BoehmenanCAS# 57296-22-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 57296-22-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5274624 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C40H40O12 | M.Wt | 712.8 |
| Type of Compound | Lignans | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
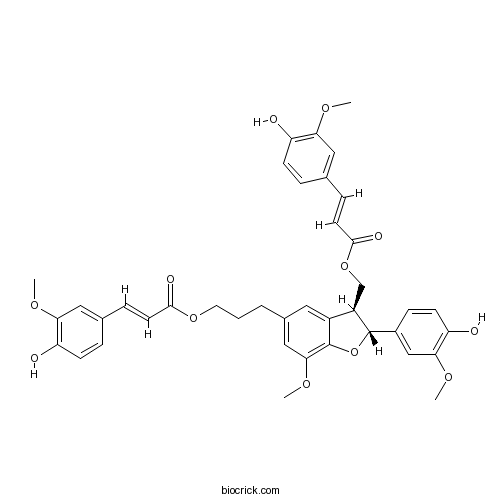
| Chemical Name | 3-[(2R,3S)-2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-3-[[(E)-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoyl]oxymethyl]-7-methoxy-2,3-dihydro-1-benzofuran-5-yl]propyl (E)-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoate | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=CC(=C1)C=CC(=O)OCCCC2=CC(=C3C(=C2)C(C(O3)C4=CC(=C(C=C4)O)OC)COC(=O)C=CC5=CC(=C(C=C5)O)OC)OC)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | OVFZHMPISOASDF-CIQYAKOOSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C40H40O12/c1-46-33-19-24(7-12-30(33)41)9-15-37(44)50-17-5-6-26-18-28-29(23-51-38(45)16-10-25-8-13-31(42)34(20-25)47-2)39(52-40(28)36(21-26)49-4)27-11-14-32(43)35(22-27)48-3/h7-16,18-22,29,39,41-43H,5-6,17,23H2,1-4H3/b15-9+,16-10+/t29-,39+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Boehmenan exhibits cytotoxicity against both Wnt-dependent (HCT116) and Wnt-independent (RKO) cells, it decreases the expression of full, cytosolic and nuclear β-catenin along with c-myc in STF/293 cells, suggestes that boehmenan may have inhibited the Wnt signal by decreasing β-catenin levels. 2. (±)-Boehmenan shows potent protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) inhibitory activity in vitro with the IC(50) values of 43.5 um, it inhibits PTP1B activity in a competitive manner. 3. Boehmenan exhibits the potent cytotoxic effects against many cancer cell lines, boehmenan-mediated anti-tumor property is mediated by modulation of mitochondria and EGFR signaling pathway in A549 NSCLC cells. |
| Targets | Wnt/β-catenin | EGFR | p53 | p21 | Caspase | PARP | MEK | Akt | ERK | STAT |

Boehmenan Dilution Calculator

Boehmenan Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.4029 mL | 7.0146 mL | 14.0292 mL | 28.0584 mL | 35.073 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.2806 mL | 1.4029 mL | 2.8058 mL | 5.6117 mL | 7.0146 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1403 mL | 0.7015 mL | 1.4029 mL | 2.8058 mL | 3.5073 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0281 mL | 0.1403 mL | 0.2806 mL | 0.5612 mL | 0.7015 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.014 mL | 0.0701 mL | 0.1403 mL | 0.2806 mL | 0.3507 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Ridaforolimus (Deforolimus, MK-8669)
Catalog No.:BCC4605
CAS No.:572924-54-0
- Boc-D-Phe(4-F)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3218
CAS No.:57292-45-2
- Boc-D-Phe(4-Cl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3176
CAS No.:57292-44-1
- Calmidazolium chloride
Catalog No.:BCC7410
CAS No.:57265-65-3
- Setiptiline
Catalog No.:BCC1945
CAS No.:57262-94-9
- Salsolinol-1-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC6731
CAS No.:57256-34-5
- 7-Ethoxyresorufin
Catalog No.:BCC6476
CAS No.:5725-91-7
- Methoxyresorufin
Catalog No.:BCC6296
CAS No.:5725-89-3
- Pamidronate Disodium
Catalog No.:BCC1193
CAS No.:57248-88-1
- H-Phe(3-CN)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3182
CAS No.:57213-48-6
- Testosterone decanoate
Catalog No.:BCC9168
CAS No.:5721-91-5
- Ayanin
Catalog No.:BCN4056
CAS No.:572-32-7
- Liriodendrin
Catalog No.:BCN5774
CAS No.:573-44-4
- Congo Red
Catalog No.:BCC8023
CAS No.:573-58-0
- Tacalcitol
Catalog No.:BCC1975
CAS No.:57333-96-7
- Dihydroepistephamiersine 6-acetate
Catalog No.:BCN5775
CAS No.:57361-74-7
- Bombinakinin-GAP
Catalog No.:BCC5903
CAS No.:573671-91-7
- Isochlorogenic acid C
Catalog No.:BCN2498
CAS No.:57378-72-0
- Irsogladine
Catalog No.:BCC4562
CAS No.:57381-26-7
- Oroxin A
Catalog No.:BCN1202
CAS No.:57396-78-8
- Benzoin ethyl ether
Catalog No.:BCC8855
CAS No.:574-09-4
- Isoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN8508
CAS No.:574-12-9
- Fraxetin
Catalog No.:BCN5903
CAS No.:574-84-5
- Fexaramine
Catalog No.:BCC7412
CAS No.:574013-66-4
Boehmenan, a lignan from Hibiscus ficulneus, showed Wnt signal inhibitory activity.[Pubmed:26026364]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015 Jul 15;25(14):2735-8.
The Wnt signal pathway modulates numerous biological processes, and its aberrant activation is related to various diseases. Therefore, inhibition of the Wnt signal may provide an effective (or efficient) strategy for these diseases. Cell-based luciferase assay targeting the Wnt signal (TOP assay) revealed that Hibiscus ficulneus extract inhibited the Wnt signal. The activity-guided isolation of the MeOH extract of H. ficulneus stems yielded four known (1-4) lignans along with myriceric acid (5). Compounds 1-4 potently inhibited the Wnt signal with TOPflash IC50 values of 1.0, 4.5, 6.3, and 1.9 muM, respectively. Compound 1 exhibited cytotoxicity against both Wnt-dependent (HCT116) and Wnt-independent (RKO) cells. Western blot analysis showed that 1 decreased the expression of full, cytosolic and nuclear beta-catenin along with c-myc in STF/293 cells. Our results suggested that 1 may have inhibited the Wnt signal by decreasing beta-catenin levels.
Chemical constituents from Sambucus adnata and their protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitory activities.[Pubmed:22041077]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2011;59(11):1396-9.
The MeOH extract from the whole plants of Sambucus adnata has shown significant protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) inhibitory activity. Chemical study on the extract resulted in the isolation of thirteen compounds, including a novel triterpene (1). The structure of 1 was determined to be 1alpha,3beta-dihydroxy-urs-12-en-11-one-3-yl palmitate on the basis of extensive spectroscopic analyses. Among the isolated compounds, ursolic acid, oleanolic acid and (+/-)-Boehmenan showed the most potent PTP1B inhibitory activity in vitro with the IC(50) values of 4.1, 14.4 and 43.5 microm, respectively. The kinetic analysis indicated that (+/-)-Boehmenan inhibits PTP1B activity in a competitive manner.
Boehmenan, a lignan from the Chinese medicinal plant Clematis armandii, induces apoptosis in lung cancer cells through modulation of EGF-dependent pathways.[Pubmed:27064005]
Phytomedicine. 2016 May 15;23(5):468-76.
BACKGROUND: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is an effective molecular target for cancer treatment. Boehmenan, a lignan from the dried stems of Clematis armandii, exhibited the potent cytotoxic effects against many cancer cell lines in previous studies. However, the effects and underlying mechanism of Boehmenan on non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) remains unclear. PURPOSE: The present study was designed to determine the in vitro anti-cancer properties and underlying molecular mechanisms of Boehmenan on A549 NSCLC cells. STUDY DESIGN/METHODS: Cellular viability and chemoattractive properties of macrophages were investigated by using MTT and transwell migration assay, respectively. Mitochondrial membrane potential (DeltaPsim), apoptotic ratio, and cell cycle were measured by flow cytometry. Protein expression was visualized by Western blot using specific antibodies. RESULTS: Boehmenan concentration-dependently suppressed proliferation and induced G1 phase arrest in A549 NSCLC cells, which were accompanied by reduction of migration, colony formation and increase of apoptosis in A549 cells. In addition, Boehmenan treatment markedly modulated apoptosis-related protein (p53, p21, cleaved caspase 3, and cleaved PARP) and cyclin D1 expression and induced DeltaPsim collapse in a concentration dependent manner. Furthermore, Boehmenan concentration-dependently inhibited EGF-induced activation of EGFR and its downstream signaling molecules, including MEK, Akt, ERK1/2, and STAT3. CONCLUSION: Taken together, our results suggested that Boehmenan-mediated anti-tumor property was mediated by modulation of mitochondria and EGFR signaling pathway in A549 NSCLC cells.


