D-(-)-Quinic acidCAS# 77-95-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 77-95-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 1064 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C7H12O6 | M.Wt | 192.17 |
| Type of Compound | Miscellaneous | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | H2O : 125 mg/mL (650.47 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
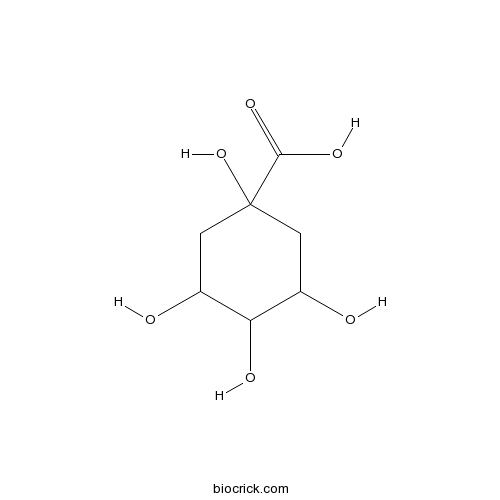
| Chemical Name | 1,3,4,5-tetrahydroxycyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1C(C(C(CC1(C(=O)O)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | AAWZDTNXLSGCEK-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C7H12O6/c8-3-1-7(13,6(11)12)2-4(9)5(3)10/h3-5,8-10,13H,1-2H2,(H,11,12) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | D-(-)-Quinic acid is a cellular metal ion chelator, capable of promoting reactions with metal M(II,III) ions under pH-specific conditions. It may possess potent inhibition against alpha-mannosidase and alpha-fucosidase. |
| Targets | Beta Amyloid | alpha-mannosidase | alpha-fucosidase |
| In vivo | Colonic availability of polyphenols and D-(-)-quinic acid after apple smoothie consumption.[Pubmed: 21370449]Mol Nutr Food Res. 2011 Mar;55(3):368-77.The aim of this study was to determine the amounts of polyphenols and D-(-)-Quinic acid reaching the ileostomy bags of probands (and thus the colon in healthy humans) after ingestion of apple smoothie, a beverage containing 60% cloudy apple juice and 40% apple puree. |
| Structure Identification | Inorg Chem. 2013 Dec 16;52(24):13849-60.Heptanuclear antiferromagnetic Fe(III)-D-(-)-quinato assemblies with an S = 3/2 ground state-pH-specific synthetic chemistry, spectroscopic, structural, and magnetic susceptibility studies.[Pubmed: 24266671]Iron is an essential metal ion with numerous roles in biological systems and advanced abiotic materials. D-(-)-Quinic acid is a cellular metal ion chelator, capable of promoting reactions with metal M(II,III) ions under pH-specific conditions.
J Org Chem. 2007 May 25;72(11):4258-61.Expeditious synthesis of tri- and tetrahydroxyazepanes from D-(-)-quinic acid as potent glycosidase inhibitors.[Pubmed: 17480095]Several new stereoisomers of 3,4,6-trihydroxyazepanes and 7-hydroxymethyl-3,4,5-trihydroxyazepanes as well as known 3,4,5-trihydroxyazepanes were synthesized as potent glycosidase inhibitors from D-(-)-Quinic acid in an efficient manner.
|

D-(-)-Quinic acid Dilution Calculator

D-(-)-Quinic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.2037 mL | 26.0186 mL | 52.0373 mL | 104.0745 mL | 130.0931 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.0407 mL | 5.2037 mL | 10.4075 mL | 20.8149 mL | 26.0186 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5204 mL | 2.6019 mL | 5.2037 mL | 10.4075 mL | 13.0093 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1041 mL | 0.5204 mL | 1.0407 mL | 2.0815 mL | 2.6019 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.052 mL | 0.2602 mL | 0.5204 mL | 1.0407 mL | 1.3009 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Triethyl citrate
Catalog No.:BCC9186
CAS No.:77-93-0
- Citric acid
Catalog No.:BCN5374
CAS No.:77-92-9
- Trometamol
Catalog No.:BCC4743
CAS No.:77-86-1
- Tigogenin
Catalog No.:BCN5327
CAS No.:77-60-1
- Tomatidine
Catalog No.:BCN2773
CAS No.:77-59-8
- Cedrol
Catalog No.:BCN8340
CAS No.:77-53-2
- Ursolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4327
CAS No.:77-52-1
- Chlorthalidone
Catalog No.:BCC4649
CAS No.:77-36-1
- Gibberellins
Catalog No.:BCN2189
CAS No.:77-06-5
- Garcinone C
Catalog No.:BCN4322
CAS No.:76996-27-5
- Euphroside
Catalog No.:BCN6633
CAS No.:76994-07-5
- Notoginsenoside T5
Catalog No.:BCN3727
CAS No.:769932-34-5
- (+,-)-Octopamine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4814
CAS No.:770-05-8
- Dehydropachymic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3648
CAS No.:77012-31-8
- Hypocrellin A
Catalog No.:BCN3396
CAS No.:77029-83-5
- Knightinol
Catalog No.:BCN1913
CAS No.:77053-06-6
- Acetylknightinol
Catalog No.:BCN1914
CAS No.:77053-07-7
- Gadobutrol
Catalog No.:BCC4164
CAS No.:770691-21-9
- 6-O-trans-Feruloylcatalpol
Catalog No.:BCN4323
CAS No.:125205-48-3
- 2H-1-Benzopyran-5-ol
Catalog No.:BCN3581
CAS No.:770729-34-5
- MK-801 (Dizocilpine)
Catalog No.:BCC4591
CAS No.:77086-21-6
- (+)-MK 801 Maleate
Catalog No.:BCC4014
CAS No.:77086-22-7
- 1H-Indole-3-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4324
CAS No.:771-50-6
- Fmoc-Sar-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3338
CAS No.:77128-70-2
Regioselectivity in the ring opening of epoxides for the synthesis of aminocyclitols from D-(-)-quinic acid.[Pubmed:22508330]
Molecules. 2012 Apr 16;17(4):4498-507.
Efficient syntheses of four aminocyclitols are reported. Each synthesis is accomplished in eight steps starting from D-(-)-Quinic acid. The key step involves a highly regioselective ring opening of epoxides by sodium azide.
Expeditious synthesis of tri- and tetrahydroxyazepanes from D-(-)-quinic acid as potent glycosidase inhibitors.[Pubmed:17480095]
J Org Chem. 2007 May 25;72(11):4258-61.
Several new stereoisomers of 3,4,6-trihydroxyazepanes and 7-hydroxymethyl-3,4,5-trihydroxyazepanes as well as known 3,4,5-trihydroxyazepanes were synthesized as potent glycosidase inhibitors from D-(-)-Quinic acid in an efficient manner. The key step employs dihydroxylation of protected chiral 1,4,5-cyclohex-2-enetriols under RuCl3/NaIO4/phosphate buffer (pH 7) condition, followed by reductive amino cyclization. We found the choice of an appropriate protecting group to C1-OH of chiral 1,4,5-cyclohex-2-enetriols would increase the yields of cyclization. The preliminary biological data indicate some of these azepanes possess potent inhibition against alpha-mannosidase and alpha-fucosidase.
Heptanuclear antiferromagnetic Fe(III)-D-(-)-quinato assemblies with an S = 3/2 ground state-pH-specific synthetic chemistry, spectroscopic, structural, and magnetic susceptibility studies.[Pubmed:24266671]
Inorg Chem. 2013 Dec 16;52(24):13849-60.
Iron is an essential metal ion with numerous roles in biological systems and advanced abiotic materials. D-(-)-Quinic acid is a cellular metal ion chelator, capable of promoting reactions with metal M(II,III) ions under pH-specific conditions. In an effort to comprehend the chemical reactivity of well-defined forms of Fe(III)/Fe(II) toward alpha-hydroxycarboxylic acids, pH-specific reactions of: (a) [Fe3O(CH3COO)6(H2O)3].(NO3).4H2O with D-(-)-Quinic acid in a molar ratio 1:3 at pH 2.5 and (b) Mohr's salt with D-(-)-Quinic acid in a molar ratio 1:3 at pH 7.5, respectively, led to the isolation of the first two heptanuclear Fe(III)-quinato complexes, [Fe7O3(OH)3(C7H10O6)6].20.5H2O (1) and (NH4)[Fe7(OH)6(C7H10O6)6].(SO4)2.18H2O (2). Compounds 1 and 2 were characterized by analytical, spectroscopic (UV-vis, FT-IR, EPR, and Mossbauer) techniques, CV, TGA-DTG, and magnetic susceptibility measurements. The X-ray structures of 1 and 2 reveal heptanuclear assemblies of six Fe(III) ions bound by six doubly deprotonated quinates and one Fe(III) ion bound by oxido- and hydroxido-bridges (1), and hydroxido-bridges (2), all in an octahedral fashion. Mossbauer spectroscopy on 1 and 2 suggests the presence of Fe(III) ions in an all-oxygen environment. EPR measurements indicate that 1 and 2 retain their structure in solution, while magnetic measurements reveal an overall antiferromagnetic behavior with a ground state S = 3/2. The collective physicochemical properties of 1 and 2 suggest that the (a) nature of the ligand, (b) precursor form of iron, (c) pH, and (d) molecular stoichiometry are key factors influencing the chemical reactivity of the binary Fe(II,III)-hydroxycarboxylato systems, their aqueous speciation, and ultimately through variably emerging hydrogen bonding interactions, the assembly of multinuclear Fe(III)-hydroxycarboxylato clusters with distinct lattice architectures of specific dimensionality (2D-3D) and magnetic signature.
Colonic availability of polyphenols and D-(-)-quinic acid after apple smoothie consumption.[Pubmed:21370449]
Mol Nutr Food Res. 2011 Mar;55(3):368-77.
SCOPE: The aim of this study was to determine the amounts of polyphenols and D-(-)-Quinic acid reaching the ileostomy bags of probands (and thus the colon in healthy humans) after ingestion of apple smoothie, a beverage containing 60% cloudy apple juice and 40% apple puree. METHODS AND RESULTS: Ten healthy ileostomy subjects each ingested 0.7 L of apple smoothie (a bottle). Their ileostomy bags were collected directly before and 1, 2, 4, 6 and 8 h after smoothie consumption, and the polyphenol and D-(-)-Quinic acid contents of the ileostomy fluids were examined using HPLC-DAD and HPLC-MS/MS. The total polyphenol and D-(-)-Quinic acid content of the apple smoothie was determined to be 1955.6+/-124.6 mg/0.7 L, which is very high compared to cloudy apple juices. The most abundant substances found in the ileostomy bags were oligomeric procyanidins (705.6+/-197.9 mg), D-(-)-Quinic acid (363.4+/-235.5 mg) and 5-caffeoylquinic acid (76.7+/-26.8 mg). Overall recovery of ingested polyphenols and D-(-)-Quinic acid in the ileostomy bags was 63.3+/-16.1%. CONCLUSIONS: The amounts of polyphenol and D-(-)-Quinic acids reaching the ileostomy bags are considerably higher after apple smoothie consumption than after the consumption of cloudy apple juice or cider. These results suggest that the food matrix might affect the colonic availability of polyphenols, and apple smoothies could be more effective in the prevention of chronic colon diseases than both cloudy apple juice and apple cider.


