DipalmitinCAS# 26657-95-4 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 26657-95-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 68149 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C35H68O5 | M.Wt | 568.9 |
| Type of Compound | Miscellaneous | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
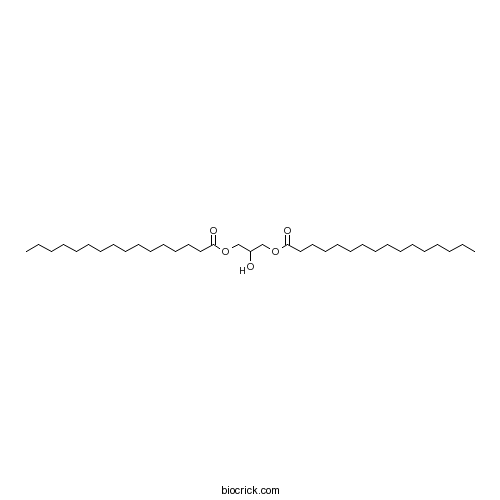
| Chemical Name | (3-hexadecanoyloxy-2-hydroxypropyl) hexadecanoate | ||
| SMILES | CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)OCC(COC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCC)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GFAZGHREJPXDMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C35H68O5/c1-3-5-7-9-11-13-15-17-19-21-23-25-27-29-34(37)39-31-33(36)32-40-35(38)30-28-26-24-22-20-18-16-14-12-10-8-6-4-2/h33,36H,3-32H2,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Dipalmitin has templating effects on soft palm mid fraction crystals. |
| Targets | PKC |
| Structure Identification | Biophys J. 1997 Nov;73(5):2603-14.Effects of dipalmitoylglycerol and fatty acids on membrane structure and protein kinase C activity.[Pubmed: 9370455]
International Journal of Food Properties, 19 Apr 2017Templating effects of dipalmitin on soft palm mid fraction crystals[Reference: WebLink]The crystallization of lipids has important implications for the industrial processing of food products, such as chocolates, margarines, spreads, confectionery, as well as bakery and dairy products. |

Dipalmitin Dilution Calculator

Dipalmitin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7578 mL | 8.7889 mL | 17.5778 mL | 35.1556 mL | 43.9445 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3516 mL | 1.7578 mL | 3.5156 mL | 7.0311 mL | 8.7889 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1758 mL | 0.8789 mL | 1.7578 mL | 3.5156 mL | 4.3944 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0352 mL | 0.1758 mL | 0.3516 mL | 0.7031 mL | 0.8789 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0176 mL | 0.0879 mL | 0.1758 mL | 0.3516 mL | 0.4394 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Salirepin
Catalog No.:BCN5149
CAS No.:26652-12-0
- Conodurine
Catalog No.:BCN7463
CAS No.:2665-57-8
- Reparixin L-lysine salt
Catalog No.:BCC1886
CAS No.:266359-93-7
- Reparixin
Catalog No.:BCC1885
CAS No.:266359-83-5
- Fmoc-β-Homo-Met-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2630
CAS No.:266359-48-2
- Zotepine
Catalog No.:BCC7838
CAS No.:26615-21-4
- 3-Ethoxyandrosta-3,5-dien-17β-ol
Catalog No.:BCC8631
CAS No.:26614-48-2
- Z-D-Ala-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3059
CAS No.:26607-51-2
- SCH 202676 hydrobromide
Catalog No.:BCC7049
CAS No.:265980-25-4
- Crenatine
Catalog No.:BCN5148
CAS No.:26585-14-8
- Dehydrocrenatine
Catalog No.:BCN5147
CAS No.:26585-13-7
- Harmalacidine
Catalog No.:BCN8033
CAS No.:26579-69-1
- N4-Benzoylcytosine
Catalog No.:BCC9073
CAS No.:26661-13-2
- 6'-O-beta-D-Apiofuranosylsweroside
Catalog No.:BCN2876
CAS No.:266678-59-5
- Boc-Glycinol
Catalog No.:BCC3093
CAS No.:26690-80-2
- Picraline
Catalog No.:BCN4762
CAS No.:2671-32-1
- [Nphe1]Nociceptin(1-13)NH2
Catalog No.:BCC5739
CAS No.:267234-08-2
- Canertinib
Catalog No.:BCN2172
CAS No.:267243-28-7
- Perivine
Catalog No.:BCN2583
CAS No.:2673-40-7
- Alibendol
Catalog No.:BCC4758
CAS No.:26750-81-2
- Amoxicillin
Catalog No.:BCC4625
CAS No.:26787-78-0
- Robtein
Catalog No.:BCN4658
CAS No.:2679-65-4
- Xanthatin
Catalog No.:BCN5150
CAS No.:26791-73-1
- Dehydrodiisoeugenol
Catalog No.:BCN1240
CAS No.:2680-81-1
Effects of dipalmitoylglycerol and fatty acids on membrane structure and protein kinase C activity.[Pubmed:9370455]
Biophys J. 1997 Nov;73(5):2603-14.
The individual and combined effects of the saturated diacylglycerol (DAG) Dipalmitin (DP) and saturated or polyunsaturated unesterified fatty acids (PUFAs) on both the structure of phosphatidylcholine/phosphatidylserine (PC/PS; 4:1 mol/mol) bilayers and on protein kinase C (PKC) activity were studied using 2H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and enzyme activity assays. In the absence of DP, PUFAs only slightly activated PKC whereas palmitic acid had no effect. In the absence of fatty acids, DP induced lateral phase separation of the bilayer into liquid-crystalline and gel phases. Under these conditions virtually all DP was sequestered into the gel phase and no activation of PKC was observed. The addition of polyunsaturated arachidonic or docosahexaenoic acids to the DP-containing bilayers significantly increased the relative amounts of DP and other lipid components in the liquid-crystalline phase, correlating with a dramatic increase in PKC activity. Furthermore, the effect was greater with PS, resulting in an enrichment of PS in the liquid-crystalline domains. In the presence of DP, palmitic acid did not decrease the amount of gel phase lipid and had no effect on PKC activity. The results explain the observed lack of PKC-activating capacity of long-chain saturated DAGs as due to the sequestration of DAG into gel domains wherein it is complexed with phospholipids and thus not available for the required interaction with the enzyme.


