Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinolic acidCAS# 23978-85-0 |
Quality Control & MSDS
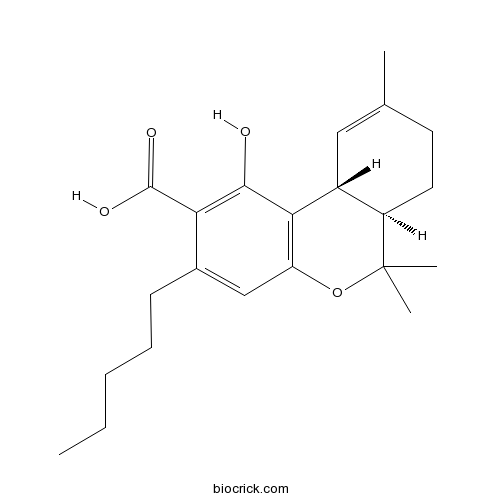
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 23978-85-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 98523 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C22H30O4 | M.Wt | 358.47 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (6aR,10aR)-1-hydroxy-6,6,9-trimethyl-3-pentyl-6a,7,8,10a-tetrahydrobenzo[c]chromene-2-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | CCCCCC1=CC2=C(C3C=C(CCC3C(O2)(C)C)C)C(=C1C(=O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | UCONUSSAWGCZMV-HZPDHXFCSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H30O4/c1-5-6-7-8-14-12-17-19(20(23)18(14)21(24)25)15-11-13(2)9-10-16(15)22(3,4)26-17/h11-12,15-16,23H,5-10H2,1-4H3,(H,24,25)/t15-,16-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid can protect dopaminergic neurons against MPP(+) induced cell death. |

Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid Dilution Calculator

Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7896 mL | 13.9482 mL | 27.8963 mL | 55.7927 mL | 69.7408 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5579 mL | 2.7896 mL | 5.5793 mL | 11.1585 mL | 13.9482 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.279 mL | 1.3948 mL | 2.7896 mL | 5.5793 mL | 6.9741 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0558 mL | 0.279 mL | 0.5579 mL | 1.1159 mL | 1.3948 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0279 mL | 0.1395 mL | 0.279 mL | 0.5579 mL | 0.6974 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Meranzin
Catalog No.:BCN5092
CAS No.:23971-42-8
- 4,4'-Bis(5-methyl-2-benzoxazolyl)stilbene
Catalog No.:BCC8657
CAS No.:2397-00-4
- Glochidonol
Catalog No.:BCN5091
CAS No.:23963-54-4
- 5-[(2R)-2-Aminopropyl]-1-[3-(benzoyloxy)propyl]-2,3-dihydro-1H-indole-7-carbonitrile (2R,3R)-2,3-dihydroxybutanedioate
Catalog No.:BCN1479
CAS No.:239463-85-5
- 5-(2-Aminopropyl)-7-cyanoindolin-1-yl)propyl benzoate
Catalog No.:BCC8718
CAS No.:239463-72-0
- Alphaxalone
Catalog No.:BCC7545
CAS No.:23930-19-0
- Dexamethasone dipropionate
Catalog No.:BCC8934
CAS No.:55541-30-5
- Z-Lys(Boc)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2763
CAS No.:2389-60-8
- H-Lys(Boc)-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2983
CAS No.:2389-48-2
- Boc-Lys(Z)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2722
CAS No.:2389-45-9
- Zapotinin
Catalog No.:BCC9192
CAS No.:14813-20-8
- Tosedostat (CHR2797)
Catalog No.:BCC2309
CAS No.:238750-77-1
- Tolnaftate
Catalog No.:BCC4869
CAS No.:2398-96-1
- 13-Deacetyltaxachitriene A
Catalog No.:BCN7390
CAS No.:239800-99-8
- Dehydroepiandrosterone enanthate
Catalog No.:BCC8930
CAS No.:23983-43-9
- Pyrocatechol monoglucoside
Catalog No.:BCN4667
CAS No.:2400-71-7
- QX 314 bromide
Catalog No.:BCC6889
CAS No.:24003-58-5
- Griffithazanone A
Catalog No.:BCN4813
CAS No.:240122-30-9
- Griffithinam
Catalog No.:BCN4744
CAS No.:240122-32-1
- 2-Amino-3-benzyloxypyridine
Catalog No.:BCC8524
CAS No.:24016-03-3
- Agathadiol diacetate
Catalog No.:BCN5093
CAS No.:24022-13-7
- H-Glu-pNA
Catalog No.:BCC2923
CAS No.:24032-35-7
- Salvicine
Catalog No.:BCN3163
CAS No.:240423-23-8
- Isocurcumenol
Catalog No.:BCN3526
CAS No.:24063-71-6
Effects of cannabinoids Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol, Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid and cannabidiol in MPP+ affected murine mesencephalic cultures.[Pubmed:22571976]
Phytomedicine. 2012 Jun 15;19(8-9):819-24.
Cannabinoids derived from Cannabis sativa demonstrate neuroprotective properties in various cellular and animal models. Mitochondrial impairment and consecutive oxidative stress appear to be major molecular mechanisms of neurodegeneration. Therefore we studied some major cannabinoids, i.e. Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA), delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) in mice mesencephalic cultures for their protective capacities against 1-methyl-4-phenyl pyridinium (MPP(+)) toxicity. MPP(+) is an established model compound in the research of parkinsonism that acts as a complex I inhibitor of the mitochondrial respiratory chain, resulting in excessive radical formation and cell degeneration. MPP(+) (10 muM) was administered for 48 h at the 9th DIV with or without concomitant cannabinoid treatment at concentrations ranging from 0.01 to 10 muM. All cannabinoids exhibited in vitro antioxidative action ranging from 669 +/- 11.1 (THC), 16 +/- 3.2 (THCA) to 356 +/- 29.5 (CBD) mug Trolox (a vitamin E derivative)/mg substance in the 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl radical (DPPH) assay. Cannabinoids were without effect on the morphology of dopaminergic cells stained by tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) immunoreaction. THC caused a dose-dependent increase of cell count up to 17.3% at 10 muM, whereas CBD only had an effect at highest concentrations (decrease of cell count by 10.1-20% at concentrations of 0.01-10 muM). It influenced the viability of the TH immunoreactive neurons significantly, whereas THCA exerts no influence on dopaminergic cell count. Exposure of cultures to 10 muM of MPP(+) for 48 h significantly decreased the number of TH immunoreactive neurons by 44.7%, and shrunken cell bodies and reduced neurite lengths could be observed. Concomitant treatment of cultures with cannabinoids rescued dopaminergic cells. Compared to MPP(+) treated cultures, THC counteracted toxic effects in a dose-dependent manner. THCA and CBD treatment at a concentration of 10 muM lead to significantly increased cell counts to 123% and 117%, respectively. Even though no significant preservation or recovery of neurite outgrowth to control values could be observed, our data show that cannabinoids THC and THCA protect dopaminergic neurons against MPP(+) induced cell death.


