Betaxolol HClCAS# 63659-19-8 |
- Amyloid β-Peptide (10-20) (human)
Catalog No.:BCC1026
CAS No.:152286-31-2
- Amyloid β-Protein (1-15)
Catalog No.:BCC1003
CAS No.:183745-81-5
- Beta-Amyloid (1-11)
Catalog No.:BCC1002
CAS No.:190436-05-6
- Myelin Basic Protein (68-82), guinea pig
Catalog No.:BCC1020
CAS No.:98474-59-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 63659-19-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 107952 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H30ClNO3 | M.Wt | 343.89 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (290.79 mM) H2O : 10 mg/mL (29.08 mM; Need ultrasonic) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
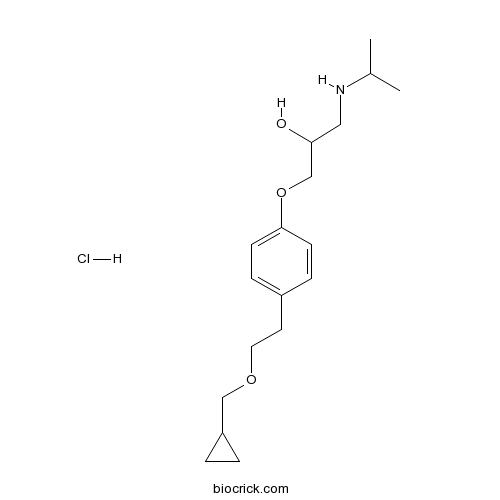
| Chemical Name | 1-[4-[2-(cyclopropylmethoxy)ethyl]phenoxy]-3-(propan-2-ylamino)propan-2-ol;hydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)NCC(COC1=CC=C(C=C1)CCOCC2CC2)O.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CHDPSNLJFOQTRK-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H29NO3.ClH/c1-14(2)19-11-17(20)13-22-18-7-5-15(6-8-18)9-10-21-12-16-3-4-16;/h5-8,14,16-17,19-20H,3-4,9-13H2,1-2H3;1H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective β1-adrenoceptor antagonist. |

Betaxolol HCl Dilution Calculator

Betaxolol HCl Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9079 mL | 14.5395 mL | 29.0791 mL | 58.1581 mL | 72.6977 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5816 mL | 2.9079 mL | 5.8158 mL | 11.6316 mL | 14.5395 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2908 mL | 1.454 mL | 2.9079 mL | 5.8158 mL | 7.2698 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0582 mL | 0.2908 mL | 0.5816 mL | 1.1632 mL | 1.454 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0291 mL | 0.1454 mL | 0.2908 mL | 0.5816 mL | 0.727 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Betaxolol is a β1 adrenergic receptor blocker with IC50 of 6 μM.
- Z-D-Glu-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2775
CAS No.:63648-73-7
- Gamma-Methoxyisoeugenol
Catalog No.:BCN3999
CAS No.:63644-71-3
- 1,5-Bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)penta-1,4-diene
Catalog No.:BCN1388
CAS No.:63644-68-8
- Coniferyl ferulate
Catalog No.:BCN8543
CAS No.:63644-62-2
- DADLE
Catalog No.:BCC6064
CAS No.:63631-40-3
- D-(+)-Maltose monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCN8423
CAS No.:6363-53-7
- 6-Hydroxydopamine hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC7403
CAS No.:636-00-0
- Terazosin
Catalog No.:BCC5162
CAS No.:63590-64-7
- Foscarnet Sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4782
CAS No.:63585-09-1
- Darunavir Ethanolate
Catalog No.:BCC5627
CAS No.:635728-49-3
- Pazopanib Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC3708
CAS No.:635702-64-6
- Microhelenin C
Catalog No.:BCN7977
CAS No.:63569-07-3
- H-Lys(Z)-OBzl.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2987
CAS No.:6366-70-7
- H-D-Asp-Obzl
Catalog No.:BCC2895
CAS No.:6367-42-6
- Nisoldipine
Catalog No.:BCC4809
CAS No.:63675-72-9
- Boc-D-Ser-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3447
CAS No.:6368-20-3
- Clofibrate
Catalog No.:BCC5308
CAS No.:637-07-0
- Pramoxine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4705
CAS No.:637-58-1
- 2-(Dimethylamino)ethanesulfonic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1752
CAS No.:637-95-6
- (R)-Baclofen hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4123
CAS No.:63701-55-3
- Z-Phenylalaninol
Catalog No.:BCC2716
CAS No.:6372-14-1
- Paspalinine
Catalog No.:BCN7386
CAS No.:63722-91-8
- Pseudoprotogracillin
Catalog No.:BCC8354
CAS No.:637349-03-2
- AEG 3482
Catalog No.:BCC8088
CAS No.:63735-71-7
Penetration of betaxolol HCL ionic suspension 0.25% and betaxolol HCL solution 0.50% into the aqueous humor.[Pubmed:17534818]
Eur J Ophthalmol. 2007 May-Jun;17(3):368-71.
PURPOSE: To determine the intraocular penetration of topical drops of Betaxolol HCl 0.25% suspension and Betaxolol HCl 0.50% solution into the aqueous humor. METHODS: Fifteen patients were randomly assigned to receive topical Betaxolol HCl 0.25% suspension (n=7) or topical Betaxolol HCl 0.50% solution (n=8) the day before cataract surgery. Aqueous samples were collected 2 hours after the administration of the morning dose during cataract surgery. Drug concentrations were determined by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. RESULTS: The mean aqueous humor concentration of topical Betaxolol HCl 0.25% suspension was 275.1+/-168.8 micro g/mL (range 570-70 micro g/mL) and the mean aqueous humor concentration of topical Betaxolol HCl 0.50% solution was 195.4+/-102.4 micro g/mL (range 334-50 micro g/mL) (p=0.281). CONCLUSIONS: The mean aqueous humor concentration of betaxolol 0.25% suspension was higher than betaxolol 0.50% solution; however, the difference was not statistically significant. With twofold reduced concentration and similar anterior chamber penetration, betaxolol 0.25% suspension could be first choice for Beta 1 selective blocker therapy when considered for patients with glaucoma.
Are there any benefits of Betoptic S (betaxolol HCl ophthalmic suspension) over other beta-blockers in the treatment of glaucoma?[Pubmed:15155109]
Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2004 May;5(5):1071-81.
The cardioselective beta-blocker, betaxolol, is an effective ocular antihypertensive agent. Its mode of action in lowering intraocular pressure is similar to that of the nonselective blockers, by suppressing the flow of aqueous humor. The most frequent adverse reaction to betaxolol is stinging upon administration, which is minimised by an ocular suspension with a similarly effective twofold reduced concentration (Betoptic S, 0.25%). The extent of beta 1-adrenoceptor occupancy of topically applied betaxolol in the systemic circulation is less than that of the nonselective blockers and beta 2-receptor occupancy is negligible, providing a better safety profile in patients with cardiopulmonary disease. Experimental studies have revealed that the drug reaches the retina after topical administration and displays a voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel blocking activity, which probably allows betaxolol to improve retinal perfusion and to serve as a neuroprotective agent recommendable in various forms of glaucoma.
Inhibitory action of betaxolol, a beta 1-selective adrenoceptor antagonist, on voltage-dependent calcium channels in guinea-pig artery and vein.[Pubmed:7647977]
Br J Pharmacol. 1995 May;115(1):198-202.
1. The effects of betaxolol, (+/-)-1-[4-[2-(cyclopropylmethoxy) ethyl] phenoxy]-3-(isopropylamino)-2-propanol hydrochloride, a beta 1-selective adrenoceptor antagonist, on voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels were investigated in single smooth muscle cells from guinea-pig mesenteric artery and portal vein using a whole-cell variant of the patch-clamp technique. Ca2+ channel currents were recorded with bath solutions contained 10 mM Ba2+ for arterial cells and 2 mM Ca2+ for venous cells. 2. Betaxolol inhibited Ca2+ channel currents dose-dependently in both mesenteric artery cells and portal vein cells. The two isomers, (+)-betaxolol and (-)-betaxolol (relative beta-antagonistic efficacies of 0.1 and 1, respectively), had similar potencies for inhibiting Ca2+ channel currents in portal vein cells. Propranolol did not inhibit the currents. Thus the inhibitory action of betaxolol on Ca2+ channel currents was independent of the beta-adrenoceptor. 3. The inhibitory action of betaxolol on Ca2+ channel currents was compared with that of diltiazem and of nifedipine in mesenteric artery cells. The current inhibition depended on the stimulation frequency with all drugs (use-dependent block). All drugs also accelerated the current decay and shifted the voltage-dependent inactivation curve in a negative direction. 4. In conclusion, betaxolol inhibited Ca2+ channel currents in vascular smooth muscle cells. The mode of inhibitory action was similar to that of diltiazem and nifedipine. Our results suggest that betaxolol is a unique beta-adrenoceptor antagonist that has a direct inhibitory action on voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels in vascular smooth muscle cells.
The affinity of betaxolol, a beta 1-adrenoceptor-selective blocking agent, for beta-adrenoceptors in the bovine trachea and heart.[Pubmed:8383566]
Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Feb;108(2):484-9.
1. The specificity of betaxolol, a beta-adrenoceptor antagonist, for beta 1- and beta 2-adrenoceptors was compared with that of other beta-antagonists, atenolol, ICI-118551, butoxamine and (+/-)-propranolol, in the bovine trachea and heart by competitive interaction with [3H]-CGP12177 as a radioligand. 2. The radioligand Kd values were 0.75 +/- 0.12 and 1.60 +/- 0.11 nM in the trachea and heart, respectively, and the Bmax values were 34.00 +/- 4.41 and 21.54 +/- 2.94 fmol mg-1 protein, respectively. 3. Using ICI-118551, we determined the ratio of beta 1:beta 2-adrenoceptors in the trachea and heart to be approximately 29:71 and 56:44, respectively. 4. In the trachea, a beta 2-predominant tissue, betaxolol and atenolol were more selective for beta 1-adrenoceptor binding sites than beta 2-adrenoceptor binding sites, whereas ICI-118551 and butoxamine were more selective for beta 2-adrenoceptor binding sites. 5. The beta 1-selectivity of betaxolol was 2.2 and 2.7 fold higher than that of atenolol in the bovine trachea and heart. These findings suggest that betaxolol may be useful in the treatment of hypertension, cardiac arrhythmia and angina pectoris.
Betaxolol. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic efficacy in hypertension.[Pubmed:2866947]
Drugs. 1986 Jan;31(1):6-28.
Betaxolol is a relatively cardioselective beta-adrenoceptor blocking drug, with no partial agonist (intrinsic sympathomimetic) activity and weak membrane-stabilising (local anaesthetic) activity. Its pharmacokinetic properties of most interest include high bioavailability after oral administration, and a long elimination half-life. It has a narrow dose-response range, which obviates the need for dose titration, with 10 to 20 mg once daily being the usual dosage. This dose reduces systolic and diastolic blood pressures by about 15 mm Hg in most patients with mild to moderate hypertension. In a few comparative studies betaxolol 20 mg daily was as effective as atenolol and moderate doses of propranolol, and more effective than acebutolol, in reducing blood pressure in such patients. Betaxolol has been well tolerated in most patients. Thus, betaxolol is an effective alternative to other beta-blocking drugs in patients with essential hypertension, with properties that may offer advantages in some patients.


