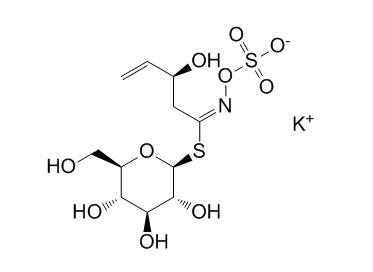
EpiprogoitrinCAS# 21087-74-1 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 21087-74-1 | SDF | File under preparation. |
| PubChem ID | N/A | Appearance | Beige-yellow powder |
| Formula | C11H18KNO10S2 | M.Wt | 427.5 |
| Type of Compound | Miscellaneous | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 2(S)-Hydroxy 3-butenylglucosinolate potassium salt | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in water | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Epiprogoitrin Dilution Calculator

Epiprogoitrin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3392 mL | 11.6959 mL | 23.3918 mL | 46.7836 mL | 58.4795 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4678 mL | 2.3392 mL | 4.6784 mL | 9.3567 mL | 11.6959 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2339 mL | 1.1696 mL | 2.3392 mL | 4.6784 mL | 5.848 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0468 mL | 0.2339 mL | 0.4678 mL | 0.9357 mL | 1.1696 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0234 mL | 0.117 mL | 0.2339 mL | 0.4678 mL | 0.5848 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 4-Hydroxyglucobrassicin
Catalog No.:BCN8967
CAS No.:83327-20-2
- 4-Methoxyglucobrassicin
Catalog No.:BCN8966
CAS No.:83327-21-3
- Glucoarabin
Catalog No.:BCN8965
CAS No.:67920-64-3
- Glucocamelinin
Catalog No.:BCN8964
CAS No.:67884-10-0
- Glucoraphasatin potassium salt
Catalog No.:BCN8963
CAS No.:245550-64-5
- Glucohirsutin
Catalog No.:BCN8962
CAS No.:21973-60-4
- Gluconasturtiin
Catalog No.:BCN8961
CAS No.:18425-76-8
- Sinalbin potassium salt
Catalog No.:BCN8960
CAS No.:16411-05-5
- Glucocheirolin
Catalog No.:BCN8959
CAS No.:15592-36-6
- Glucobrassicin
Catalog No.:BCN8958
CAS No.:143231-38-3
- Glucoraphasatin
Catalog No.:BCN8957
CAS No.:28463-23-2
- Noratropine
Catalog No.:BCN8955
CAS No.:16839-98-8
- Phyllalbine
Catalog No.:BCN8969
CAS No.:4540-25-4
- Glucobarbarin
Catalog No.:BCN8970
CAS No.:21087-78-5
- Glucolimnanthin
Catalog No.:BCN8971
CAS No.:111810-95-8
- Glucocapparin
Catalog No.:BCN8972
CAS No.:15592-33-3
- Sinalbin
Catalog No.:BCN8973
CAS No.:20196-67-2
- Glucobrassicanapin
Catalog No.:BCN8974
CAS No.:245550-58-7
- Glucoiberin
Catalog No.:BCN8975
CAS No.:15592-34-4
- Glucoberteroin
Catalog No.:BCN8976
CAS No.:245550-65-6
- Glucoerucin
Catalog No.:BCN8977
CAS No.:15592-37-7
- Glucotropaeolin
Catalog No.:BCN8978
CAS No.:5115-71-9
- Glucomoringin
Catalog No.:BCN8979
CAS No.:316165-49-8
- Lupinine
Catalog No.:BCN8981
CAS No.:486-70-4
Stereoselective pharmacokinetic study of epiprogoitrin and progoitrin in rats with UHPLC-MS/MS method.[Pubmed:32416341]
J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2020 May 7;187:113356.
An accurate and precise liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-MS/MS) method was developed and validated for the pharmacokinetic study of Epiprogoitrin and progoitrin, a pair of epimers that can be deglycosylated to epigoitrin and goitrin, respectively. These analytes were administered intravenously or intragastrically to male Sprague-Dawley rats, and the influence of 3(R/S)-configuration on the pharmacokinetics of both epimers in rat plasma was elucidated. The analytes and an internal standard (i.e., sinigrin) were resolved by LC-MS/MS on a reverse-phase ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 column equilibrated and eluted with acetonitrile and water (0.1 % formic acid) at a fl ow rate of 0.3mL/min. Quantitation was achieved by applying the multiple reaction monitoring mode, in the negative ion mode, at transitions of m/z 388 --> 97 and m/z 358 --> 97 for the epimers and sinigrin, respectively. The method demonstrated good linearity over the concentration range of 2-5000ng/mL (r > 0.996). The lower limit of quantification for Epiprogoitrin and progoitrin was 2ng/mL. The interday and intraday accuracy and precision were within +/-15 %. The extraction recovery, stability, and matrix effect were demonstrated to be within acceptable limits. The validated method was thus successfully applied for the pharmacokinetic study of both the epimers. After the rats received the same oral dose of the epimers, the pharmacokinetic profiles were similar. The maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) and AUC values of Epiprogoitrin were a bit higher than those of progoitrin, whereas the pharmacokinetic behaviours of the epimers were obviously different upon intravenous administration. The Cmax and AUC values of Epiprogoitrin were approximately three-fold higher than those of progoitrin, and the half-life of progoitrin was much shorter than that of Epiprogoitrin. The oral bioavailability of progoitrin was 20.1 %-34.1 %, which is three times higher than that of Epiprogoitrin.
Antiviral activity of Isatidis Radix derived glucosinolate isomers and their breakdown products against influenza A in vitro/ovo and mechanism of action.[Pubmed:31918015]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Apr 6;251:112550.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Isatidis Radix, the sun-dried roots of Isatis indigotica Fortune ex Lindl., is one of the most usually used traditional Chinese medicines. For centuries, the herb has been employed in clinical practice for treatment of virus infection and inflammation. However, its active ingredients remain unclear. AIM OF THE STUDY: In the present study, the anti-influenza virus activity of Epiprogoitrin, progoitrin, epigoitrin and goitrin, the Isatidis Radix derived glucosinolate isomers and their breakdown products, was firstly evaluated in vitro and in ovo and their mechanism of action was investigated. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Epiprogoitrin, progoitrin, epigoitrin and goitrin were isolated from Isatidis Radix by chiral separation. In vitro and in ovo evaluations were performed on Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells and embryonated eggs respectively, both using protocols including prevention, treatment and virus neutralization. Hemagglutination (HA) and neuraminidase (NA) inhibition assays were performed for further understanding of the antiviral mechanism. RESULTS: Isatidis Radix derived glucosinolate isomers and their breakdown products all exhibited dose-dependent inhibition effect against influenza A virus (H1N1) without toxicity. The antiviral potency of the components was in the order of progoitrin > goitrin > epigoitrin > Epiprogoitrin. The attachment of the constituents to the viral envelope conduced to the mechanism of their antiviral action without disturbing viral adsorption or budding. CONCLUSION: Taken together, these results are promising for further development of Isatidis Radix and may contribute an adjunct to pharmacotherapy for influenza virus infection.
Separation and Quantification of Four Main Chiral Glucosinolates in Radix Isatidis and Its Granules Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Diode Array Detector Coupled with Circular Dichroism Detection.[Pubmed:29844266]
Molecules. 2018 May 29;23(6). pii: molecules23061305.
As chemical drugs, separation and quantification of the specific enantiomer from the chiral compounds in herbal medicines are becoming more important. To clarify the chemical characterization of chiral glucosinolates-the antiviral active ingredients of Radix Isatidis, an optimized efficient method of HPLC-UV-CD was developed to simultaneously separate and quantify the four main chiral glucosinolates: progoitrin, Epiprogoitrin, and R,S-goitrin. The first step was to determine progoitrin, Epiprogoitrin, and R,S-goitrin using HPLC-UV, and then determine the R-goitrin and S-goitrin by coupling with CD detection. Subsequently, through the linear relations between anisotropy factor (g factor) and the percent optical purity of R-goitrin, the contents of R-goitrin and S-goitrin from the R,S-goitrin mixture were calculated separately. Furthermore, the chemical composition features of the four chiral glucosinolates in 37 samples from crude drugs, decoction pieces, and granules of R. Isatidis were conducted. The total content of the four glucosinolates was obviously higher in crude drugs, and the variance character of each glucosinolate contents was different. In summary, the accurate measurement method reported here allows for better control of the internal quality of R. Isatidis and its granules and provides a powerful approach for the analysis of other chiral components in traditional Chinese medicines.


