DetomidineCAS# 76631-46-4 |
- Mozavaptan
Catalog No.:BCC5095
CAS No.:137975-06-5
- Tolvaptan
Catalog No.:BCC5096
CAS No.:150683-30-0
- Conivaptan HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3756
CAS No.:168626-94-6
- Desmopressin Acetate
Catalog No.:BCC1526
CAS No.:62288-83-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

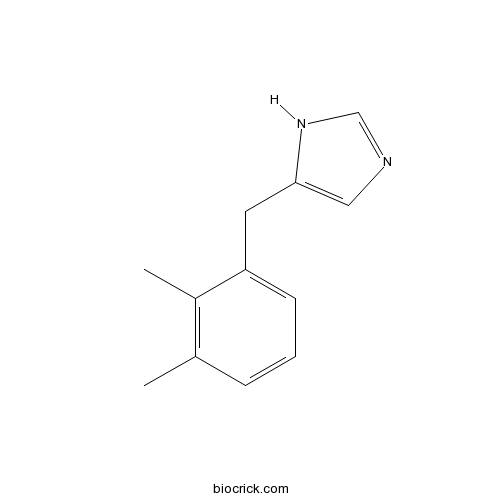
| Cas No. | 76631-46-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 56032 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C12H14N2 | M.Wt | 186.25 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | 5-[(2,3-dimethylphenyl)methyl]-1H-imidazole | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(C(=CC=C1)CC2=CN=CN2)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | RHDJRPPFURBGLQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C12H14N2/c1-9-4-3-5-11(10(9)2)6-12-7-13-8-14-12/h3-5,7-8H,6H2,1-2H3,(H,13,14) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Detomidine Dilution Calculator

Detomidine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.3691 mL | 26.8456 mL | 53.6913 mL | 107.3826 mL | 134.2282 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.0738 mL | 5.3691 mL | 10.7383 mL | 21.4765 mL | 26.8456 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5369 mL | 2.6846 mL | 5.3691 mL | 10.7383 mL | 13.4228 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1074 mL | 0.5369 mL | 1.0738 mL | 2.1477 mL | 2.6846 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0537 mL | 0.2685 mL | 0.5369 mL | 1.0738 mL | 1.3423 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Detomidine produce dose-dependent sedative and analgesic effects, is a nonnarcotic, synthetic α2-adrenergic agonist
- BAM 22P
Catalog No.:BCC5797
CAS No.:76622-26-9
- beta-D-Fructopyranose
Catalog No.:BCC8176
CAS No.:7660-25-5
- Imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazine
Catalog No.:BCC9001
CAS No.:766-55-2
- 3-Ethyl-4-methyl-3-pyrrolin-2-one
Catalog No.:BCC8632
CAS No.:766-36-9
- OR-486
Catalog No.:BCC5661
CAS No.:7659-29-2
- Divalproex Sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4379
CAS No.:76584-70-8
- SR 202
Catalog No.:BCC7243
CAS No.:76541-72-5
- Heraclenol 3'-O-[beta-D-apiofuranosyl-(1-6)-beta-D-glucopyranoside]
Catalog No.:BCN1362
CAS No.:765316-44-7
- 1-2-Cyclohexanedione
Catalog No.:BCN2265
CAS No.:765-87-7
- 10-Hydroxy-2-decenoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2654
CAS No.:765-01-5
- 15,16-Dinor-8(17),11-labdadien-13-one
Catalog No.:BCN4312
CAS No.:76497-69-3
- Ligustrazine Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN1009
CAS No.:76494-51-4
- RU 26752
Catalog No.:BCC7531
CAS No.:76676-33-0
- RU 28318, potassium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7146
CAS No.:76676-34-1
- E-64-c
Catalog No.:BCC3588
CAS No.:76684-89-4
- 1-Deacetylnimbolinin B
Catalog No.:BCN4313
CAS No.:76689-98-0
- Mallorepine
Catalog No.:BCN4317
CAS No.:767-98-6
- Decumbenine
Catalog No.:BCC8312
CAS No.:76733-83-0
- Pyronaridine Tetraphosphate
Catalog No.:BCC1144
CAS No.:76748-86-2
- Lupalbigenin
Catalog No.:BCN4314
CAS No.:76754-24-0
- GBR 12935
Catalog No.:BCC5381
CAS No.:76778-22-8
- 2'-Hydroxydaidzein
Catalog No.:BCN4585
CAS No.:7678-85-5
- 3-Hydroxy-4',5,7-trimethoxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN4316
CAS No.:76792-94-4
- Azathramycin
Catalog No.:BCC1392
CAS No.:76801-85-9
Pharmacokinetics of detomidine following intravenous or oral-transmucosal administration and sedative effects of the oral-transmucosal treatment in dogs.[Pubmed:27027842]
Am J Vet Res. 2016 Apr;77(4):413-20.
OBJECTIVE: To determine the pharmacokinetics of Detomidine hydrochloride administered IV (as an injectable formulation) or by the oral-transmucosal (OTM) route (as a gel) and assess sedative effects of the OTM treatment in healthy dogs. ANIMALS: 12 healthy adult dogs. PROCEDURES: In phase 1, Detomidine was administered by IV (0.5 mg/m(2)) or OTM (1 mg/m(2)) routes to 6 dogs. After a 24-hour washout period, each dog received the alternate treatment. Blood samples were collected for quantification via liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry and pharmacokinetic analysis. In phase 2, 6 dogs received dexmeDetomidine IV (0.125 mg/m(2)) or Detomidine gel by OTM administration (0.5 mg/m(2)), and sedation was measured by a blinded observer using 2 standardized sedation scales while dogs underwent jugular catheter placement. After a l-week washout period, each dog received the alternate treatment. RESULTS: Median maximum concentration, time to maximum concentration, and bioavailability for Detomidine gel following OTM administration were 7.03 ng/mL, 1.00 hour, and 34.52%, respectively; harmonic mean elimination half-life was 0.63 hours. All dogs were sedated and became laterally recumbent with phase 1 treatments. In phase 2, median global sedation score following OTM administration of Detomidine gel was significantly lower (indicating a lesser degree of sedation) than that following IV dexmeDetomidine treatment; however, total sedation score during jugular vein catheterization did not differ between treatments. The gel was subjectively easy to administer, and systemic absorption was sufficient for sedation. CONCLUSIONS AND CLINICAL RELEVANCE: Detomidine gel administered by the OTM route provided sedation suitable for a short, minimally invasive procedure in healthy dogs.
Sedation and mechanical hypoalgesia after sublingual administration of detomidine hydrochloride gel to donkeys.[Pubmed:27308886]
J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2016 Jul 1;249(1):83-9.
OBJECTIVE To compare sedative and mechanical hypoalgesic effects of sublingual administration of 2 doses of Detomidine gel to donkeys. DESIGN Randomized blinded controlled trial. ANIMALS 6 healthy castrated male donkeys. PROCEDURES In a crossover study design, donkeys received each of the following sublingual treatments 1 week apart in a randomly assigned order: 1 mL of molasses (D0) or Detomidine hydrochloride gel at 20 mug/kg (9 mug/lb; D20) or 40 mug/kg (18 mug/lb; D40). Sedation score (SS), head height above the ground (HHAG), and mechanical nociceptive threshold (MNT) were assessed before and for 180 minutes after treatment. Areas under the effect change-versus-time curves (AUCs) from 0 to 30, 30 to 60, 60 to 120, and 120 to 180 minutes after administration were computed for SS, HHAG, and MNT and compared among treatments. RESULTS D20 and D40 resulted in greater SS AUCs from 60 to 120 minutes and smaller HHAG AUCs from 30 through 180 minutes than did D0. The D40 resulted in smaller HHAG AUCs from 60 to 120 minutes than did D20. Compared with D0 values, MNT AUCs from 60 to 120 minutes were higher for D20, whereas MNT AUCs from 30 through 180 minutes were higher for D40. CONCLUSIONS AND CLINICAL RELEVANCE D20 and D40 induced sedation and mechanical hypoalgesia in donkeys by > 30 minutes after administration, but only sedation was dose dependent. Sublingual administration of Detomidine gel at 40 mug/kg may be useful for sedation of standing donkeys prior to potentially painful minor procedures.
Effect of the alpha2 -receptor agonists medetomidine, detomidine, xylazine, and romifidine on the ketamine metabolism in equines assessed with enantioselective capillary electrophoresis.[Pubmed:28251651]
Electrophoresis. 2017 Aug;38(15):1895-1904.
The combination of ketamine and an alpha2 -receptor agonist is often used in veterinary medicine. Four different alpha2 -receptor agonists, meDetomidine, Detomidine, xylazine, and romifidine, which differ in their chemical structure and thus in selectivity for the alpha2 -receptor and in the sedative and analgesic potency, are typically employed during surgery of equines. Recovery following anesthesia with ketamine and an alpha2 -receptor agonist is dependent on the alpha2 -receptor agonist. This prompted us to investigate (i) the inhibition characteristics for the N-demethylation of ketamine to norketamine and (ii) the formation of the ketamine metabolites norketamine, 6-hydroxynorketamine (6HNK), and 5,6-dehydronorketamine (DHNK) in presence of the four alpha2 -receptor agonists and equine liver microsomes. Samples were analyzed with enantioselective capillary electrophoresis using highly sulfated gamma-cyclodextrin as chiral selector. All four alpha2 -receptor agonists have an impact on the ketamine metabolism. MeDetomidine was found to be the strongest inhibitor, followed by Detomidine, whereas xylazine and romifidine showed almost no effect on the ketamine N-demethylation in the inhibition studies with a short-incubation period of the reaction mixture. After prolonged incubation, inhibition with xylazine and romifidine was also observed. The formation of 6HNK and DHNK is affected by all selected alpha2 -receptor agonists. With meDetomidine, levels of these metabolites are reduced compared to the case without an alpha2 -receptor agonist. For Detomidine, xylazine, and romifidine, the opposite was found.


