Oroxin ACAS# 57396-78-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 57396-78-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5320313 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
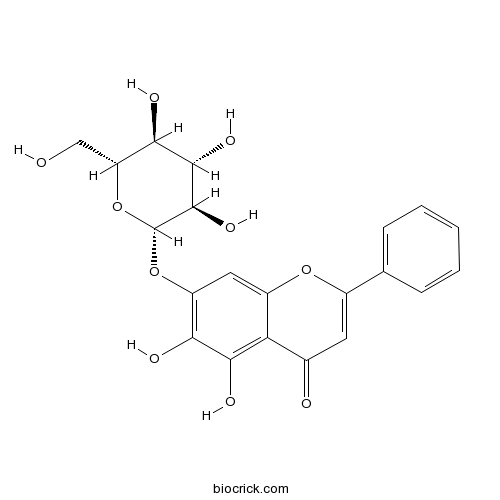
| Formula | C21H20O10 | M.Wt | 432.38 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Oroxin A; 5,6,7-Trihydroxyflavone 7-glucoside | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in methanol and water | ||
| Chemical Name | 5,6-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-7-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxychromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C=C1)C2=CC(=O)C3=C(C(=C(C=C3O2)OC4C(C(C(C(O4)CO)O)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | IPQKDIRUZHOIOM-IAAKTDFRSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H20O10/c22-8-14-17(25)19(27)20(28)21(31-14)30-13-7-12-15(18(26)16(13)24)10(23)6-11(29-12)9-4-2-1-3-5-9/h1-7,14,17,19-22,24-28H,8H2/t14-,17-,19+,20-,21-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Oroxin A is a xanthine oxidase (XO) inhibitor, it exerts its antibreast cancer effects by inducing ER stress-mediated senescence, activating the key stress signaling pathway, and increasing key ER stress genes and expression levels. |
| Targets | XO |
| In vitro | Oroxin A inhibits breast cancer cell growth by inducing robust endoplasmic reticulum stress and senescence.[Pubmed: 26599214 ]Anticancer Drugs. 2016 Mar;27(3):204-15.Breast cancer is a major cause of cancer death among women. Although various anticancer drugs have been used in clinics, drugs that are effective against advanced and metastatic breast cancer are still lacking and in great demand.
|
| Structure Identification | Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2006 Apr;41(4):380-4.[Qualitative and quantitative determination of the main components of huanglianjiedu decoction by HPLC-UV/MS].[Pubmed: 16856488]To establish a comprehensive HPLC analytical method of Huanglianjiedu decoction.
|

Oroxin A Dilution Calculator

Oroxin A Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3128 mL | 11.5639 mL | 23.1278 mL | 46.2556 mL | 57.8195 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4626 mL | 2.3128 mL | 4.6256 mL | 9.2511 mL | 11.5639 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2313 mL | 1.1564 mL | 2.3128 mL | 4.6256 mL | 5.782 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0463 mL | 0.2313 mL | 0.4626 mL | 0.9251 mL | 1.1564 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0231 mL | 0.1156 mL | 0.2313 mL | 0.4626 mL | 0.5782 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Irsogladine
Catalog No.:BCC4562
CAS No.:57381-26-7
- Isochlorogenic acid C
Catalog No.:BCN2498
CAS No.:57378-72-0
- Bombinakinin-GAP
Catalog No.:BCC5903
CAS No.:573671-91-7
- Dihydroepistephamiersine 6-acetate
Catalog No.:BCN5775
CAS No.:57361-74-7
- Tacalcitol
Catalog No.:BCC1975
CAS No.:57333-96-7
- Congo Red
Catalog No.:BCC8023
CAS No.:573-58-0
- Liriodendrin
Catalog No.:BCN5774
CAS No.:573-44-4
- Boehmenan
Catalog No.:BCN5773
CAS No.:57296-22-7
- Ridaforolimus (Deforolimus, MK-8669)
Catalog No.:BCC4605
CAS No.:572924-54-0
- Boc-D-Phe(4-F)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3218
CAS No.:57292-45-2
- Boc-D-Phe(4-Cl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3176
CAS No.:57292-44-1
- Calmidazolium chloride
Catalog No.:BCC7410
CAS No.:57265-65-3
- Benzoin ethyl ether
Catalog No.:BCC8855
CAS No.:574-09-4
- Isoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN8508
CAS No.:574-12-9
- Fraxetin
Catalog No.:BCN5903
CAS No.:574-84-5
- Fexaramine
Catalog No.:BCC7412
CAS No.:574013-66-4
- 8-O-Acetylshanzhiside methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN5776
CAS No.:57420-46-9
- (2S)-2alpha-(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)-3,5-dihydro-5alpha-methoxy-3beta-methyl-5-allyl-2H-benzofuran-6-one
Catalog No.:BCN6606
CAS No.:57430-03-2
- Methylergometrine maleate
Catalog No.:BCC6691
CAS No.:57432-61-8
- Resiniferatoxin
Catalog No.:BCC6951
CAS No.:57444-62-9
- p-Menth-8-ene-1,2-diol
Catalog No.:BCN5777
CAS No.:57457-97-3
- 2-Epi-3a-epiburchellin
Catalog No.:BCN7013
CAS No.:57457-99-5
- Stigmasta-3,5-diene
Catalog No.:BCC8254
CAS No.:4970-37-0
- H-Asn-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2876
CAS No.:57461-34-4
Oroxin A inhibits breast cancer cell growth by inducing robust endoplasmic reticulum stress and senescence.[Pubmed:26599214]
Anticancer Drugs. 2016 Mar;27(3):204-15.
Breast cancer is a major cause of cancer death among women. Although various anticancer drugs have been used in clinics, drugs that are effective against advanced and metastatic breast cancer are still lacking and in great demand. In this study, we found that Oroxin A, an active component isolated from the herb Oroxylum indicum (L.) Kurz, effectively inhibited the growth of human breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231 and MCF7 by inducing endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-mediated senescence. Oroxin A caused breast cancer cell cycle arrest at the G2/M stage, and reorganization of microtubules and actin cytoskeleton accompanied by a decrease in cellular mitosis. ER-specific probe ER-Tracker Red and confocal microscope imaging showed that ER-Tracker Red-positive cells increased in an Oroxin A dosage-dependent manner. In addition, Oroxin A increased cell population with high beta-Gal activity and SAHF-positive staining; these data suggest that Oroxin A induces breast cancer cell ER stress and senescence. Mechanistic studies showed that Oroxin A led to a significant increase in intracellular reactive oxygen species levels, promoted expression of ER stress markers ATF4 and GRP78, and increased the phosphorylation of a key stress-response signaling protein p38, resulting in an ER stress-mediated senescence. Taken together, our data indicate that Oroxin A exerts its antibreast cancer effects by inducing ER stress-mediated senescence, activating the key stress p38 signaling pathway, and increasing key ER stress genes ATF4 and GRP78 expression levels.
Discovery of xanthine oxidase inhibitors from a complex mixture using an online, restricted-access material coupled with column-switching liquid chromatography with a diode-array detection system.[Pubmed:24510210]
Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014 Mar;406(7):1975-84.
To find potential lead compounds for antigout drug discovery, an automated online, restricted-access material coupled with column-switching liquid chromatography with a diode-array detection (RAM-LC-DAD) system was developed for screening of xanthine oxidase (XO) inhibitors and their affinity rankings in complex mixtures. The system was first evaluated by analyzing a mixture of six compounds with known inhibition of XO. Nonspecific binding to the denatured XO was investigated and used as the control for screening. Subsequently, the newly developed system was applied to screening of a natural product, Oroxylum indicum extract, and four compounds which could specifically interact with XO were found and identified as oroxin B, Oroxin A, baicalin, and baicalein. The results were verified by a competitive binding test using the known competitive inhibitor allopurinol and were further validated by an inhibition assay in vitro. The online RAM-LC-DAD system developed was shown to be a simple and effective strategy for the rapid screening of bioactive compounds from a complex mixture.
[Qualitative and quantitative determination of the main components of huanglianjiedu decoction by HPLC-UV/MS].[Pubmed:16856488]
Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2006 Apr;41(4):380-4.
AIM: To establish a comprehensive HPLC analytical method of Huanglianjiedu decoction. METHODS: This study was performed by HPLC-UV/MS to identify the chemical constituents of the whole and individual herbs of the "Huanglianjiedu decoction". Zorbax Extend C18 (150 mm x 4. 6 mm ID, 5 microm) column was used; the mobile phase was composed of acetonitrile (A) and water (B, with 0.5% acetic acid) with gradient elution; the flow rate was 1.0 mL x min(-1) and the column temperature was setup at 25 degrees C. The detection wavelength was 254 nm. RESULTS: The chromatogram of Huanglianjiedu decoction showed 21 main peaks. Peaks 1, 2, 5 and 18 were from Gardenia jasminoides Ellis, Peaks 8, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 19 and 21 from Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. While 10 from Coptis chinensis Franch and 20 from Phellodendron amurense Rupr., Peaks 3, 4, 6, 9, 11 and 12 came from them together. Peak 7 presented in the chromatograms of the herbs except Gardenia jasminoides Ellis. By comparison of the retention time, the on-line UV spectra and MS spectra, 11 peaks were identified as 5 (geniposide), 9 (jatrorrhizine), 10 (coptisine), 11 (palmatine), 12 (berberine), 13 (baicalin), 15 (Oroxin A), 17 (wogonoside), 19 (baicalein), 20 (obaculactone), 21 (wogonin), then eight of them were quantified by HPLC-UV. CONCLUSION: The method could represent the characteristics of Huanglianjiedu decoction, and it could be used to evaluate the quality and quantity of Huanglianjiedu decoction. It distinguished between Coptis chinensis Franch and Phellodendron amurense Rupr. by HPLC for the first time.


