CanertinibHER family tyrosine kinase inhibitor CAS# 267243-28-7 |
- Perindopril Erbumine
Catalog No.:BCC3586
CAS No.:107133-36-8
- Losartan Potassium (DuP 753)
Catalog No.:BCC1080
CAS No.:124750-99-8
- Telmisattan
Catalog No.:BCC3863
CAS No.:144701-48-4
- Rosuvastatin Calcium
Catalog No.:BCC3853
CAS No.:147098-20-2
- Imidapril HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3792
CAS No.:89396-94-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 267243-28-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 156414 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C24H25ClFN5O3 | M.Wt | 485.94 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | CI-1033; PD-183805 | ||
| Solubility | Ethanol : 12.5 mg/mL (25.72 mM; Need ultrasonic) DMSO : 4.9 mg/mL (10.08 mM; Need warming) Methanol : 2.22 mg/mL (4.57 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
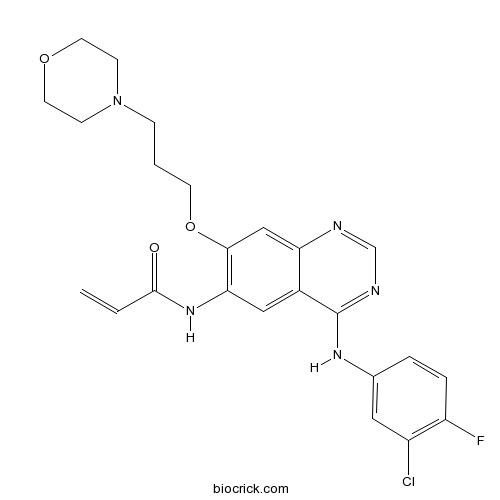
| Chemical Name | N-[4-(3-chloro-4-fluoroanilino)-7-(3-morpholin-4-ylpropoxy)quinazolin-6-yl]prop-2-enamide | ||
| SMILES | C=CC(=O)NC1=C(C=C2C(=C1)C(=NC=N2)NC3=CC(=C(C=C3)F)Cl)OCCCN4CCOCC4 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | OMZCMEYTWSXEPZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C24H25ClFN5O3/c1-2-23(32)30-21-13-17-20(14-22(21)34-9-3-6-31-7-10-33-11-8-31)27-15-28-24(17)29-16-4-5-19(26)18(25)12-16/h2,4-5,12-15H,1,3,6-11H2,(H,30,32)(H,27,28,29) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Canertinib is a pan-ErbB inhibitor for EGFR and ErbB2 with IC50 of 1.5 nM and 9.0 nM, no activity to PDGFR, FGFR, InsR, PKC, or CDK1/2/4. Canertinib displays anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects in human myeloid leukemia cells devoid of ErbB-receptors, downregulates important signaling pathways and activates caspase-mediated intrinsic apoptosis pathway in human T-cell leukemia cells. |
| Targets | P-gp | Akt | ERK | STAT | PARP | Caspase | PI3K | MAPK | EGFR | ErbB2 |
| In vitro | Kinase scaffold repurposing for neglected disease drug discovery: discovery of an efficacious, lapatinib-derived lead compound for trypanosomiasis.[Pubmed: 23597080 ]J. Med. Chem.,2013 May, 56(10):3820-32.Human African trypanosomiasis (HAT) is a neglected tropical disease caused by the protozoan parasite Trypanosoma brucei . Because drugs in use against HAT are toxic and require intravenous dosing, new drugs are needed. Enhanced brain accumulation of pazopanib by modulating P-gp and Bcrp1 mediated efflux with canertinib or erlotinib.[Pubmed: 22688250]Int J Pharm. 2012 Oct 15;436(1-2):127-34.Primary objective of this investigation was to delineate the differential impact of efflux transporters P-glycoprotein (P-gp/Abcb1) and breast cancer resistance protein (Bcrp1/Abcg2) on brain disposition and plasma pharmacokinetics of pazopanib. In addition, this research investigated whether inhibition of these efflux transporters with clinically relevant efflux modulators Canertinib or erlotinib could be a viable strategy for improving pazopanib brain delivery. |
| In vivo | Irreversible pan-ERBB inhibitor canertinib elicits anti-leukaemic effects and induces the regression of FLT3-ITD transformed cells in mice.[Pubmed: 21848891]Br J Haematol. 2011 Oct;155(2):198-208.Recent findings have indicated that tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) targeting the ERBB receptor family display anti-leukaemic effects, despite the lack of receptor expression on human leukaemic cells. |
| Kinase Assay | The pan-ErbB tyrosine kinase inhibitor canertinib induces caspase-mediated cell death in human T-cell leukemia (Jurkat) cells.[Pubmed: 21669187 ]Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Jul 8;410(3):422-7.Canertinib is a novel ErbB-receptor inhibitor currently in clinical development for the treatment of solid tumors overexpressing ErbB-receptors. We have recently demonstrated that Canertinib displays anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects in human myeloid leukemia cells devoid of ErbB-receptors. The mechanism mediating these effects are however unknown. |
| Cell Research | The pan-ErbB receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor canertinib induces ErbB-independent apoptosis in human leukemia (HL-60 and U-937) cells.[Pubmed: 20096663]The pan-ErbB receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor canertinib promotes apoptosis of malignant melanoma in vitro and displays anti-tumor activity in vivo.[Pubmed: 21982771]Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Oct 28;414(3):563-8.The ErbB receptor family has been suggested to constitute a therapeutic target for tumor-specific treatment of malignant melanoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010 Feb 26;393(1):6-10.Epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors have recently been shown to display anti-neoplastic effects in human malignant myeloid cells. |

Canertinib Dilution Calculator

Canertinib Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0579 mL | 10.2893 mL | 20.5787 mL | 41.1573 mL | 51.4467 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4116 mL | 2.0579 mL | 4.1157 mL | 8.2315 mL | 10.2893 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2058 mL | 1.0289 mL | 2.0579 mL | 4.1157 mL | 5.1447 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0412 mL | 0.2058 mL | 0.4116 mL | 0.8231 mL | 1.0289 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0206 mL | 0.1029 mL | 0.2058 mL | 0.4116 mL | 0.5145 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Canertinib (also known as CI-1033), a 3-chloro, 4-fluoro, 4-anilinoquinazoline, is an orally available, potent and irreversible Pan-erbB tyrosine kinase inhibitor that inhibits EGFR, HER2 and HER4 in vitro with the half maximal inhibition concentration IC50 of 0.8 nM, 19 nM and 7 nM respectively [1].
Canertinib irreversibly binds into the ATP pocket within the TK domain of all erbB family members, where the acrylamide side-chain at position C6 of canertinib is brought into close proximity with cysteines of erbB members, followed by the rapid formation of a covalent bond, which permanently inactivates the catalytically active erB1, erB2 and erB4 family members and effectively inhibits erbB3-dependent signaling [2].
References:
[1] Michelle Arkin, Mark M. Moasser. HER2 directed small molecule antagonists. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 February 1. Published in final edited form as: Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2008 December; 9(12): 1264–1276.
[2] Calvo E, Tolcher AW, Hammond LA, Patnaik A, de Bono JS, Eiseman IA, Olson SC, Lenehan PF, McCreery H, Lorusso P, Rowinsky EK. Administration of CI-1033, an irreversible pan-erbB tyrosine kinase inhibitor, is feasible on a 7-day on, 7-day off schedule: a phase I pharmacokinetic and food effect study. Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Nov 1;10(21):7112-20.
- [Nphe1]Nociceptin(1-13)NH2
Catalog No.:BCC5739
CAS No.:267234-08-2
- Picraline
Catalog No.:BCN4762
CAS No.:2671-32-1
- Boc-Glycinol
Catalog No.:BCC3093
CAS No.:26690-80-2
- 6'-O-beta-D-Apiofuranosylsweroside
Catalog No.:BCN2876
CAS No.:266678-59-5
- N4-Benzoylcytosine
Catalog No.:BCC9073
CAS No.:26661-13-2
- Dipalmitin
Catalog No.:BCN2214
CAS No.:26657-95-4
- Salirepin
Catalog No.:BCN5149
CAS No.:26652-12-0
- Conodurine
Catalog No.:BCN7463
CAS No.:2665-57-8
- Reparixin L-lysine salt
Catalog No.:BCC1886
CAS No.:266359-93-7
- Reparixin
Catalog No.:BCC1885
CAS No.:266359-83-5
- Fmoc-β-Homo-Met-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2630
CAS No.:266359-48-2
- Zotepine
Catalog No.:BCC7838
CAS No.:26615-21-4
- Perivine
Catalog No.:BCN2583
CAS No.:2673-40-7
- Alibendol
Catalog No.:BCC4758
CAS No.:26750-81-2
- Amoxicillin
Catalog No.:BCC4625
CAS No.:26787-78-0
- Robtein
Catalog No.:BCN4658
CAS No.:2679-65-4
- Xanthatin
Catalog No.:BCN5150
CAS No.:26791-73-1
- Dehydrodiisoeugenol
Catalog No.:BCN1240
CAS No.:2680-81-1
- Indapamide
Catalog No.:BCC4788
CAS No.:26807-65-8
- Debilon
Catalog No.:BCN7696
CAS No.:26808-51-5
- Udenafil
Catalog No.:BCC5213
CAS No.:268203-93-6
- Coronalolide methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN5151
CAS No.:268214-50-2
- Coronalolide
Catalog No.:BCN5152
CAS No.:268214-51-3
- Coronalolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5153
CAS No.:268214-52-4
The pan-ErbB receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor canertinib induces ErbB-independent apoptosis in human leukemia (HL-60 and U-937) cells.[Pubmed:20096663]
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010 Feb 26;393(1):6-10.
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors have recently been shown to display anti-neoplastic effects in human malignant myeloid cells. Our study was initiated in order to determine the effect of the pan-ErbB receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, Canertinib (CI-1033), on growth and survival of human leukemia (HL-60 and U-937) cells. We show that treatment of HL-60 and U-937 cells with Canertinib significantly inhibits growth of both cell lines in a dose-dependent manner; half maximal effective dose (IC(50)) in HL-60 and U-937 cells was approximately 2.5 microM and 1.0 microM, respectively. Treatment with 2 microM Canertinib promoted a G(1) cell cycle arrest, whereas doses of 5 microM or more induced apoptosis as determined by the Annexin V method and cleavage of poly-(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP). HL-60 and U-937 cells lacked EGF-receptor transcript but expressed ErbB2-4 mRNA as determined by RT-PCR. However, none of the corresponding ErbB-receptor proteins could be detected by Western blot analysis. We conclude that Canertinib induces apoptosis in HL-60 and U-937 cells devoid of functional ErbB1-4 receptors. Our results suggest that Canertinib could be of potential clinical interest in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia.
The pan-ErbB receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor canertinib promotes apoptosis of malignant melanoma in vitro and displays anti-tumor activity in vivo.[Pubmed:21982771]
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Oct 28;414(3):563-8.
The ErbB receptor family has been suggested to constitute a therapeutic target for tumor-specific treatment of malignant melanoma. Here we investigate the effect of the pan-ErbB tyrosine kinase inhibitor Canertinib on cell growth and survival in human melanoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Canertinib significantly inhibited growth of cultured melanoma cells, RaH3 and RaH5, in a dose-dependent manner as determined by cell counting. Half-maximum growth inhibitory dose (IC(50)) was approximately 0.8 muM and by 5 muM both cell lines were completely growth-arrested within 72 h of treatment. Incubation of exponentially growing RaH3 and RaH5 with 1 muM Canertinib accumulated the cells in the G(1)-phase of the cell cycle within 24h of treatment without induction of apoptosis as determined by flow cytometry. Immunoblot analysis showed that 1 muM Canertinib inhibited ErbB1-3 receptor phosphorylation with a concomitant decrease of Akt-, Erk1/2- and Stat3 activity in both cell lines. In contrast to the cytostatic effect observed at doses Canertinib, higher concentrations induced apoptosis as demonstrated by the Annexin V method and Western blot analysis of PARP cleavage. Furthermore, Canertinib significantly inhibited growth of RaH3 and RaH5 melanoma xenografts in nude mice. Pharmacological targeting of the ErbB receptors may prove successful in the treatment of patients with metastatic melanoma.
Kinase scaffold repurposing for neglected disease drug discovery: discovery of an efficacious, lapatinib-derived lead compound for trypanosomiasis.[Pubmed:23597080]
J Med Chem. 2013 May 23;56(10):3820-32.
Human African trypanosomiasis (HAT) is a neglected tropical disease caused by the protozoan parasite Trypanosoma brucei . Because drugs in use against HAT are toxic and require intravenous dosing, new drugs are needed. Initiating lead discovery campaigns by using chemical scaffolds from drugs approved for other indications can speed up drug discovery for neglected diseases. We demonstrated recently that the 4-anilinoquinazolines lapatinib (GW572016, 1) and Canertinib (CI-1033) kill T. brucei with low micromolar EC50 values. We now report promising activity of analogues of 1, which provided an excellent starting point for optimization of the chemotype. Our compound optimization that has led to synthesis of several potent 4-anilinoquinazolines, including NEU617, 23a, a highly potent, orally bioavailable inhibitor of trypanosome replication. At the cellular level, 23a blocks duplication of the kinetoplast and arrests cytokinesis, making it a new chemical tool for studying regulation of the trypanosome cell cycle.
The pan-ErbB tyrosine kinase inhibitor canertinib induces caspase-mediated cell death in human T-cell leukemia (Jurkat) cells.[Pubmed:21669187]
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Jul 8;410(3):422-7.
Canertinib is a novel ErbB-receptor inhibitor currently in clinical development for the treatment of solid tumors overexpressing ErbB-receptors. We have recently demonstrated that Canertinib displays anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects in human myeloid leukemia cells devoid of ErbB-receptors. The mechanism mediating these effects are however unknown. In this study, we show that Canertinib is able to act as a multi-kinase inhibitor by inhibition of several intracellular kinases involved in T-cell signaling such as Akt, Erk1/2 and Zap-70, and reduced Lck protein expression in the human T-cell leukemia cell line Jurkat. Treatment with Canertinib at a concentration of 2 muM caused accumulation of Jurkat cells in the G(1) cell cycle phase and increased doses induced apoptosis in a time-dependent manner. Apoptotic signs of treated cells were detected by Annexin V staining and cleavage of PARP, caspase-3, -8, -9, -10 and Bid. A subset of the pro-apoptotic signals mediated by Canertinib could be significantly reduced by specific caspase inhibitors. Taken together, these results demonstrate the dual ability of Canertinib to downregulate important signaling pathways and to activate caspase-mediated intrinsic apoptosis pathway in human T-cell leukemia cells.
Irreversible pan-ERBB inhibitor canertinib elicits anti-leukaemic effects and induces the regression of FLT3-ITD transformed cells in mice.[Pubmed:21848891]
Br J Haematol. 2011 Oct;155(2):198-208.
Recent findings have indicated that tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) targeting the ERBB receptor family display anti-leukaemic effects, despite the lack of receptor expression on human leukaemic cells. The occurrence of activating mutations in the gene encoding FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) in patients with acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) has rendered inhibition of this receptor a promising therapeutic target. Due to possibility of cross-reactivity, we investigated the effect of the irreversible pan-ERBB inhibitor Canertinib (CI-1033) on leukaemic cells expressing FLT3. The drug had anti-proliferative and apoptotic effects on primary AML cells and human leukaemic cell lines expressing mutated FLT3. In several AML patient samples, a blast cell population expressing FLT3-internal tandem duplication (ITD) was eradicated by Canertinib. Canertinib inhibited receptor autophosphorylation and kinase activity of both mutated and FLT3 ligand stimulated wildtype FLT3, leading to inhibition of the PI3-kinase and MAP kinase pathways. Apoptotic induction was dependent on pro-apoptotic BH3-only protein BCL2L11/BIM because siRNA silencing attenuated apoptosis. Moreover, the drug induced regression of cells expressing FLT3-ITD in a murine in vivo-transplantation model at previously described tolerated doses. These results indicate that Canertinib, as an irreversible TKI, could constitute a novel treatment regimen in patients with mutated or overexpressed FLT3.
Enhanced brain accumulation of pazopanib by modulating P-gp and Bcrp1 mediated efflux with canertinib or erlotinib.[Pubmed:22688250]
Int J Pharm. 2012 Oct 15;436(1-2):127-34.
Primary objective of this investigation was to delineate the differential impact of efflux transporters P-glycoprotein (P-gp/Abcb1) and breast cancer resistance protein (Bcrp1/Abcg2) on brain disposition and plasma pharmacokinetics of pazopanib. In addition, this research investigated whether inhibition of these efflux transporters with clinically relevant efflux modulators Canertinib or erlotinib could be a viable strategy for improving pazopanib brain delivery. In vitro assays with MDCKII cell monolayers suggested that pazopanib is a high affinity substrate for Bcrp1 and a moderate substrate for P-gp. Co-incubation with specific transport inhibitors restored cell accumulation and completely abolished the directionality of pazopanib flux. Brain and plasma pharmacokinetic studies were conducted in FVB wild type mice in the absence and presence of specific transport inhibitors. Drug levels in plasma and brain were determined using a validated high performance liquid chromatography method using vandetanib as an internal standard. In vivo studies indicated that specific inhibition of either P-gp (by zosuquidar or LY335979) or Bcrp1 (by Ko143) alone did not significantly alter pazopanib brain accumulation. However, dual P-gp/Bcrp1 inhibition by elacridar (GF120918), significantly enhanced pazopanib brain penetration by ~5-fold without altering its plasma concentrations. Thus, even though Bcrp1 showed higher affinity towards pazopanib in vitro, in vivo at the mouse BBB both P-gp and Bcrp1 act in concert to limit brain accumulation of pazopanib. Furthermore, erlotinib and Canertinib as clinically relevant efflux modulators efficiently abrogated directionality in pazopanib efflux in vitro and their co-administration resulted in 2-2.5-fold increase in pazopanib brain accumulation in vivo. Further pre-clinical and clinical investigations are warranted as erlotinib or Canertinib may have a synergistic pharmacological effect in addition to their primary role of pazopanib efflux modulation as a combination regimen for the treatment of recurrent brain tumors.


