EHT 1864Rac family small GTPases inhibitor CAS# 754240-09-0 |
- Tenofovir
Catalog No.:BCC2500
CAS No.:147127-20-6
- Nelfinavir
Catalog No.:BCC4138
CAS No.:159989-64-7
- Nelfinavir Mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC1794
CAS No.:159989-65-8
- Tenofovir hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4261
CAS No.:206184-49-8
- Dapivirine (TMC120)
Catalog No.:BCC3882
CAS No.:244767-67-7
- Zidovudine
Catalog No.:BCC5024
CAS No.:30516-87-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 754240-09-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9938202 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C25H29Cl2F3N2O4S | M.Wt | 581.48 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | H2O : ≥ 100 mg/mL (171.97 mM) DMSO : ≥ 32 mg/mL (55.03 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-(morpholin-4-ylmethyl)-5-[5-[7-(trifluoromethyl)quinolin-4-yl]sulfanylpentoxy]pyran-4-one;dihydrochloride | ||
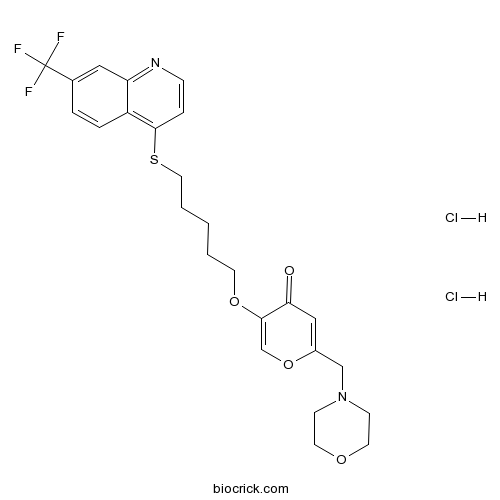
| SMILES | C1COCCN1CC2=CC(=O)C(=CO2)OCCCCCSC3=C4C=CC(=CC4=NC=C3)C(F)(F)F.Cl.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LSECOAJFCKFQJG-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C25H27F3N2O4S.2ClH/c26-25(27,28)18-4-5-20-21(14-18)29-7-6-24(20)35-13-3-1-2-10-33-23-17-34-19(15-22(23)31)16-30-8-11-32-12-9-30;;/h4-7,14-15,17H,1-3,8-13,16H2;2*1H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Inhibitor of Rac family GTPases. Blocks activation by direct binding to Rac1, Rac1b, Rac2 and Rac3 (KD values are 40, 50, 60 and 250 nM respectively). Inhibits Rac, Ras and Tiam-induced growth transformation of NIH-3T3 fibroblasts. Reduces β-amyloid peptide production in vivo. |

EHT 1864 Dilution Calculator

EHT 1864 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7197 mL | 8.5987 mL | 17.1975 mL | 34.395 mL | 42.9937 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3439 mL | 1.7197 mL | 3.4395 mL | 6.879 mL | 8.5987 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.172 mL | 0.8599 mL | 1.7197 mL | 3.4395 mL | 4.2994 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0344 mL | 0.172 mL | 0.3439 mL | 0.6879 mL | 0.8599 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0172 mL | 0.086 mL | 0.172 mL | 0.3439 mL | 0.4299 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
EHT 1864 is a small-molecule inhibitor of Rac family small GTPases with Kd value of 40nM for Rac1 [1].
In NIH 3T3 mouse fibroblasts, EHT 1864 treatment shows an 80% reduction in PDGF-induced lamellipodia formation. EHT 1864 at concentration of 50μM can completely inhibit the complex formation between Rac1 and PAK-RBD and cause the release of nucleotide from Rac1. The reassociation of nucleotide with Rac1 induced by EDTA or the Tiam1 can also be blocked by EHT 1864. EHT 1864 is most potent to Rac1, both in the binding affinity and stimulation of nucleotide release. It binds to Rac1b, Rac2 and Rac3 with Kd values of 50nM, 60nM and 250nM, respectively. Moreover, EHT 1864 can suppress cellular transformation induced by Rac1 with an 80% inhibition of focus-forming activity [1].
References:
[1] Shutes A, Onesto C, Picard V, et al. Specificity and mechanism of action of EHT 1864, a novel small molecule inhibitor of Rac family small GTPases. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 2007, 282(49): 35666-35678.
- Boc-Asp(OBzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2608
CAS No.:7536-58-5
- Boc-Asn-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3071
CAS No.:7536-55-2
- Indacaterol Maleate
Catalog No.:BCC4358
CAS No.:753498-25-8
- Lovastatin
Catalog No.:BCN1060
CAS No.:75330-75-5
- H-Leucinol
Catalog No.:BCC2725
CAS No.:7533-40-6
- H-Pro-NH2
Catalog No.:BCC3018
CAS No.:7531-52-4
- Kukoamine A
Catalog No.:BCN3835
CAS No.:75288-96-9
- HEPES Sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7591
CAS No.:75277-39-3
- Nemonapride
Catalog No.:BCC7165
CAS No.:75272-39-8
- H-Trp-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3114
CAS No.:7524-52-9
- H-Phe-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3009
CAS No.:7524-50-7
- Ophiopogonanone A
Catalog No.:BCN6630
CAS No.:75239-63-3
- Moxonidine
Catalog No.:BCC2142
CAS No.:75438-57-2
- CGP 37157
Catalog No.:BCC6943
CAS No.:75450-34-9
- N-Methylnuciferine
Catalog No.:BCN3971
CAS No.:754919-24-9
- Regorafenib
Catalog No.:BCC3646
CAS No.:755037-03-7
- BI 2536
Catalog No.:BCC2081
CAS No.:755038-02-9
- BI6727 (Volasertib)
Catalog No.:BCC3886
CAS No.:755038-65-4
- Flupirtine maleate
Catalog No.:BCC4456
CAS No.:75507-68-5
- Cedrin
Catalog No.:BCN4748
CAS No.:75513-81-4
- Nilvadipine
Catalog No.:BCC3799
CAS No.:75530-68-6
- Moxonidine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5163
CAS No.:75536-04-8
- Dencichin
Catalog No.:BCN2555
CAS No.:7554-90-7
- Ingenol 3-Angelate
Catalog No.:BCN2961
CAS No.:75567-37-2
EHT 1864, a small molecule inhibitor of Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (Rac1), attenuates glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in pancreatic beta-cells.[Pubmed:25725286]
Cell Signal. 2015 Jun;27(6):1159-67.
Glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) in the pancreatic beta-cells entails a variety of signaling mechanisms including activation of small GTP-binding proteins (G-proteins). Previous studies from our laboratory in human islets, rodent islets and clonal beta-cells have demonstrated that G-proteins (e.g., Arf6, Cdc42 and Rac1) play novel roles in cytoskeletal remodeling, which is a critical step in the trafficking of insulin-laden secretory granules for fusion with plasma membrane and release of insulin. To further understand regulatory roles of Rac1 in GSIS, we utilized, herein, EHT 1864, a small molecule inhibitor, which attenuates Rac1 activation by retaining the G-protein in an inert/inactive state, thereby preventing activation of its downstream effector proteins. We demonstrate that EHT 1864 markedly attenuated GSIS in INS-1 832/13 cells. In addition, EHT 1864 significantly reduced glucose-induced activation and membrane targeting of Rac1 in INS-1 832/13 cells. This Rac1 inhibitor also suppressed glucose-induced activation of ERK1/2 and p53, but not Akt. Lastly, unlike the inhibitors of protein prenylation (simvastatin), EHT 1864 did not exert any significant effects on cell morphology (cell rounding) under the conditions it attenuated Rac1-sensitive signaling steps leading to GSIS. Based on these findings, we conclude that EHT 1864 specifically inhibits glucose-induced Rac1 activation and membrane association and associated downstream signaling events culminating in inhibition of GSIS.
Characterization of EHT 1864, a novel small molecule inhibitor of Rac family small GTPases.[Pubmed:18374160]
Methods Enzymol. 2008;439:111-29.
There is now considerable experimental evidence that aberrant activation of Rho family small GTPases promotes uncontrolled proliferation, invasion, and metastatic properties of human cancer cells. Therefore, there is considerable interest in the development of small molecule inhibitors of Rho GTPase function. However, to date, most efforts have focused on inhibitors that block Rho GTPase function indirectly, either by targeting enzymes involved in post-translational processing or downstream protein kinase effectors. We have reported the identification and characterization of the EHT 1864 small molecule as an inhibitor of Rac family small GTPases, placing Rac1 in an inert and inactive state and then impairing Rac1-mediated functions in vivo. Our work suggests that EHT 1864 selectively inhibits Rac1 downstream signaling and cellular transformation by a novel mechanism involving guanine nucleotide displacement. This chapter provides the details for some of the biochemical and biological methods used to characterize the mode of action of EHT 1864 on Rac1 and its impact on Rac1-dependent cellular functions.
Specificity and mechanism of action of EHT 1864, a novel small molecule inhibitor of Rac family small GTPases.[Pubmed:17932039]
J Biol Chem. 2007 Dec 7;282(49):35666-78.
There is now considerable experimental evidence that aberrant activation of Rho family small GTPases promotes the uncontrolled proliferation, invasion, and metastatic properties of human cancer cells. Therefore, there is considerable interest in the development of small molecule inhibitors of Rho GTPase function. However, to date, most efforts have focused on inhibitors that indirectly block Rho GTPase function, by targeting either enzymes involved in post-translational processing or downstream protein kinase effectors. We recently determined that the EHT 1864 small molecule can inhibit Rac function in vivo. In this study, we evaluated the biological and biochemical specificities and biochemical mechanism of action of EHT 1864. We determined that EHT 1864 specifically inhibited Rac1-dependent platelet-derived growth factor-induced lamellipodia formation. Furthermore, our biochemical analyses with recombinant Rac proteins found that EHT 1864 possesses high affinity binding to Rac1, as well as the related Rac1b, Rac2, and Rac3 isoforms, and this association promoted the loss of bound nucleotide, inhibiting both guanine nucleotide association and Tiam1 Rac guanine nucleotide exchange factor-stimulated exchange factor activity in vitro. EHT 1864 therefore places Rac in an inert and inactive state, preventing its engagement with downstream effectors. Finally, we evaluated the ability of EHT 1864 to block Rac-dependent growth transformation, and we determined that EHT 1864 potently blocked transformation caused by constitutively activated Rac1, as well as Rac-dependent transformation caused by Tiam1 or Ras. Taken together, our results suggest that EHT 1864 selectively inhibits Rac downstream signaling and transformation by a novel mechanism involving guanine nucleotide displacement.
RAC1 inhibition targets amyloid precursor protein processing by gamma-secretase and decreases Abeta production in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed:16150730]
J Biol Chem. 2005 Nov 11;280(45):37516-25.
beta-Amyloid peptides (Abeta) that form the senile plaques of Alzheimer disease consist mainly of 40- and 42-amino acid (Abeta 40 and Abeta 42) peptides generated from the cleavage of the amyloid precursor protein (APP). Generation of Abeta involves beta-secretase and gamma-secretase activities and is regulated by membrane trafficking of the proteins involved in Abeta production. Here we describe a new small molecule, EHT 1864, which blocks the Rac1 signaling pathways. In vitro, EHT 1864 blocks Abeta 40 and Abeta 42 production but does not impact sAPPalpha levels and does not inhibit beta-secretase. Rather, EHT 1864 modulates APP processing at the level of gamma-secretase to prevent Abeta 40 and Abeta 42 generation. This effect does not result from a direct inhibition of the gamma-secretase activity and is specific for APP cleavage, since EHT 1864 does not affect Notch cleavage. In vivo, EHT 1864 significantly reduces Abeta 40 and Abeta 42 levels in guinea pig brains at a threshold that is compatible with delaying plaque accumulation and/or clearing the existing plaque in brain. EHT 1864 is the first derivative of a new chemical series that consists of candidates for inhibiting Abeta formation in the brain of AD patients. Our findings represent the first pharmacological validation of Rac1 signaling as a target for developing novel therapies for Alzheimer disease.


