XanthatinCAS# 26791-73-1 |
- 8-Epixanthatin
Catalog No.:BCN7782
CAS No.:30890-35-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 26791-73-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5281511 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C15H18O3 | M.Wt | 246.3 |
| Type of Compound | Sesquiterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
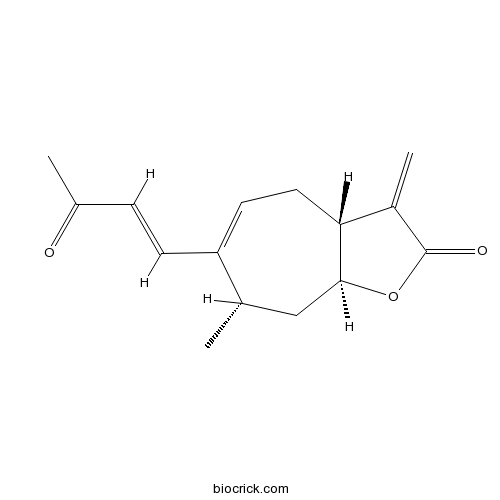
| Chemical Name | (3aR,7S,8aS)-7-methyl-3-methylidene-6-[(E)-3-oxobut-1-enyl]-4,7,8,8a-tetrahydro-3aH-cyclohepta[b]furan-2-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1CC2C(CC=C1C=CC(=O)C)C(=C)C(=O)O2 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | RBRPTFMVULVGIC-ZTIIIDENSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H18O3/c1-9-8-14-13(11(3)15(17)18-14)7-6-12(9)5-4-10(2)16/h4-6,9,13-14H,3,7-8H2,1-2H3/b5-4+/t9-,13+,14-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Xanthatin is a novel potent inhibitor of VEGFR2 signaling, has significant antitumor activity against a variety of cancer cells through cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induction, it can inhibit angiogenesis and tumor growth in breast cancer cells. Xanthatin has bactericidal and fungicidal activity, including against Colletotrichum gloesporoides, Trichothecium roseum, Bacillus cereus and Staphylococcus aureus. |
| Targets | Wnt/β-catenin | GSK-3 | STAT | Bcl-2/Bax | p65 | NF-kB | Chk | Antifection | VEGFR |
| In vitro | Antimicrobial activity of xanthatin from Xanthium spinosum L.[Reference: WebLink]Lett. Appl. Microbiol., 1994, 18(4): 206-8.
Xanthatin, a novel potent inhibitor of VEGFR2 signaling, inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth in breast cancer cells.[Pubmed: 26617743 ]Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Sep 1;8(9):10355-64.Anti-angiogenesis targeting vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) has emerged as an important tool for cancer treatment.
|
| In vivo | Characterization of xanthatin: anticancer properties and mechanisms of inhibited murine melanoma in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed: 23664560]Phytomedicine. 2013 Jul 15;20(10):865-73.Anti-cancer investigations on Xanthatin mainly focus on in vitro experiments. We herein reported the anti-tumor effects of Xanthatin both in vitro and in vivo. |
| Kinase Assay | Concerted suppression of STAT3 and GSK3β is involved in growth inhibition of non-small cell lung cancer by Xanthatin.[Pubmed: 24312384]PLoS One. 2013 Nov 28;8(11):e81945.Xanthatin, a sesquiterpene lactone purified from Xanthium strumarium L., possesses prominent anticancer activity.
|
| Cell Research | Xanthatin induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human gastric carcinoma MKN-45 cells.[Pubmed: 22532019]Planta Med. 2012 Jun;78(9):890-5.Xanthatin, a natural bioactive compound of sesquiterpene lactones, was isolated and purified from air-dried aerial part of Xanthium sibiricum Patrin ex Widder. In the present study, we demonstrated the significant antiproliferative and proapoptotic effects of Xanthatin on human gastric carcinoma MKN-45 cells.
|
| Structure Identification | Eur J Med Chem. 2015 Jan 27;90:491-6.Optimization of xanthatin extraction from Xanthium spinosum L. and its cytotoxic, anti-angiogenesis and antiviral properties.[Pubmed: 25481815]
|

Xanthatin Dilution Calculator

Xanthatin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.0601 mL | 20.3004 mL | 40.6009 mL | 81.2018 mL | 101.5022 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.812 mL | 4.0601 mL | 8.1202 mL | 16.2404 mL | 20.3004 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.406 mL | 2.03 mL | 4.0601 mL | 8.1202 mL | 10.1502 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0812 mL | 0.406 mL | 0.812 mL | 1.624 mL | 2.03 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0406 mL | 0.203 mL | 0.406 mL | 0.812 mL | 1.015 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Robtein
Catalog No.:BCN4658
CAS No.:2679-65-4
- Amoxicillin
Catalog No.:BCC4625
CAS No.:26787-78-0
- Alibendol
Catalog No.:BCC4758
CAS No.:26750-81-2
- Perivine
Catalog No.:BCN2583
CAS No.:2673-40-7
- Canertinib
Catalog No.:BCN2172
CAS No.:267243-28-7
- [Nphe1]Nociceptin(1-13)NH2
Catalog No.:BCC5739
CAS No.:267234-08-2
- Picraline
Catalog No.:BCN4762
CAS No.:2671-32-1
- Boc-Glycinol
Catalog No.:BCC3093
CAS No.:26690-80-2
- 6'-O-beta-D-Apiofuranosylsweroside
Catalog No.:BCN2876
CAS No.:266678-59-5
- N4-Benzoylcytosine
Catalog No.:BCC9073
CAS No.:26661-13-2
- Dipalmitin
Catalog No.:BCN2214
CAS No.:26657-95-4
- Salirepin
Catalog No.:BCN5149
CAS No.:26652-12-0
- Dehydrodiisoeugenol
Catalog No.:BCN1240
CAS No.:2680-81-1
- Indapamide
Catalog No.:BCC4788
CAS No.:26807-65-8
- Debilon
Catalog No.:BCN7696
CAS No.:26808-51-5
- Udenafil
Catalog No.:BCC5213
CAS No.:268203-93-6
- Coronalolide methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN5151
CAS No.:268214-50-2
- Coronalolide
Catalog No.:BCN5152
CAS No.:268214-51-3
- Coronalolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5153
CAS No.:268214-52-4
- Harringtonine
Catalog No.:BCN6794
CAS No.:26833-85-2
- Homoharringtonine
Catalog No.:BCN4958
CAS No.:26833-87-4
- Triptohypol F
Catalog No.:BCN5154
CAS No.:268541-26-0
- Penfluridol
Catalog No.:BCC4696
CAS No.:26864-56-2
- 1,3-Bis[2-(4-aminophenyl)-2-propyl]benzene
Catalog No.:BCC8419
CAS No.:2687-27-6
Xanthatin induces cell cycle arrest at G2/M checkpoint and apoptosis via disrupting NF-kappaB pathway in A549 non-small-cell lung cancer cells.[Pubmed:22450683]
Molecules. 2012 Mar 26;17(4):3736-50.
Xanthatin, a natural sesquiterpene lactone, has significant antitumor activity against a variety of cancer cells, yet little is known about its anticancer mechanism. In this study, we demonstrated that Xanthatin had obvious dose-/time-dependent cytotoxicity against the human non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell line A549. Flow cytometry analysis showed Xanthatin induced cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase. Xanthatin also had pro-apoptotic effects on A549 cells as evidenced by Hoechst 33258 staining and annexin V-FITC staining. Mechanistic data revealed that Xanthatin downregulated Chk1, Chk2, and phosphorylation of CDC2, which contributed to the cell cycle arrest. Xathatin also increased total p53 protein levels, decreased Bcl-2/Bax ratio and expression of the downstream factors procaspase-9 and procaspase-3, which triggered the intrinsic apoptosis pathway. Furthermore, Xanthatin blocked phosphorylation of NF-kappaB (p65) and IkappaBa, which might also contribute to its pro-apoptotic effects on A549 cells. Xanthatin also inhibited TNFa induced NF-kappaB (p65) translocation. We conclude that Xanthatin displays significant antitumor effects through cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induction in A549 cells. These effects were associated with intrinsic apoptosis pathway and disrupted NF-kappaB signaling. These results suggested that Xanthatin may have therapeutic potential against NSCLC.
Concerted suppression of STAT3 and GSK3beta is involved in growth inhibition of non-small cell lung cancer by Xanthatin.[Pubmed:24312384]
PLoS One. 2013 Nov 28;8(11):e81945.
Xanthatin, a sesquiterpene lactone purified from Xanthium strumarium L., possesses prominent anticancer activity. We found that disruption of GSK3beta activity was essential for Xanthatin to exert its anticancer properties in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), concurrent with preferable suppression of constitutive activation of STAT3. Interestingly, inactivation of the two signals are two mutually exclusive events in Xanthatin-induced cell death. Moreover, we surprisingly found that exposure of Xanthatin failed to trigger the presumable side effect of canonical Wnt/beta-Catenin followed by GSK3beta inactivation. We further observed that the downregulation of STAT3 was required for Xanthatin to fine-tune the risk. Thus, the discovery of Xanthatin, which has ability to simultaneously orchestrate two independent signaling cascades, may have important implications for screening promising drugs in cancer therapies.
Characterization of xanthatin: anticancer properties and mechanisms of inhibited murine melanoma in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed:23664560]
Phytomedicine. 2013 Jul 15;20(10):865-73.
Anti-cancer investigations on Xanthatin mainly focus on in vitro experiments. We herein reported the anti-tumor effects of Xanthatin both in vitro and in vivo. MTS assay results showed that Xanthatin had a remarkable anti-proliferative effect on B16-F10 cells. Moreover, the expression of beta-catenin was up-regulated both in vitro and in vivo. Animal studies further revealed that Xanthatin killed the tumor cells around the blood vessels which contributes to reduce microvascular density extremely. All these results indicate that Xanthatin inhibited murine melanoma B16-F10 cell proliferation possibly associated with activation of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway and its activity against melanoma tumor might also be relevant to inhibition of angiogenesis.
Xanthatin, a novel potent inhibitor of VEGFR2 signaling, inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth in breast cancer cells.[Pubmed:26617743]
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Sep 1;8(9):10355-64. eCollection 2015.
Anti-angiogenesis targeting vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) has emerged as an important tool for cancer treatment. In this study, we described a novel VEGFR2 inhibitor, Xanthatin, which inhibits tumor angiogenesis and growth. The biochemical profiles of Xanthatin were investigated using kinase assay, migration assay, tube formation, Matrigel plug assay, western blot, immunofluorescence and human tumor xenograft model. Xanthatin significantly inhibited growth, migration and tube formation of human umbilical vascular endothelial cell as well as inhibited vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-stimulated angiogenesis. In addition, it inhibited VEGF-induced phosphorylation of VEGFR2 and its downstream signaling regulator. Moreover, Xanthatin directly inhibit proliferation of breast cancer cells MDA-MB-231. Oral administration of Xanthatin could markedly inhibit human tumor xenograft growth and decreased microvessel densities (MVD) in tumor sections. Taken together, these preclinical evaluations suggest that Xanthatin inhibits angiogenesis and may be a promising anticancer drug candidate.
Optimization of xanthatin extraction from Xanthium spinosum L. and its cytotoxic, anti-angiogenesis and antiviral properties.[Pubmed:25481815]
Eur J Med Chem. 2015 Jan 27;90:491-6.
The aqueous extraction of the sesquiterpene lactone Xanthatin from Xanthium spinosum L. favours the conversion of xanthinin (1) to Xanthatin (2) via the loss of acetic acid. The cytotoxic (Hep-G2 and L1210 human cell lines) and antiviral activities of isolated Xanthatin are established. This natural compound shows significant cytotoxicity against the Hep-G2 cell line and our experimental results reveal its strong anti-angiogenesis capacity in vitro. The structure of Xanthatin is determined by spectroscopic methods and for the first time confirmed by X-ray diffraction.
Xanthatin induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human gastric carcinoma MKN-45 cells.[Pubmed:22532019]
Planta Med. 2012 Jun;78(9):890-5.
Xanthatin, a natural bioactive compound of sesquiterpene lactones, was isolated and purified from air-dried aerial part of Xanthium sibiricum Patrin ex Widder. In the present study, we demonstrated the significant antiproliferative and proapoptotic effects of Xanthatin on human gastric carcinoma MKN-45 cells. MTS assay showed that Xanthatin produced obvious cytotoxicity in MKN-45 cells with IC50 values of 18.6, 9.3, and 3.9 microM for 12, 24, and 48 h, respectively. Results of flow cytometry analysis indicated that the antiproliferative activity induced by Xanthatin might be executed via G2/M cell cycle arrest and proapoptosis in MKN-45 cells. Western blot analysis elucidated that: a) Xanthatin downregulated expression of Chk1 and Chk2 and phosphorylation of CDC2, which are known as key G2/M transition regulators; b) Xanthatin increased p53 activation, decreased the bcl-2/bax ratio and the levels of downstream procaspase-9 and procaspase-3, which are key regulators in the intrinsic apoptosis pathway; c) Xanthatin blocked phosphorylation of NF-kappaB (p65 subunit) and of IkappaBalpha, which might contribute to its proapoptotic effects on MKN-45 cells. In conclusion, our results suggest that Xanthatin may have therapeutic potential against human gastric carcinoma.


