Bz-Tyr-OetCAS# 3483-82-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 3483-82-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 253239 | Appearance | Powder |
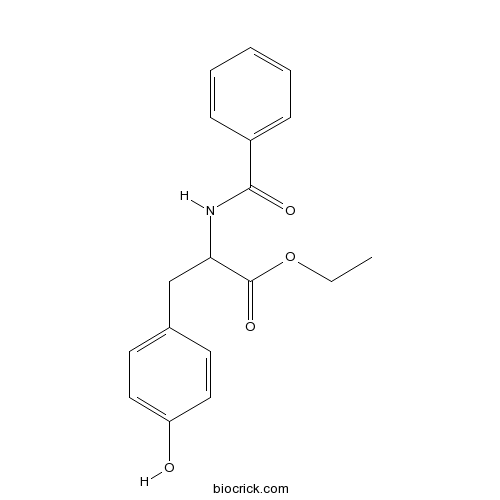
| Formula | C18H19NO4 | M.Wt | 313.4 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | ethyl 2-benzamido-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoate | ||
| SMILES | CCOC(=O)C(CC1=CC=C(C=C1)O)NC(=O)C2=CC=CC=C2 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | SRLROPAFMUDDRC-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H19NO4/c1-2-23-18(22)16(12-13-8-10-15(20)11-9-13)19-17(21)14-6-4-3-5-7-14/h3-11,16,20H,2,12H2,1H3,(H,19,21) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Bz-Tyr-Oet Dilution Calculator

Bz-Tyr-Oet Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1908 mL | 15.9541 mL | 31.9081 mL | 63.8162 mL | 79.7703 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6382 mL | 3.1908 mL | 6.3816 mL | 12.7632 mL | 15.9541 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3191 mL | 1.5954 mL | 3.1908 mL | 6.3816 mL | 7.977 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0638 mL | 0.3191 mL | 0.6382 mL | 1.2763 mL | 1.5954 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0319 mL | 0.1595 mL | 0.3191 mL | 0.6382 mL | 0.7977 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Bz-Tyr-Oet
- DL-Dithiothreitol
Catalog No.:BCC7586
CAS No.:3483-12-3
- 4'-Demethyleucomin
Catalog No.:BCN5283
CAS No.:34818-83-2
- Marilactone
Catalog No.:BCN7363
CAS No.:34818-17-2
- 8-Acetonyldihydroavicine
Catalog No.:BCN3303
CAS No.:348098-59-9
- BAY 57-1293
Catalog No.:BCC4050
CAS No.:348086-71-5
- Boc-Met(O)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3425
CAS No.:34805-21-5
- H-Tyr(Bzl)-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3132
CAS No.:34805-17-9
- H-D-Met-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2997
CAS No.:348-67-4
- Z-Asp(OBzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2791
CAS No.:3479-47-8
- Sodium usnate
Catalog No.:BCN8376
CAS No.:34769-44-3
- ITX3
Catalog No.:BCC6066
CAS No.:347323-96-0
- Ferrostatin-1 (Fer-1)
Catalog No.:BCC2323
CAS No.:347174-05-4
- Metiamide
Catalog No.:BCC1742
CAS No.:34839-70-8
- 12-Hydroxyabietic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5284
CAS No.:3484-61-5
- Methyl 3-methoxyacrylate
Catalog No.:BCN2258
CAS No.:34846-90-7
- Optovin
Catalog No.:BCC6323
CAS No.:348575-88-2
- Coptisine
Catalog No.:BCN6320
CAS No.:3486-66-6
- Palmatine
Catalog No.:BCN5285
CAS No.:3486-67-7
- UK 383367
Catalog No.:BCC2308
CAS No.:348622-88-8
- Vineridine
Catalog No.:BCN5286
CAS No.:3489-06-3
- HC-030031
Catalog No.:BCC4910
CAS No.:349085-38-7
- GSK 137647
Catalog No.:BCC8045
CAS No.:349085-82-1
- JX 401
Catalog No.:BCC7443
CAS No.:349087-34-9
- Cryptomeridiol 11-rhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN4648
CAS No.:349112-30-7
Detection of a trypsin-like serine protease and its endogenous inhibitor in hake skeletal muscle.[Pubmed:1898057]
Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Aug 15;289(1):1-5.
When dialyzed extracts from hake (Merluccius hubbsi) skeletal muscle were chromatographed in DEAE-Sephacel, an alkaline protease (37 degrees C, pH 8.5) and a trypsin inhibitor were isolated. The enzyme showed its maximal activity against azocasein in the range of pH between 7 and 9. The protease was able to hydrolyze the trypsin substrates Bz-Arg-OEt and Tos-Arg-OMe and did not cleave the chymotrypsin substrate Bz-Tyr-Oet. The enzyme was strongly inhibited by several serine protease inhibitors, whereas inhibitors of the other types of proteases scarcely affected it. The protease was able to degrade the major contractile and cytoskeletal constituent proteins of myofibrils and to accumulate acid-soluble products. The protease activity was completely suppressed by the addition of the trypsin inhibitor isolated from the same muscle. These results indicate that hake skeletal muscle contains a trypsin-like serine protease which might be involved in the catabolism of myofibrillar proteins, as well as in the proteolytic events that take place during post mortem storage of fish muscle.
Application of carboxypeptidase C for peptide synthesis.[Pubmed:1366863]
Enzyme Microb Technol. 1990 Nov;12(11):836-40.
Carboxypeptidase C partially purified from the flavedo of citrus fruit by a new, simple procedure was studied as a catalyst for peptide-bond formation. Dipeptides were obtained in high yields (80-95%) with Bz--Tyr--OEt as carboxyl-compound, and amino acid amides and amino acid alkylesters as nucleophiles. To characterize the synthesis reaction, a number of parameters such as pH, excess of the nucleophile, and the molarity of the buffer were evaluated. The yield of dipeptides depends on the side chain of the amino acid alkylester used as the carboxyl component as well as on the N-terminal protecting group. Esterase activity was minimal in the absence of a nucleophile, suggesting a modified mechanism for the synthesis reaction compared to other serine proteases. No secondary hydrolysis of the peptides formed was observed.
Substrate specificity of honeydew melon protease D, a plant serine endopeptidase.[Pubmed:9301107]
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1997 Aug;61(8):1277-80.
The substrate specificity of honeydew melon (Cucumis melo var. inodorus Naud) protease D was studied by the use of synthetic substrates and oligopeptides derived from a protein hydrolyzate. The hydrolysis rates of succinyl-(L-Ala)1-3-p-nitroanilide (Suc-(Ala)1-3-pNA) the hydrolysis rate progressively rose in proportion to the increased chain length. Benzyloxycarbonyl-L-tyrosine p-nitrophenyl ester (Z-Tyr-ONp) and benzoyl-L-tyrosine ethyl ester (Bz-Tyr-Oet) were cleaved by honeydew melon protease D, but benzoyl-L-arginine p-nitroanilide (Bz-Arg-pNA), benzyloxycarbonyl-L-lysine p-nitrophenyl ester (Z-Lys-ONp) and tosyl-L-arginine methyl ester (Tos-Arg-OMe) were not hydrolyzed. Contrary to the results obtained by using synthetic substrates, the carboxyl sides of charged amino acid residues were preferentially cleaved by the enzyme in the oligopeptide substrates. The substrates that had charged or polar amino acids at P2 positions were not cleaved. On the other hand, the non-polar amino acid or proline at P2 were favored for hydrolysis. The information concerning the subsite of protease D was obtained and is useful for synthesis of a good substrate. As it is distinct from molecular mass, the substrate specificity of honeydew melon protease D is most analogous to cucumisin [EC 3.4.21.25] among serine proteases from cucurbitaceous plants.
Improved isolation, stability and substrate specificity of cucumisin, a plant serine endopeptidase.[Pubmed:7576259]
Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 1995 Oct;22(2):215-22.
Cucumisin (EC 3.4.21.25), a serine endopeptidase, was isolated by a simple purification procedure from the prince melon (Cucumis melo ssp. melo, cv. 'Prince Melon'). The enzyme is stable over a wide pH range (4-11) and to heat, 80% of its initial activity remaining even at pH 11.1 and at 60 degrees C for 20 min. The enzyme was inactive at 72 degrees C and pH 8.0, but 38% of the activity remained in the presence of 10% (w/v) glycerol. Caseinolysis by cucumisin indicated full activity in 8 M urea at pH 9.1 and 50 degrees C. Cucumisin was inactivated by treatment with trypsin at 37 degrees C for 24 h, but was not affected by alpha-chymotrypsin. The synthetic substrates benzyloxycarbonyltyrosine nitrophenyl ester (Z-Tyr-ONp) and benzoyltyrosine ethyl ester (Bz-Tyr-Oet) were cleaved, but Z-Lys-ONp and tosylarginine methyl ester (Tos-Arg-OMe) were not cleaved by cucumisin. Oxidized insulin B-chain was hydrolysed by cucumisin at 37 degrees C for 24 h, 21 cleavage sites being detected. Cucumisin could not cleave the C-termini of all the valine residues in the oxidized insulin B-chain molecule.
Purification and characterization of two serine collagenolytic proteases from crab Paralithodes camtschatica.[Pubmed:7953075]
Comp Biochem Physiol Biochem Mol Biol. 1994 Aug;108(4):561-8.
Two enzymes possessing collagenolytic activity were isolated from the hepatopancreas of crab Paralithodes camtschatica by ammonium sulfate fractionation and DEAE-Sepharose chromatography. It was shown that the specific activities of proteases A and C toward insoluble collagen were equal to 400 and 300 Mandl units/mg protein, respectively. The mol. wt of homogenous proteases A and C determined by gradient polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in the presence of SDS and 2-mercaptoethanol were equal to 30 and 24 kDa, respectively. The isoelectric point values for the enzymes were determined as 2.5 and 2.9. Both enzymes lack carbohydrates. The amino acid compositions of two crab proteases were measured. The optimal conditions for the enzyme catalysis and the catalytic constants for collagenolytic proteases A and C with respect to Bz-Arg-pNA and Bz-Tyr-Oet have been determined. Inhibition data led to classification of the purified enzymes as serine proteases.


