DehydrodiisoeugenolCAS# 2680-81-1 |
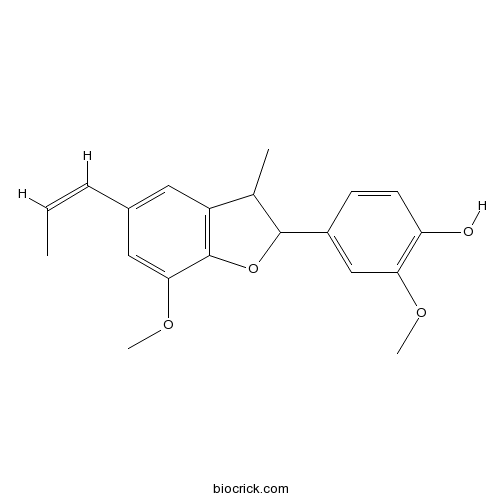
- (-)-licarin A
Catalog No.:BCN5087
CAS No.:23518-30-1
- (+)-Licarin A
Catalog No.:BCC9008
CAS No.:51020-86-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 2680-81-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5354672 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C20H22O4 | M.Wt | 326.39 |
| Type of Compound | Lignans | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 250 mg/mL (765.95 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-methoxy-4-[7-methoxy-3-methyl-5-[(Z)-prop-1-enyl]-2,3-dihydro-1-benzofuran-2-yl]phenol | ||
| SMILES | CC=CC1=CC2=C(C(=C1)OC)OC(C2C)C3=CC(=C(C=C3)O)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ITDOFWOJEDZPCF-WAYWQWQTSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H22O4/c1-5-6-13-9-15-12(2)19(24-20(15)18(10-13)23-4)14-7-8-16(21)17(11-14)22-3/h5-12,19,21H,1-4H3/b6-5- | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Dehydrodiisoeugenol has anti-inflammatory activity, it inhibited the expression of the COX-2, proteolysis of inhibitor κB-α and transcriptional activity of NF-κB. Dehydrodiisoeugenol can cross the blood-brain barrier rapidly, it may be developed into an effective anxiogenic agent. |
| Targets | NF-kB | COX | IκB/IKK |
| In vitro | Metabolism of the lignan dehydrodiisoeugenol in rats.[Pubmed: 21544774]Planta Med. 2011 Oct;77(15):1712-7.Dehydrodiisoeugenol (DDIE), a major active lignan from the seed and aril of the fruit of Myristica fragrans Houtt., functions as a potential anti-inflammatory agent by inhibiting lipopolysaccharide-stimulated nuclear factor kappa B activation and cyclooxygenase-2 expression in macrophages. However, the metabolism of DDIE remains unknown.
|
| Cell Research | Dehydrodiisoeugenol, an isoeugenol dimer, inhibits lipopolysaccharide-stimulated nuclear factor kappa B activation and cyclooxygenase-2 expression in macrophages.[Pubmed: 15639233]Arch Biochem Biophys. 2005 Feb 15;434(2):326-32.o-Methoxyphenols such as eugenol and isoeugenol exhibit anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory activities, but at higher concentrations act as oxidants and potent allergens.
|
| Structure Identification | Fitoterapia. 2013 Jan;84:47-53.Cerebral nuclei distribution study of dehydrodiisoeugenol as an anxiogenic agent determined by RP-HPLC.[Pubmed: 23059843]
|

Dehydrodiisoeugenol Dilution Calculator

Dehydrodiisoeugenol Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0638 mL | 15.3191 mL | 30.6382 mL | 61.2764 mL | 76.5955 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6128 mL | 3.0638 mL | 6.1276 mL | 12.2553 mL | 15.3191 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3064 mL | 1.5319 mL | 3.0638 mL | 6.1276 mL | 7.6595 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0613 mL | 0.3064 mL | 0.6128 mL | 1.2255 mL | 1.5319 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0306 mL | 0.1532 mL | 0.3064 mL | 0.6128 mL | 0.766 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Xanthatin
Catalog No.:BCN5150
CAS No.:26791-73-1
- Robtein
Catalog No.:BCN4658
CAS No.:2679-65-4
- Amoxicillin
Catalog No.:BCC4625
CAS No.:26787-78-0
- Alibendol
Catalog No.:BCC4758
CAS No.:26750-81-2
- Perivine
Catalog No.:BCN2583
CAS No.:2673-40-7
- Canertinib
Catalog No.:BCN2172
CAS No.:267243-28-7
- [Nphe1]Nociceptin(1-13)NH2
Catalog No.:BCC5739
CAS No.:267234-08-2
- Picraline
Catalog No.:BCN4762
CAS No.:2671-32-1
- Boc-Glycinol
Catalog No.:BCC3093
CAS No.:26690-80-2
- 6'-O-beta-D-Apiofuranosylsweroside
Catalog No.:BCN2876
CAS No.:266678-59-5
- N4-Benzoylcytosine
Catalog No.:BCC9073
CAS No.:26661-13-2
- Dipalmitin
Catalog No.:BCN2214
CAS No.:26657-95-4
- Indapamide
Catalog No.:BCC4788
CAS No.:26807-65-8
- Debilon
Catalog No.:BCN7696
CAS No.:26808-51-5
- Udenafil
Catalog No.:BCC5213
CAS No.:268203-93-6
- Coronalolide methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN5151
CAS No.:268214-50-2
- Coronalolide
Catalog No.:BCN5152
CAS No.:268214-51-3
- Coronalolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5153
CAS No.:268214-52-4
- Harringtonine
Catalog No.:BCN6794
CAS No.:26833-85-2
- Homoharringtonine
Catalog No.:BCN4958
CAS No.:26833-87-4
- Triptohypol F
Catalog No.:BCN5154
CAS No.:268541-26-0
- Penfluridol
Catalog No.:BCC4696
CAS No.:26864-56-2
- 1,3-Bis[2-(4-aminophenyl)-2-propyl]benzene
Catalog No.:BCC8419
CAS No.:2687-27-6
- Isomahanimbine
Catalog No.:BCN3175
CAS No.:26871-46-5
Cerebral nuclei distribution study of dehydrodiisoeugenol as an anxiogenic agent determined by RP-HPLC.[Pubmed:23059843]
Fitoterapia. 2013 Jan;84:47-53.
A sensitive RP-HPLC-DAD method was established to quantify Dehydrodiisoeugenol (DDIE) in rat cerebral nuclei. The assay procedure involved one-step extraction of DDIE and daidzein, as an internal standard, from rat plasma and various cerebral nuclei with ethyl acetate. Chromatographic separation was performed on a Diamonsil ODS C(18) column with methanol-water (81:19, v/v) as a mobile phase. The UV absorbance of the samples was measured at the wavelength of 270nm. The analysis method was proved to be precise and accurate at linearity ranges in plasma and each cerebral nucleus with correlation coefficients of >/=0.9971. The results indicated that the method established was successfully applied to cerebral nuclei distribution study of DDIE after intravenous administration at a single dose of 40mg/kg to rat. DDIE showed high concentration in all of cerebral nuclei at 8min, which indicated that DDIE could cross the blood-brain barrier rapidly and might be one of the main bioactive substances of nutmeg. The results provide fundamental data for evaluating the effects of DDIE on the central nervous system and to be developed into an effective anxiogenic agent.
Metabolism of the lignan dehydrodiisoeugenol in rats.[Pubmed:21544774]
Planta Med. 2011 Oct;77(15):1712-7.
Dehydrodiisoeugenol (DDIE), a major active lignan from the seed and aril of the fruit of Myristica fragrans Houtt., functions as a potential anti-inflammatory agent by inhibiting lipopolysaccharide-stimulated nuclear factor kappa B activation and cyclooxygenase-2 expression in macrophages. However, the metabolism of DDIE remains unknown. This report describes the metabolic fate of DDIE in liver microsomes, urine, and feces of rats treated with DDIE. DDIE metabolites were isolated by sequential column chromatography and high-performance liquid chromatography from liver microsomes incubations, urine, and feces. Nine metabolites ( M-1 to M-9), including 5 new metabolites, were determined spectroscopically using ultra-violet (UV), mass spectrometry (MS), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), and circular dichroism (CD). Analysis of the isolated metabolites showed that DDIE undergoes four major pathways of metabolism in the rat: oxidation (including hydroxylation, hydroformylation, and acetylation), demethylation, ring-opening, and dehydrogenation. In contrast to the metabolites from liver microsomes, the major metabolites In vivo were generated from DDIE by multiple metabolic reactions. Given these results, we describe a metabolic pathway for DDIE in the rat that gives insight into the metabolism of DDIE and the mechanism of DDIE bioactivity in humans.
Analysis of anti-inflammatory dehydrodiisoeugenol and metabolites excreted in rat feces and urine using HPLC-UV.[Pubmed:21932389]
Biomed Chromatogr. 2012 Jun;26(6):703-7.
Dehydrodiisoeugenol (DDIE) is a lignan in the fruit of Myristica fragrans. It can be converted into several metabolites in in vitro and in vivo metabolism. In this study, the excretion of DDIE in urine and feces was investigated after intravenous (i.v.) and intragastric (i.g.) administration to rats. DDIE and its metabolites (M-1 and M-2) were measured using HPLC. The amount of DDIE and its metabolites excreted was higher in feces than in urine, suggesting that DDIE and its metabolites are eliminated primarily in the feces. Significant differences in the excretion levels of DDIE and its metabolites were seen between i.v. and i.g. administration. Greater amounts of DDIE and its metabolites were excreted following i.v. administration, suggesting that DDIE can exert a longer period of anti-inflammatory activity following i.g. administration. The accuracy, precision, recovery and stability of the analytical method in this study were satisfactory for the measurement of DDIE and its metabolites in rat urine and feces. Observations made in this study will contribute to understanding of the absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion pathway of DDIE and will aid decision-making regarding the best mode of DDIE administration during treatment to maximize its anti-inflammatory effects.
Dehydrodiisoeugenol, an isoeugenol dimer, inhibits lipopolysaccharide-stimulated nuclear factor kappa B activation and cyclooxygenase-2 expression in macrophages.[Pubmed:15639233]
Arch Biochem Biophys. 2005 Feb 15;434(2):326-32.
o-Methoxyphenols such as eugenol and isoeugenol exhibit anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory activities, but at higher concentrations act as oxidants and potent allergens. We recently demonstrated the eugenol dimer bis-eugenol to be an efficient inhibitor of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory cytokine expression in macrophages without cytotoxicity. This result suggested that dimer compound of o-methoxyphenols may possess anti-inflammatory activity. Thus, we further synthesized Dehydrodiisoeugenol and alpha-diisoeugenol from isoeugenols, and investigated whether these dimers could inhibit LPS-stimulated nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) activation and cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 gene expression, both of which are closely involved in inflammation and mutagenesis. The expression of the COX-2 gene was strongly inhibited by Dehydrodiisoeugenol in RAW264.7 murine macrophages stimulated with LPS. In contrast, isoeugenol and alpha-diisoeugenol did not inhibit it. Dehydrodiisoeugenol also significantly inhibited LPS-stimulated phosphorylation-dependent proteolysis of inhibitor kappaB-alpha and transcriptional activity of NF-kappaB in the cells. These findings suggest that Dehydrodiisoeugenol acts as a potent anti-inflammatory agent.


