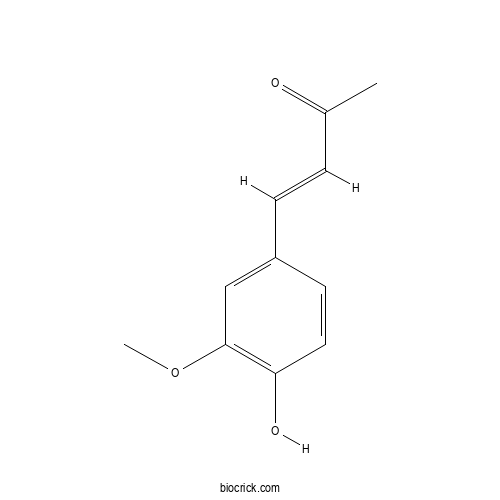
DehydrozingeroneCAS# 1080-12-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1080-12-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5354238 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C11H12O3 | M.Wt | 192.21 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (E)-4-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)but-3-en-2-one | ||
| SMILES | CC(=O)C=CC1=CC(=C(C=C1)O)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | AFWKBSMFXWNGRE-ONEGZZNKSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C11H12O3/c1-8(12)3-4-9-5-6-10(13)11(7-9)14-2/h3-7,13H,1-2H3/b4-3+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Dehydrozingerone Dilution Calculator

Dehydrozingerone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.2026 mL | 26.0132 mL | 52.0264 mL | 104.0529 mL | 130.0661 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.0405 mL | 5.2026 mL | 10.4053 mL | 20.8106 mL | 26.0132 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5203 mL | 2.6013 mL | 5.2026 mL | 10.4053 mL | 13.0066 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1041 mL | 0.5203 mL | 1.0405 mL | 2.0811 mL | 2.6013 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.052 mL | 0.2601 mL | 0.5203 mL | 1.0405 mL | 1.3007 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- (2S,3S)-Pteroside C
Catalog No.:BCX0249
CAS No.:98855-62-0
- (2R,3S)-Pteroside C
Catalog No.:BCX0248
CAS No.:68399-16-6
- Pterosin L 2'-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX0247
CAS No.:61102-11-2
- Pyridylpaeoniflorin
Catalog No.:BCX0246
CAS No.:1427054-19-0
- Malaysianol D
Catalog No.:BCX0245
CAS No.:1646330-59-7
- Bisacurone A
Catalog No.:BCX0244
CAS No.:127214-84-0
- ar-Turmerol
Catalog No.:BCX0243
CAS No.:1178899-16-5
- (S,E)-2-Methyl-6-(p-tolyl)hept-3-en-2-ol
Catalog No.:BCX0242
CAS No.:18383-55-6
- Creticoside A
Catalog No.:BCX0241
CAS No.:34336-00-0
- Kaempferol 3-O-neohesperidoside 7-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX0240
CAS No.:78527-48-7
- Pteroside B
Catalog No.:BCX0239
CAS No.:29774-74-1
- 1-O-β-D-Glucopyranosylpaeonisuffrone
Catalog No.:BCX0238
CAS No.:1003888-20-7
- Kaempferol 3-O-(2''-O-glucosyl)rutinoside
Catalog No.:BCX0251
CAS No.:55696-58-7
- Sanggenon B
Catalog No.:BCX0252
CAS No.:81381-67-1
- Chasmanthin
Catalog No.:BCX0253
CAS No.:20379-19-5
- Dulcisxanthone B
Catalog No.:BCX0254
CAS No.:869669-62-5
- (E)-4-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)but-3-en-2-one
Catalog No.:BCX0255
CAS No.:22214-30-8
- (E)-α-Atlantone
Catalog No.:BCX0256
CAS No.:26294-59-7
- Arucadiol
Catalog No.:BCX0257
CAS No.:105037-85-2
- Suffruticosol B
Catalog No.:BCX0258
CAS No.:220936-87-8
- Sibiriquinone B
Catalog No.:BCX0259
CAS No.:723300-09-2
- Sanggenon O
Catalog No.:BCX0260
CAS No.:101664-32-8
- (2S,3S)-Pterosin S 14-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX0261
CAS No.:62043-50-9
- Pruniflorone R
Catalog No.:BCX0262
CAS No.:1238102-65-2
Investigation of the cellular and molecular effects of dehydrozingerone formulation on various days of diabetic wound repair.[Pubmed:38566928]
3 Biotech. 2024 Apr;14(4):124.
Cases of diabetes are significantly increasing year by year, attracting the attention of medical professionals and researchers to focus on diabetes and its underlying complications. One among such are diabetic wounds which are difficult to heal, creating severe implications in the day-to-day chores of not only patients, but also family members. Dehydrozingerone (DHZ) is known to possess various effects like anti-inflammatory, anti-microbial, antioxidant, and wound-healing properties. The effect of DHZ on different phases of diabetic wound healing remains untested. Hence, this study was proposed to find out the effect of oral and topical formulation of DHZ on day 5, 10 and 15 of diabetic wound healing. Excisional wounds were created on the dorsal side of animals using punch biopsy to mimic human diabetic wounds. Topical DHZ gel (100 mg in 1 gm of gel) was prepared using 1% Carbopol 934 and was applied twice a day. The treated groups had increased percentage of wound closure; western blotting suggested that DHZ significantly increased ERK and JNK levels and decreased TNF and MMP 2 and 9 levels. From histopathological studies, it was observed that angiogenesis, collagen formation, granulation tissue formation, and fibroblast proliferation were improved on days 5, 10, and 15 of diabetic wound healing. These findings indicate that DHZ (both systemic and topical) are effective during the early phases of wound healing which gets impaired in diabetic wounds. Dehydrozingerone accelerated diabetic wound healing by regulating the various hallmarks of wound healing process.
Neuroprotective Effects of the Nutraceutical Dehydrozingerone and Its C(2)-Symmetric Dimer in a Drosophila Model of Parkinson's Disease.[Pubmed:38540694]
Biomolecules. 2024 Feb 24;14(3):273.
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons responsible for unintended or uncontrollable movements. Mutations in the leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 locus contribute to genetic forms of PD. The fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster carrying this mutation (LRRK2-Dm) is an in vivo model of PD that develops motor impairment and stands for an eligible non-mammalian paradigm to test novel therapeutic approaches. Dehydrozingerone (DHZ) is a natural phenolic compound isolated from ginger and presents anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and neuroprotective properties, making it a potential therapeutic target for PD. We administered DHZ and its C(2)-symmetric dimer (DHZ-DIM) at 0.5 and 1 mM for 14 and 21 days in the LRRK2-Dm, with the aim of assessing changes in rescuing motor behavior, brain dopaminergic neurons, mitochondria and synapses (T-bars). The shorter treatment with both molecules revealed efficacy at the higher dose, improving climbing behavior with a prevention of dopaminergic neuronal demise. After 21 days, a recovery of the motor disability, dopaminergic neuron loss, mitochondrial damage and T-bars failure was observed with the DHZ-DIM. Our data indicate that the DHZ-DIM exerts a more potent neuroprotective effect with respect to the monomer in LRRK2-Dm, prompting further investigation of these compounds in rodent models of PD.
Enhancing temozolomide antiglioma response by inhibiting O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase with selected phytochemicals: in silico and in vitro approach.[Pubmed:37928438]
3 Biotech. 2023 Dec;13(12):385.
The aim of our study was to investigate the potential of rutin, catechin, Dehydrozingerone, naringenin, and quercetin, both alone and in combination with temozolomide, to inhibit the expression of O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) in glioma cells. MGMT has been shown to be a major cause of temozolomide resistance in glioma. Our study used both in silico and in vitro methods to assess the inhibitory activity of these phytochemicals on MGMT, with the goal of identifying the most effective combination of compounds for reducing temozolomide resistance. After conducting an initial in silico screening of natural compounds against MGMT protein, five phytochemicals were chosen based on their high docking scores and favorable binding energies. From the molecular docking and simulation studies, we found that quercetin showed a good inhibitory effect of MGMT with its high binding affinity. C6 glioma cells showed increased cytotoxicity when treated with the temozolomide and quercetin combination. It was understood from the isobologram and combination index plot that the drug combination showed a synergistic effect at the lowest dose. Quercetin when combined with temozolomide significantly decreased the MGMT levels in C6 cells in comparison with the other drugs as estimated by ELISA. The percentage of apoptotic cells increased significantly in the temozolomide-quercetin group indicating the potency of quercetin in decreasing the resistance of temozolomide as confirmed by acridine orange/ethidium bromide staining. Our experiment hence suggests that temozolomide resistance can be reduced by combining the drug with quercetin which will serve as an effective therapeutic target for glioblastoma treatment. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s13205-023-03821-7.
Sustainable Electropolymerization of Zingerone and Its C2 Symmetric Dimer for Amperometric Biosensor Films.[Pubmed:37630267]
Molecules. 2023 Aug 11;28(16):6017.
Polymeric permselective films are frequently used for amperometric biosensors to prevent electroactive interference present in the target matrix. Phenylenediamines are the most commonly used for the deposition of shielding polymeric films against interfering species; however, even phenolic monomers have been utilized in the creation of these films for microsensors and biosensors. The purpose of this paper is to evaluate the performances of electrosynthesized polymers, layered by means of constant potential amperometry (CPA), of naturally occurring compound zingerone (ZING) and its dimer Dehydrozingerone (ZING DIM), which was obtained by straight oxidative coupling reaction. The polymers showed interesting shielding characteristics against the main interfering species, such as ascorbic acid (AA): actually, polyZING exhibited an AA shielding aptitude comprised between 77.6 and 99.6%, comparable to that obtained with PPD. Moreover, a marked capability of increased monitoring of hydrogen peroxide (HP), when data were compared with bare metal results, was observed. In particular, polyZING showed increases ranging between 55.6 and 85.6%. In the present work, the molecular structures of the obtained polymers have been theorized and docking analyses were performed to understand their peculiar characteristics better. The structures were docked using the Lamarckian genetic algorithm (LGA). Glutamate biosensors based on those polymers were built, and their performances were compared with biosensors based on PPD, which is the most widespread polymer for the construction of amperometric biosensors.
Synthesis, characterization, and biological activity of some 2,4-diketo esters containing dehydrozingerone fragment: DNA and protein binding study.[Pubmed:37499986]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2023 Sep 1;93:129413.
Due to the increased resistance to antibiotics, in recent years there has been a growing interest in the discovery of new antimicrobial agents from different sources. Bacteria that are resistant to most antibiotics are a global public health concern. In order to find a new antimicrobial drug, we synthesized a small series of 2,4-diketo esters and tested them on some gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial strains. Two compounds showed very good antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis, respectively. Trichophyton mentagrophytes proved to be the most sensitive of the tested species regarding antifungal activity. Also, research was conducted on the biomolecule of bovine serum albumin. Examining these interactions, we concluded that all compounds have the appropriate binding affinity for bovine serum albumin, which is vital. Furthermore, to investigate the potential antitumor activity, interactions with DNA were carried out. Examining the interactions between our compounds and DNA using fluorescence, we concluded that all but one of the compounds interacts with the DNA molecule by intercalation. In addition, a molecular docking study was performed to investigate the binding mode of the tested compounds to DNA and bovine serum albumin. In conclusion, all the results indicate a great potential for the future application of these compounds in clinical practice in the future.
Dehydrozingerone alleviates pulmonary fibrosis via inhibition of inflammation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway.[Pubmed:37245857]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 15;953:175820.
In idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), excessive collagen deposition predisposes to irreversible lung function decline, respiratory failure, and ultimately death. Due to the limited therapeutic efficacy of FDA-approved medications, novel drugs are warranted for better treatment outcomes. Dehydrozingerone (DHZ) is an analogue of curcumin that has been investigated against pulmonary fibrosis using a bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis model in rats. In in vitro, TGF-beta-induced differentiation models (using NHLF, LL29, DHLF and A549 cells) were adopted to assess fibrotic markers expression and explored the mechanism of action. DHZ administration attenuated the bleomycin-induced elevation of lung index, inflammatory cell infiltrations, and hydroxyproline levels in lung tissues. Furthermore, treatment with DHZ mitigated the bleomycin-mediated elevation of extracellular matrix (ECM), epithelial-to-mesenchymal-transition (EMT), and collagen deposition markers and improved lung mechanics. In addition, treatment with DHZ significantly suppressed the BLM-induced apoptosis and rescued the BLM-induced pathological abnormalities in lung tissues. In vitro assays revealed that DHZ suppressed the expression of TGF-beta-elevated collagen deposition, EMT and ECM markers in both mRNA/protein levels. Our findings showed that DHZ has anti-fibrotic effect against pulmonary fibrosis by modulating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling, suggesting that DHZ may serve as a potential treatment option for IPF.
Dehydrozingerone enhances the fungicidal activity of glabridin against Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Candida albicans.[Pubmed:36990694]
Lett Appl Microbiol. 2023 Apr 3;76(4):ovad040.
Drug resistance commonly occurs when treating immunocompromized patients with fungal infections. Dehydrozingerone-a phenolic compound isolated from the rhizome of Zingiber officinale-inhibits drug efflux in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by overexpression of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter Pdr5p. We aimed to investigate whether Dehydrozingerone enhances the antifungal activity of glabridin-an isoflavan isolated from the roots of Glycyrrhiza glabra L.-by attenuating multidrug resistance through the intrinsic expression system of multidrug-efflux-related genes in a wild-type strain of the model yeast. The antifungal activity of 50 mumol l-1 glabridin alone was weak and temporary against S. cerevisiae; however, cell viability was significantly inhibited when the cells were co-treated with glabridin and Dehydrozingerone. This enhancement was also observed in human pathogenic Candida albicans. Glabridin efflux did not depend on a particular drug efflux pump; instead, the transcription factors PDR1 and PDR3-regulating the transcription of multiple genes encoding drug efflux pumps-were involved in the antifungal activity and efflux of glabridin. qRT-PCR analysis revealed that Dehydrozingerone reduced glabridin-induced overexpression of the ABC transporter-related genes PDR1, PDR3, and PDR5 to the levels observed in untreated cells. Our findings indicated that Dehydrozingerone potentiates the efficacy of plant-derived antifungals through its effects on ABC transporters.
Two new phenylbutenoids from the rhizomes of cassumunar ginger and their alpha-glucosidase inhibitory activity.[Pubmed:36576074]
Nat Prod Res. 2024 May;38(9):1545-1552.
An extract from the rhizomes of Cassumunar ginger (Zingiber purpureum Roscoe). was found to have significant alpha-glucosidase inhibitory activity with an IC(50) value of 6.3 microg/mL. Two new phenylbutenoids, cassudimin A (1) and cassumunol N (2), and seven known compounds (3-9) were isolated. Their structures and relative configurations of two new compounds were elucidated based on spectra interpretation. Compounds 1-3, 6-9 showed more potent alpha-glucosidase inhibitory activity than a positive control, acarbose (IC(50) = 168.0 microM). Dehydrozingerone (6) exhibited the most potent alpha-glucosidase inhibition with an IC(50) value of 8.3 muM. Compounds 7 and 9 were found in Z. purpureum rhizomes for the first time.
[Quantitative Analysis of Bisacurone in Turmeric by HPLC Using Relative Molar Sensitivity].[Pubmed:36575034]
Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi. 2022;63(6):202-209.
A novel method was developed for quantification of bisacuron (BC) and Dehydrozingerone (DZ), the functional component of turmeric (Curcuma longa.L)-containing foods, using a relative molar sensitivity (RMS) method based on the combination of HPLC-UV and (1)H-NMR. The RMSs of BC and DZ using 4-hydroxybenzoic acid ethyl ester (HBE) as the internal standard were calculated to 1.66 and 2.55, respectively. Analysis of fourteen beverage products showed the high correlations between the concentrations of BC and DZ quantified by the RMS method and those quantified by absolute calibration curve method. A collaborative study was conducted by four laboratories on one beverage and one tablet products. The repeatable relative standard deviation (RSD(r)) of intra-laboratories ranged from 0.7 to 1.7%, and the reproducible relative standard deviation (RSD(R)) of inter-laboratories ranged from 2.0 to 7.3%. The RMS method enabled the quantification of analytes for which difficultly obtain standard materials such as BC and DZ, using an internal standard for which obtain routinely readily available. This RMS method is expected to be applied to quality control for food products containing turmeric.
Dehydrozingerone ameliorates thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis via inhibition of hepatic stellate cells activation through modulation of the MAPK pathway.[Pubmed:36375494]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2022 Dec 15;937:175366.
Hepatic fibrosis is a progressive consequence of injury to the liver cells. Liver fibrosis causes hepatic dysfunction and also plays a key role in the pathogenesis of other chronic ailments. Dehydrozingerone (DHZ) is a half-structural analogue of curcumin and is known to have several therapeutic benefits. However, the impact of DHZ on liver fibrosis was not investigated. The current investigation attempted to determine the anti-fibrotic effect of DHZ against thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis in rats and TGF-beta-induced differentiation in human HSC-LX2 cells and to uncover the possible mechanisms. In in-vivo, DHZ significantly reduced the TAA-induced liver index and ameliorated the liver functional parameters. TAA elevated the fibrotic marker's expression in TAA control, on the other hand, DHZ treatment significantly mitigated the same in mRNA and protein levels. Additionally, these findings were supported by histological investigations and immunohistochemistry studies of the fibrotic marker's expressions. DHZ treatment effectively reduced oxidative stress by increasing catalase activity and decreased the expression of inflammatory markers (myeloperoxidase and neutrophil-elastase) in liver tissues. Additionally, collagen staining and histological findings confirmed that DHZ administration significantly reduced TAA induced pathological deformities and elevated collagen levels. In-vitro results showed that TGF-beta-induced differentiation was suppressed by DHZ treatment in a dose-dependent manner. Mechanistic approaches in HSC-LX2 and liver tissues revealed that DHZ treatment mitigated fibrosis by modulating the MAPK-pathway. Overall, these results show that DHZ exhibited anti-fibrotic action by reducing fibrotic markers and their activities through regulation of the MAPK-pathway, suggesting that DHZ may be a promising therapeutic molecule for liver fibrosis.
Dehydrozingerone promotes healing of diabetic foot ulcers: a molecular insight.[Pubmed:36280629]
J Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Sep;17(3):673-688.
INTRODUCTION: One of the most common problems of diabetes are diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs). According to National Institute for Health, initial management of DFUs can decrease the complication of limb amputations and can improve the patient's quality of life. DFU treatment can be optimized with the help of multidisciplinary approach. Based on many studies, control of glucose levels in blood, antioxidant activity, reduction in cytokine levels, re-epithelialization, collagen formation, migration of fibroblasts are major phases involved in managing DFU. Dehydrozingerone (DHZ), has been known for its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and wound healing properties. METHODOLOGY: Three months high-fat diet and low dose of streptozotocin-induced type-II diabetic foot ulcer model was used to evaluate the effectiveness of Dehydrozingerone. DHZ was given orally to rats for 15 days post wounding. TNF-alpha, IL-1beta and antioxidant parameters like lipid peroxidation, glutathione reductase were estimated. Immunoblotting was done to investigate the effect of DHZ on the expression of ERK, JNK, HSP-27, P38, SIRT-1, NFkappaB, SMA, VEGF and MMP-9 in skin tissue. Histopathology was performed for analyzing DHZ effect on migration of fibroblasts, formation of epithelium, granulation tissue formation, angiogenesis and collagen formation. RESULTS: DHZ decreased the levels of malondialdehyde, TNF-alpha, IL-1beta and increased glutathione levels in wound tissue. Western blotting results suggested that DHZ activated ERK1/2/JNK/p38 signaling, increased expression of HSP-27, SIRT-1, VEGF, SMA thus facilitating the migration and proliferation of fibroblasts, angiogenesis and decreased inflammation. Masson Trichrome & histopathology showed an increase in collagen, epithelial and granulation tissue formation. CONCLUSION: DHZ significantly accelerates the healing of diabetic foot ulcers in high fat diet fed plus low dose streptozotocin induced type-II diabetic Wistar rats.
Dehydrozingerone Alleviates Hyperalgesia, Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Factors in Complete Freund's Adjuvant-Induced Arthritic Rats.[Pubmed:36105319]
Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022 Sep 8;16:3015-3022.
PURPOSE: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease with severe inflammatory responses. Dehydrozingerone (DHZ) is a potent bioactive compound found in the rhizomes of Zingiber officinale, and it has been reported as an excellent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant agent. This study evaluated the anti-arthritic effects of DHZ in complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA)-induced arthritis. METHODS: CFA administered rats were intragastrically treated with DHZ (100 mg/kg) for 28 days, and arthritis severity was assessed via body weight, arthritic score, paw edema and hyperalgesia. Serum inflammation biomarkers, oxidative stress markers, inflammatory cytokines and liver function enzymes were evaluated. RESULTS: The results indicated that DHZ significantly ameliorated arthritis severity as shown by reduced arthritic score, thymus and spleen indexes, paw circumference, paw withdrawal threshold and latency as well as increased body weight gain. Furthermore, DHZ treatment persuasively reduced serum levels of alkaline phosphatase (ALP), aspartate transaminase (AST), alanine transaminase (ALT), rheumatoid factor (RF), C-reactive protein (CRP), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), interleukin-1beta and 6 (IL-1beta and IL-6), malondialdehyde (MDA), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta). In addition, DHZ observably increased serum superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione (GSH) levels in treated rats. CONCLUSION: These findings suggest that DHZ possesses anti-RA effect properties via modulating the inflammatory responses and oxidative stress.
Dietary agents in mitigating chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment (chemobrain or chemofog): first review addressing the benefits, gaps, challenges and ways forward.[Pubmed:34704580]
Food Funct. 2021 Nov 15;12(22):11132-11153.
Chemobrain or chemofog is one of the important but less investigated side effects, where the cancer survivors treated with chemotherapy develop long-term cognitive impairments, affecting their quality of life. The biological mechanisms triggering the development of chemobrain are largely unknown. However, a literature study suggests the generation of free radicals, oxidative stress, inflammatory cytokines, epigenetic chromatin remodeling, decreased neurogenesis, secretion of brain-derived neurotropic factor (BDNF), dendritic branching, and neurotransmitter release to be the cumulative contributions to the ailment. Unfortunately, there is no means to prevent/mitigate the development and intensity of chemobrain. Given the lack of effective prevention strategies or treatments, preclinical studies have been underway to ascertain the usefulness of natural products in mitigating chemobrain in the recent past. Natural products used in diets have been shown to provide beneficial effects by inhibition of free radicals, oxidative stress, inflammatory processes, and/or concomitant upregulation of various cell survival proteins. For the first time, this review focuses on the published effects of astaxanthin, omega-3 fatty acids, ginsenoside, cotinine, resveratrol, polydatin, catechin, rutin, naringin, curcumin, Dehydrozingerone, berberine, C-phycocyanin, the higher fungi Cordyceps militaris, thyme (Thymus vulgaris) and polyherbal formulation Mulmina in mitigating cognitive impairments in preclinical models of study, and also addresses their potential neuro-therapeutic mechanisms and applications in preventing/ameliorating chemobrain.
6-Gingerol and Semisynthetic 6-Gingerdione Counteract Oxidative Stress Induced by ROS in Zebrafish.[Pubmed:34599795]
Chem Biodivers. 2021 Dec;18(12):e2100650.
6-Gingerol (1) is one of the major components in ginger and developing new synthetic methodologies could bring semisynthetic analogs with improved therapeutic properties. Towards this, multigram scale isolation of 6-gingerol with excellent purity was optimized using a simple and robust extraction, followed by column purification. Synthesis of 6-gingerdione, 7 from 6-gingerol was then achieved through selective -OTBDMS protection, DMP oxidation and deprotection reaction sequence for the first time. Compounds 1, 7 and 8 (Dehydrozingerone) exhibited excellent cell-free antioxidant properties in DPPH, ABTS, superoxide radical scavenging assay and H(2) O(2) assay at 10-50 muM concentrations. The hemolytic study suggests that up to 50 muM, all three compounds did not exhibit toxicity to human erythrocytes. When H(2) O(2) treated zebrafish larvae groups (96hpf) were exposed to compounds 1, 7 and 8, it increases the SOD (19, 19.1 and 18.7 U/mg protein), CAT (18.1, 16.5, and 15.8 mumol/mg levels and decreases the lipid peroxidation level (13, 15 and 18 nmol/mg protein), respectively. In vivo ROS levels and degree of cell death were studied using DCFDA and Acridine orange assays. Compounds 1, 7 and 8 decreases the ROS and cell death level significantly. Taken together, compounds 1, 7 and 8 exhibit excellent antioxidant properties, counteract H(2) O(2) induced oxidative stress, reduces cell death in zebrafish larvae.
Dehydrozingerone ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide induced acute respiratory distress syndrome by inhibiting cytokine storm, oxidative stress via modulating the MAPK/NF-kappaB pathway.[Pubmed:34517257]
Phytomedicine. 2021 Nov;92:153729.
BACKGROUND: Inflammation-mediated lung injury is a major cause of health problems in many countries and has been the leading cause of morbidity/mortality in intensive care units. In the current COVID-19 pandemic, the majority of the patients experienced serious pneumonia resulting from inflammation (Acute respiratory distress syndrome/ARDS). Pathogenic infections cause cytokine release syndrome (CRS) by hyperactivation of immune cells, which in turn release excessive cytokines causing ARDS. Currently, there are no standard therapies for viral, bacterial or pathogen-mediated CRS. PURPOSE: This study aimed to investigate and validate the protective effects of Dehydrozingerone (DHZ) against LPS induced lung cell injury by in-vitro and in-vivo models and to gain insights into the molecular mechanisms that mediate these therapeutic effects. METHODS: The therapeutic activity of DHZ was determined in in-vitro models by pre-treating the cells with DHZ and exposed to LPS to stimulate the inflammatory cascade of events. We analysed the effect of DHZ on LPS induced inflammatory cytokines, chemokines and cell damage markers expression/levels using various cell lines. We performed gene expression, ELISA, and western blot analysis to elucidate the effect of DHZ on inflammation and its modulation of MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways. Further, the prophylactic and therapeutic effect of DHZ was evaluated against the LPS induced ARDS model in rats. RESULTS: DHZ significantly (p < 0.01) attenuated the LPS induced ROS, inflammatory cytokine, chemokine gene expression and protein release in macrophages. Similarly, DHZ treatment protected the lung epithelial and endothelial cells by mitigating the LPS induced inflammatory events in a dose-dependent manner. In vivo analysis showed that DHZ treatment significantly (p < 0.001) mitigated the LPS induced ARDS pathophysiology of increase in the inflammatory cells in BALF, inflammatory cytokine and chemokines in lung tissues. LPS stimulated neutrophil-mediated events, apoptosis, alveolar wall thickening and alveolar inflammation were profoundly reduced by DHZ treatment in a rat model. CONCLUSION: This study demonstrates for the first time that DHZ has the potential to ameliorate LPS induced ARDS by inhibiting cytokine storm and oxidative through modulating the MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways. This data provides pre-clinical support to develop DHZ as a potential therapeutic agent against ARDS.


