Coumarin 343CAS# 55804-65-4 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 55804-65-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 108770.0 | Appearance | Powder |
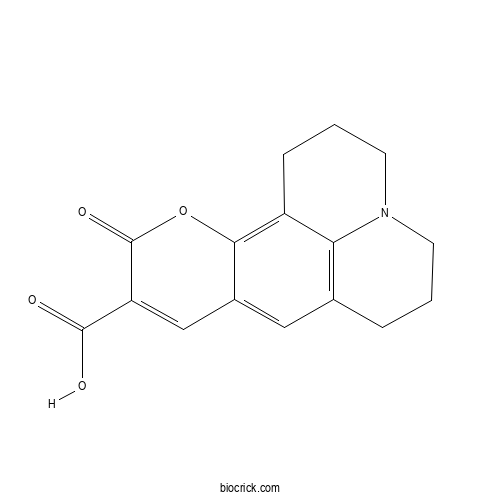
| Formula | C16H15NO4 | M.Wt | 285.29 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 4-oxo-3-oxa-13-azatetracyclo[7.7.1.02,7.013,17]heptadeca-1,5,7,9(17)-tetraene-5-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1CC2=C3C(=C4C(=C2)C=C(C(=O)O4)C(=O)O)CCCN3C1 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KCDCNGXPPGQERR-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H15NO4/c18-15(19)12-8-10-7-9-3-1-5-17-6-2-4-11(13(9)17)14(10)21-16(12)20/h7-8H,1-6H2,(H,18,19) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Coumarin 343 Dilution Calculator

Coumarin 343 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5052 mL | 17.526 mL | 35.0521 mL | 70.1041 mL | 87.6301 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.701 mL | 3.5052 mL | 7.0104 mL | 14.0208 mL | 17.526 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3505 mL | 1.7526 mL | 3.5052 mL | 7.0104 mL | 8.763 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0701 mL | 0.3505 mL | 0.701 mL | 1.4021 mL | 1.7526 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0351 mL | 0.1753 mL | 0.3505 mL | 0.701 mL | 0.8763 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Hydroxypinacolone Retinoate
Catalog No.:BCX0934
CAS No.:893412-73-2
- 2-Methoxybenzoicacid
Catalog No.:BCX0933
CAS No.:529-75-9
- Nicotinamidemononucleotide
Catalog No.:BCX0932
CAS No.:1094-61-7
- Cepharanoline
Catalog No.:BCX0931
CAS No.:27686-34-6
- PhysalinF
Catalog No.:BCX0930
CAS No.:57517-46-1
- 3-(3-hydroxylphenyl)propanol
Catalog No.:BCX0929
CAS No.:621-54-5
- (+)-Pinoresinolmonomethylether4-O-β-D-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX0928
CAS No.:74957-57-6
- Hydroxyisogermafurenolide
Catalog No.:BCX0927
CAS No.:20267-91-8
- 14-Deoxy-11-oxoandrographolide
Catalog No.:BCX0926
CAS No.:42895-57-8
- MogrosideIIA
Catalog No.:BCX0925
CAS No.:1613527-65-3
- Pseudojervine
Catalog No.:BCX0924
CAS No.:36069-05-3
- BoeravinoneA
Catalog No.:BCX0923
CAS No.:114567-33-8
- LINOLELAIDICACIDMETHYLESTER
Catalog No.:BCX0936
CAS No.:2566-97-4
- Ginno
Catalog No.:BCX0937
CAS No.:2606-50-0
- β-Elemene
Catalog No.:BCX0938
CAS No.:515-13-9
- PhlorigidosideC
Catalog No.:BCX0939
CAS No.:276691-32-8
- (S)-(-)-Norcoclaurinehydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCX0940
CAS No.:105990-27-0
- 14-hydroxylatedbrassinosteroid
Catalog No.:BCX0941
CAS No.:457603-63-3
- Harmalinehydrochloridedihydrate
Catalog No.:BCX0942
CAS No.:6027-98-1
- Lycobetaineacetate
Catalog No.:BCX0943
CAS No.:61221-41-8
- CompoundK
Catalog No.:BCX0944
CAS No.:160729-91-9
- 11-hydroxy-1-isomangostin
Catalog No.:BCX0945
CAS No.:164365-71-3
- GarcixanthonesB
Catalog No.:BCX0946
CAS No.:2522597-99-3
- MangostanaxanthoneIV
Catalog No.:BCX0947
CAS No.:2182593-73-1
Vanadocene-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles: platforms for the development of theranostic materials against breast cancer.[Pubmed:38387062]
Biomed Mater. 2024 Mar 6;19(3).
Nanoscale materials have demonstrated a very high potential in anticancer therapy by properly adjusting their functionalization and physicochemical properties. Herein, we report the synthesis of some novel vanadocene-loaded silica-based nanomaterials incorporating four different S-containing amino acids (penicillamine, methionine, captopril, and cysteine) and different fluorophores (rhodamine B, Coumarin 343 or Alexa Fluor 647), which have been characterized by diverse solid-state spectroscopic techniques viz; FTIR, diffuse reflectance spectroscopies,(13)C and(51)V solid-state NMR spectroscopy, thermogravimetry and TEM. The analysis of the biological activity of the novel vanadocene-based nanostructured silicas showed that the materials containing cysteine and captopril aminoacids demonstrated high cytotoxicity and selectivity against triple negative breast cancer cells, making them very promising antineoplastic drug candidates. According to the biological results it seems that vanadium activity is connected to its incorporation through the amino acid, resulting in synergy that increases the cytotoxic activity against cancer cells of the studied materials presumably by increasing cell internalization. The results presented herein hold significant potential for future developments in mesoporous silica-supported metallodrugs, which exhibit strong cytotoxicity while maintaining low metal loading. They also show potential for theranostic applications highlighted by the analysis of the optical properties of the studied systems after incorporating rhodamine B, Coumarin 343 (possible)in vitroanticancer analysis, or Alexa Fluor 647 (in vivostudies of cancer models).
A golgi-targeting and polarity-specific fluorescent probe for the diagnosis of cancer and fatty liver in living cells and tissues.[Pubmed:37913597]
Talanta. 2024 Feb 1;268(Pt 1):125367.
Elucidating the intrinsic relationship between diseases and Golgi apparatus polarity remains a great challenge owing to the lack of the Golgi-specific fluorescent probe for polarity. Until now, the visualization of abnormal Golgi apparatus polarity in clinical cancer patient samples has not been achieved. To meet this urgent challenge, we facilely synthesized a robust Golgi-targeting and polarity-specific fluorescent probe (GCSP), which consists of an electron-acceptor solvatochromic Coumarin 343 and an electron-donor Golgi-targeting group phenylsulfonamide. Owing to the typical D-pi-A molecular configuration with unique intramolecular charge transfer effect, GCSP exhibits high sensitivity to polarity change in different solvents. Moreover, we revealed that GCSP possessed a satisfactory ability to sensitively monitor Golgi apparatus polarity changes in living cells. Using GCSP, we have successfully shown that Golgi apparatus polarity may serve as an ubiquitous marker for cancer and fatty liver detection. Surprisingly, the visualization of Golgi polarity has been achieved not only at the cellular levels, but also in clinical tissue samples from cancer patients, thus holding great potential in the clinical diagnosis of human cancer. All these features render GCSP an effective tool for the accurate diagnosis of Golgi apparatus related diseases.
Fluorescent hydrophobic ion pairs: A powerful tool to investigate cellular uptake of hydrophobic drug complexes via lipid-based nanocarriers.[Pubmed:37839235]
J Colloid Interface Sci. 2024 Jan 15;654(Pt A):174-188.
HYPOTHESIS: Hydrophobic ion pairs (HIPs) between two fluorescent components and incorporation into nanoemulsions (NE) allows tracking in cellular uptake studies. EXPERIMENTS: HIPs were formed between propidium iodide and 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-(7-nitro-2-1,3-benzoxadiazol-4-yl) (NBD-PE), azure A chloride and NBD-PE or Coumarin 343 and 4-(4-dihexadecylaminostyryl)-N-methylpyridinium iodide) (DiA). Fluorescence spectra of the resulting complexes were recorded. HIPs were loaded into zwitterionic NE and their size, stability in different media, haemolytic properties and cytotoxicity were evaluated. Furthermore, cellular uptake at 37 degrees C and 4 degrees C was investigated via flow cytometry and confocal microscopy. FINDINGS: HIP-formation increased lipophilicity of the hydrophilic model drugs. NE exhibited a size between 80 and 150 nm and were not toxic in concentrations up to 0.1 % but showed high haemolytic properties. Cellular uptake of propidium, azure A and Coumarin 343 were 8-fold, 115-fold and 1.3-fold improved by the formation of HIPs and up to 59-fold, 120-fold and 50-fold by incorporating these HIPs in NE, respectively. Lower uptake was observed at 4 degrees C. In case of propidium/ NBD-PE and azure A/ NBD-PE HIPs, propidium and azure A were delivered into the cytosol, whereas NBD-PE was unable to enter cells. In case of Coumarin 343/ DiA HIPs, both components accumulated in the cell membrane. Therefore, HIPs between two fluorescent compounds are a powerful tool to investigate cellular uptake of hydrophobic complexes via nanocarriers by visualization of their cellular distribution.
Facile Photoresponsive Actuators Based on Ferrocene-Doped Poly(butyl methacrylate).[Pubmed:37537978]
ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023 Aug 16;15(32):38846-38856.
This paper presents facile photoresponsive actuators comprising ferrocene as a guest chromophore and poly(butyl methacrylate) (PBMA) as a host matrix. The ferrocene-doped PBMA film exhibits mechanical expansion and contraction when a 445 nm laser is turned on and off, respectively. The photoresponsive film is attached by a commercially available acetylcellulose adhesive tape, which exhibits a bending motion that is controlled by turning the laser on and off. Thereafter, the double-layer film is employed to fabricate a table-shaped lifting machine (0.7 mg) that lifts a 10.5 mg object up and down by turning the laser on and off, respectively, and the mechanical force offered by the double-layer film is recorded. Additionally, the film is coated with gold and applied to an electric circuit that serves as a reversible photoresponsive switch. This film preparation technique is applied to other chromophores (e.g., Coumarin 343, Rhodamine 6G, Sudan Blue II, and Solvent Green 3) to independently control the motions of the films with 445, 520, and 655 nm lasers. The ferrocene-containing films also exhibit photoinduced healing from mechanical damage. Finally, the photoirradiation-accompanied morphological changes in the film are observed via small-angle X-ray scattering.
Degenerate and non-degenerate two-photon absorption of coumarin dyes.[Pubmed:37318284]
Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2023 Jun 28;25(25):16772-16780.
Two-photon absorption (2PA) spectroscopy is a robust bioimaging tool that depends on the determined cross-sections (sigma(2PA)). The absorption of both photons occurs simultaneously with equivalent (degenerate) or different (non-degenerate) photon energies, D-2PA and ND-2PA, respectively. The former has been investigated experimentally and computationally for many systems, while the latter remains relatively unexplored computationally and limited experimentally. In this study, response theory using time-dependent density functional theory (TD-DFT) and the 2-state model (2SM) have been utilized to investigate sigma(D-2PA) and sigma(ND-2PA) for the excitation to the lowest energy singlet state (S(1)) of coumarin, coumarin 6, coumarin 120, coumarin 307, and Coumarin 343. Solvents involved were methanol (MeOH), chloroform (ClForm), and dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO), where the latter leads to the largest sigma(2PA). Values of sigma(2PA) are largest for coumarin 6 and lowest for coumarin, which illustrates the effect of substituents. The 2SM clarifies how the largest cross-sections correspond to molecules with the largest transition dipole moments, mu(01). In general, sigma(D-2SM) computations agree with sigma(D-2PA). Moreover, sigma(ND-2SM) are in qualitative agreement with sigma(ND-2PA) with comparable enhancement relative to sigma(D-2PA). Overall, sigma(ND-2PA) are larger than sigma(D-2PA) where the increase is in the range of 22% to 49%, depending on the coumarin as well as the relative energies of the two photons. This work aids in future investigations into various fluorophores to understand their photophysical properties for ND-2PA.
Metal-enhanced fluorescence of dyes with quadrupole surface plasmon resonance of silver nanoparticles.[Pubmed:36132004]
Nanoscale Adv. 2022 May 3;4(13):2794-2805.
Silver colloidal films (SCFs) composed of homogeneous 60-220 nm silver nanoparticles were synthesized for optimal fluorescence enhancement of chromophores with the dipole and quadrupole surface plasmons. The fluorescence enhancements with the SCFs of three chromophores, 4-(dicyanomethylene)-2-methyl-6-(4-dimethylaminostyryl)-4H-pyran, 4-dimethylamino-4'-nitrobiphenyl, and Coumarin 343 whose emission spectra are centered distinctively in the 470-560 nm wavelength range were compared. Fluorescence enhancements and lifetime changes were investigated via time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy. The spectral overlap between the chromophore's emission and the dipole or quadrupole surface plasmon resonance (SPR) bands determined the fluorescence enhancements with the SCFs. The dipole and quadrupole SPR bands both appeared to provide effective fluorescence enhancements of chromophores. This knowledge allows researchers to develop sensitive fluorescence sensors by combining nanoparticles with optimal dipole or quadrupole SPR bands in order to achieve fluorescence enhancement of a specific chromophore. The emission dynamics measurements with the SCFs were combined with the finite-difference time-domain simulation results for the local electric fields around the silver nanoparticles to enable discussion of metal-enhanced fluorescence mechanisms, including excitation and emission enhancements.
Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy based insights into diffusion in electrochemical energy systems.[Pubmed:35961301]
Methods Appl Fluoresc. 2022 Aug 24;10(4).
Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy, a commonly used technique for measuring diffusion of biomolecules and tracer dyes in different solvents, is employed to characterise the local transport properties in battery electrolytes. Diffusion of ions, a major limiting factor in battery capacity and charging rates, depends on the local interactions and structuredness of the electrolytic species. Structuredness in the electrolyte results from typical solvation behaviour of diffusing ions/molecules leading to long-range interactions. In this work, we have used FCS to measure tracer diffusion of Coumarin 343 in a mixture of Ethylene Carbonate (EC) and Dimethyl Carbonate (DMC), commonly used as electrolyte solvent in Li-ion batteries. The measured diffusion is found to depend on lithium-ion concentrations. It is found that the addition of LiPF(6)to an EC-DMC equimolar mixture slows down tracer diffusion significantly. Indeed, the bulk viscosity of the electrolyte added with LiPF(6)salt varies with salt concentration. However, the change in bulk viscosity (global behaviour) at high ion concentrations does not match the one inferred from applying Stoke-Einstein's relation to the diffusion data (local behaviour). This indicates that the homogeneity of the electrolyte does not extend spatially to molecular scales around the diffusing tracer molecule. Measurements made on coin cells prepared with different concentrations of LiPF(6)show battery performance limited at higher concentrations, characterized by specific capacity loss at faster charging cycles. This limitation is directly related to the local behaviour of the electrolyte as quantified by measurements of tracer diffusion, which slows down, which remarkably outweighs the advantage of high carrier densities.
Coumarin 343 in aqueous solution: theoretical analysis of absorption.[Pubmed:35460442]
J Mol Model. 2022 Apr 23;28(5):126.
Vibronic coupling and hydration were taken into account when describing the absorption of coumarin C343 (both neutral and anionic forms) in an aqueous media. It was shown that the B3LYP functional with the 6-31 + + G(d,p) basis set and the IEFPCM solvent continuum model give theoretical vibronic absorption spectra, which are coincide with the experimental ones. Of the structural differences between C343(0) and C343(-), there is a different twisting of the carboxyl group additionally changing due to excitation. Upon excitation, a significant shift in the electron density occurs from the C10 atom to the C4 atom only. Thus, a charge transfer on the scale of the entire molecule does not occur. Different hydration complexes with strongly bound water molecules have been analyzed.
A PET-based fluorescent probe for monitoring labile Fe(II) pools in macrophage activations and ferroptosis.[Pubmed:35147150]
Chem Commun (Camb). 2022 Mar 1;58(18):2979-2982.
A fluorescent probe (COU-LIP-1) for monitoring labile Fe(II) pools (LIP) with high selectivity and sensitivity was developed utilizing Coumarin 343 as the fluorophore and 3-nitrophenylazanyl ester as both the reactive group and the fluorescence quenching group. Fe(II)-induced reductive cleavage of the N-O bond results in a turn-on response via a photo-induced photon transfer (PET) mechanism. The probe was applied for monitoring labile iron(II) changes in M1 and M2a macrophage activations and also erastin-induced ferroptosis, providing a powerful tool for selectively sensing LIP under both physiological and stressed conditions.
Assessing rotation and solvation dynamics in ethaline deep eutectic solvent and its solutions with methanol.[Pubmed:34293899]
J Chem Phys. 2021 Jul 21;155(3):034505.
Steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence were used to investigate the solvation of coumarin 153 (C153) and Coumarin 343 (C343) in methanol + ethaline binary solutions, a deep eutectic solvent composed of a 1:2 molar ratio choline chloride + ethylene glycol. In addition, time-resolved anisotropy decays were used to determine the solute's rotational reorientation time as a function of viscosity. Measurements were made in solutions covering the entire range of mole fraction. Viscosity measurements were used to characterize the bulk solvent properties, and as expected, addition of methanol resulted in an decreased viscosity, showing an exponential decrease with mole fraction, up to approximately 50-fold at x(MeOH) = 1.0. Probe rotational reorientation times were found to be biexponential at x(MeOH) < 0.3 for C153 and x(MeOH) < 0.5 for C343 and monoexponential at richer methanol content. In proportion to viscosity, C153 and C343 average rotation times decreased approximately 30-fold from x(MeOH) = 0 to 0.9 and showed a power law dependence of approximately eta(0.85). Rotation times approached the stick boundary limit on dilution with methanol. Time-resolved Stokes shifts quantified the solvation dynamics and were nearly single exponential for C153 but were clearly biexponential for C343. Solvation times also tracked with viscosity according to a power law dependence, with exponents of 0.3 and 0.4 for C153 and C343, respectively. The dilution effect of methanol was not linear in proportion to the viscosity change and alone cannot account for the change in solvation. Dilution also showed a different correlation to solvation than did temperature variations to govern the viscosity change.
A dual-fluorophore sensor approach for ratiometric fluorescence imaging of potassium in living cells.[Pubmed:34163931]
Chem Sci. 2020 Dec 15;12(5):1720-1729.
Potassium is the most abundant intracellular metal in the body, playing vital roles in regulating intracellular fluid volume, nutrient transport, and cell-to-cell communication through nerve and muscle contraction. On the other hand, aberrant alterations in K(+) homeostasis contribute to a diverse array of diseases spanning cardiovascular and neurological disorders to diabetes to kidney disease to cancer. There is an unmet need for studies of K(+) physiology and pathology owing to the large differences in intracellular versus extracellular K(+) concentrations ([K(+)](intra) = 150 mM, [K(+)](extra) = 3-5 mM). With a relative dearth of methods to reliably measure dynamic changes in intracellular K(+) in biological specimens that meet the dual challenges of low affinity and high selectivity for K(+), particularly over Na(+), currently available fluorescent K(+) sensors are largely optimized with high-affinity receptors that are more amenable for extracellular K(+) detection. We report the design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of Ratiometric Potassium Sensor 1 (RPS-1), a dual-fluorophore sensor that enables ratiometric fluorescence imaging of intracellular potassium in living systems. RPS-1 links a potassium-responsive fluorescent sensor fragment (PS525) with a low-affinity, high-selectivity crown ether receptor for K(+) to a potassium-insensitive reference fluorophore (Coumarin 343) as an internal calibration standard through ester bonds. Upon intracellular delivery, esterase-directed cleavage splits these two dyes into separate fragments to enable ratiometric detection of K(+). RPS-1 responds to K(+) in aqueous buffer with high selectivity over competing metal ions and is sensitive to potassium ions at steady-state intracellular levels and can respond to decreases or increases from that basal set point. Moreover, RPS-1 was applied for comparative screening of K(+) pools across a panel of different cancer cell lines, revealing elevations in basal intracellular K(+) in metastatic breast cancer cell lines vs. normal breast cells. This work provides a unique chemical tool for the study of intracellular potassium dynamics and a starting point for the design of other ratiometric fluorescent sensors based on two-fluorophore approaches that do not rely on FRET or related energy transfer designs.
Two-photon absorption enhancement for organic acceptor molecules with QD antennas.[Pubmed:34031687]
Nanoscale. 2021 Jun 3;13(21):9808-9815.
The photophysics of an inorganic/organic hybrid system was studied by time-resolved optical spectroscopy, focusing on the goal of increasing the two-photon efficiency of photoresponsive systems. The hybrid system consists of CdS/ZnS core/shell quantum dots (QDs) as energy donor and coumarin derivatives as energy acceptor molecules. The spectral overlap of QD emission and Coumarin 343 absorption promotes a Forster resonance energy tranfer (FRET) mechanism leading to a FRET efficiency up to nearly 90%. Additionally, time-correlated single photon counting showed a faster fluorescence decay while acceptor molecules were attached to the QD surface. Femtosecond transient absorption measurements demonstrated an ultrafast FRET reaction. Importantly, FRET was observed also after two-photon excitation of the QDs indicating that the chosen QDs can act as two-photon antennas.
Development of Fluorescent and Biotin Probes Targeting NLRP3.[Pubmed:33996748]
Front Chem. 2021 Apr 22;9:642273.
Extracellular signals drive the nucleation of the NLRP3 inflammasome which leads to the release of cytokines and causes inflammatory events. Hence, the inflammasome has gained enormous momentum in biomedical basic research. The detailed mechanisms of inflammasome generation and regulation remain to be elucidated. Our study was directed toward the design, convergent synthesis, and initial biochemical evaluation of activity-based probes addressing NLRP3. For this purpose, probes were assembled from a CRID3/MCC950-related NLRP3-binding unit, a linker portion and a Coumarin 343 fluorophore or biotin. The affinity of our probes to NLRP3 was demonstrated through SPR measurements and their cellular activity was confirmed by reduction of the interleukin 1beta release from stimulated bone marrow-derived macrophages. The initial characterizations of NLRP3-targeting probes highlighted the coumarin probe 2 as a suitable tool compound for the cellular and biochemical analysis of the NLRP3 inflammasome.
Cloud Point Driven Dynamics in Aqueous Solutions of Thermoresponsive Copolymers: Are They Akin to Criticality Driven Solution Dynamics?[Pubmed:31794221]
J Phys Chem B. 2019 Dec 26;123(51):11042-11054.
Cloud point driven interaction and relaxation dynamics of aqueous solutions of amphiphilic thermoresponsive copolymers were explored through picosecond resolved and steady state fluorescence measurements employing hydrophilic (Coumarin 343, C343) and hydrophobic (coumarin 153, C153) solute probes of comparable sizes. These thermoresponsive random copolymers, with tunable cloud point temperatures (T(cp)'s) between 298 and 323 K, were rationally designed first and then synthesized via reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) copolymerization of methyl methacrylate (MMA) and poly(ethylene glycol) monomethyl ether methacrylate (PEGMA). Subsequently, copolymers were characterized by NMR spectroscopy and size exclusion chromatography (SEC). A balance between the hydrophilic (PEGMA) and the hydrophobic (MMA) content dictates the critical aggregation concentration (CAC), with CAC approximately 2-14 mg/L for these copolymers in aqueous media. No abrupt changes in the steady state spectral features of both C153 and C343 in the aqueous solutions of these polymers near but below the cloud point temperatures were observed. Interestingly, spectral properties of C153 in these solutions show the impact of hydrophobic/hydrophilic interaction balance but not by those of C343. More specifically, C153 reported a blue shift (relative to that in neat water) and heterogeneity in its local environment. This suggested different locations for the hydrophilic (C343) and the hydrophobic (C153) probes. In addition, the excited state fluorescence lifetime (⟨tau(life)⟩) of C153 increased with the increase of hydrophobic (MMA) content in these copolymers. However, C343 reported no such variations, although fluorescence anisotropy decays for both solutes were significantly slowed down in these aqueous solutions compared to neat water. Anisotropy decays indicated bimodal time-dependent friction for these solutes in aqueous solutions of these copolymers but monomodal in neat water. A linear dependence of the average rotational relaxation rates (⟨k(rot)⟩ = ⟨tau(rot)⟩(-1)) of the type ⟨k(rot)⟩ proportional, variant (|T - T(cp)|/T(cp))(gamma) with negative values for the exponent gamma was observed for both solutes. No slowing down of the solute rotation with temperature approaching the T(cp) was detected; rather, rotation became faster upon increasing the solution temperature, suggesting domination of the local friction.


