indicated that the acidic moiety rendered little effects on RXR activation. Our results have thereby provided new insights into the structure-based selective rexinoids design with Bigelovin as a potential lead compound.
Nuclear factor kappaB-mediated down-regulation of adhesion molecules: possible mechanism for inhibitory activity of bigelovin against inflammatory monocytes adhesion to endothelial cells.[Pubmed:19429369]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2009 Jun 22;123(2):250-6.
The flowers of Inula britannica L. var. chinensis (Rupr.) Reg. (Compositae) are used in traditional medicine to treat asthma, chronic bronchitis, and acute pleurisy in China and Korea. However, the pharmacological actions of Inula britannica L. var. chinensis on endothelial cells and inflammatory monocytes are not clear. In this study, we investigated whether Bigelovin, a sesquiterpene lactone isolated from the flowers of Inula britannica L. var. chinensis, inhibits monocyte adhesion and adhesion molecule expression in brain endothelial cells. We measured tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha)-enhanced Raw264.7 monocyte binding to brain endothelial cells and the levels of cell adhesion molecules, including vascular adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), intracellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), and endothelial-selectin (E-selectin) on the surface of brain endothelial cells. Bigelovin significantly inhibited these in a dose-dependent manner without affecting cell viability. Furthermore, Bigelovin suppressed the nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB) promoter-driven luciferase activity, NF-kappaB activation, and degradation of NF-kappaB inhibitor protein alpha (IkappaBalpha). These results indicate that Bigelovin inhibits inflammatory monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells and the expression of VCAM-1, ICAM-1, and E-selectin by blocking IkappaBalpha degradation and NF-kappaB activation.
Apoptosis inducement of bigelovin from Inula helianthus-aquatica on human Leukemia U937 cells.[Pubmed:19107858]
Phytother Res. 2009 Jun;23(6):885-91.
Inula helianthus-aquatica C. Y. Wu is a traditional medicinal plant used to treat some cancers in folk herbal medicine of Yunnan, China. Bigelovin, a sesquiterpene lactone isolated from this herb, potently inhibits the growth of a panel of eight cancer cell lines, especially in human monoblastic leukemia U937 cells with an IC(50) value of 0.47 microM. Characteristic morphological features of apoptosis were observed in U937 cells treated with Bigelovin. Annexin V and nuclear DNA content distribution assays showed that the percentage of Annexin V positive cells increased to 8.86% (24 h) with 1 microM Bigelovin treatment, and cells treated with Bigelovin at this concentration apparently arrested at G(0)/G(1) phase compared with the control. These data suggested that cytotoxic effect of Bigelovin on U937 cells involves induction of apoptosis, and the cell cycle is arrested at G(0)/G(1) phase.
New eudesmane derivatives and other sesquiterpenes from the epigeal parts of Dittrichia graveolens.[Pubmed:18981602]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2008 Nov;56(11):1535-45.
In bioassay-guided searches for novel bioactive natural products from higher plants of the Egyptian flora, two new eudesmane sesquiterpene derivatives, 3alpha-hydroxyilicic acid methyl ester (1) and 2alpha-hydroxy-4-epi-ilicic acid (2), together with 11 known sesquiterpenes were isolated from bioactive fractions of the active epigeal parts extracts of Dittrichia graveolens (L.) GREUTER (Asteraceae) growing in the coastal regions of northwestern Egypt. Four other known sesquiterpene lactones with different carbon skeletons, named 2alpha-hydroxy-2R-xanthalongin (8), 4-epi-isoinuviscolide (9), 8-epi-helenalin (10), and Bigelovin (11), were also isolated for the first time from the same source. The stereochemical structures of the isolated compounds were elucidated on the basis of physical and spectroscopic methods including UV, IR, 1H-, 13C-NMR, distortionless enhancement by polarization transfer, 2D NMR, 1H-1H correlation spectroscopy, 1H-13C heteronuclear single-quantum coherence, 1H-13C heteronuclear multiple-bond connectivity, 1H-1H nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy experiments, and high-resolution mass spectrometry, as well as some chemical transformations. The antimicrobial, antiinflammatory, and antipyretic activities of D. graveolens extracts and chromatographic fractions were carried out and the various bioactivities of our findings are discussed.


