GlucoberteroinCAS# 245550-65-6 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

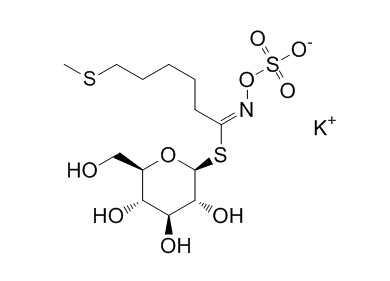
| Cas No. | 245550-65-6 | SDF | File under preparation. |
| PubChem ID | N/A | Appearance | Beige powder |
| Formula | C13H24KNO9S3 | M.Wt | 473.6 |
| Type of Compound | Miscellaneous | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 5-(Methylthio)pentylglucosinolate potassium salt | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in methanol and water | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Glucoberteroin Dilution Calculator

Glucoberteroin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1115 mL | 10.5574 mL | 21.1149 mL | 42.2297 mL | 52.7872 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4223 mL | 2.1115 mL | 4.223 mL | 8.4459 mL | 10.5574 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2111 mL | 1.0557 mL | 2.1115 mL | 4.223 mL | 5.2787 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0422 mL | 0.2111 mL | 0.4223 mL | 0.8446 mL | 1.0557 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0211 mL | 0.1056 mL | 0.2111 mL | 0.4223 mL | 0.5279 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Glucoiberin
Catalog No.:BCN8975
CAS No.:15592-34-4
- Glucobrassicanapin
Catalog No.:BCN8974
CAS No.:245550-58-7
- Sinalbin
Catalog No.:BCN8973
CAS No.:20196-67-2
- Glucocapparin
Catalog No.:BCN8972
CAS No.:15592-33-3
- Glucolimnanthin
Catalog No.:BCN8971
CAS No.:111810-95-8
- Glucobarbarin
Catalog No.:BCN8970
CAS No.:21087-78-5
- Phyllalbine
Catalog No.:BCN8969
CAS No.:4540-25-4
- Epiprogoitrin
Catalog No.:BCN8968
CAS No.:21087-74-1
- 4-Hydroxyglucobrassicin
Catalog No.:BCN8967
CAS No.:83327-20-2
- 4-Methoxyglucobrassicin
Catalog No.:BCN8966
CAS No.:83327-21-3
- Glucoarabin
Catalog No.:BCN8965
CAS No.:67920-64-3
- Glucocamelinin
Catalog No.:BCN8964
CAS No.:67884-10-0
- Glucoerucin
Catalog No.:BCN8977
CAS No.:15592-37-7
- Glucotropaeolin
Catalog No.:BCN8978
CAS No.:5115-71-9
- Glucomoringin
Catalog No.:BCN8979
CAS No.:316165-49-8
- Lupinine
Catalog No.:BCN8981
CAS No.:486-70-4
- Glucoalyssin
Catalog No.:BCN8982
CAS No.:499-37-6
- Neoglucobrassicin potassium salt
Catalog No.:BCN8983
CAS No.:5187-84-8
- Gluconapin
Catalog No.:BCN8984
CAS No.:245550-57-6
- Progoitrin
Catalog No.:BCN8985
CAS No.:21087-77-4
- 18-Hydroxyspartioidine
Catalog No.:BCN8941
CAS No.:
- Heliotridine N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN8944
CAS No.:
- Rinderine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN8947
CAS No.:26131-12-4
- Jacoline N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN8954
CAS No.:
Glucosinolates in two endemic plants of the Aurinia genus and their chemotaxonomic significance.[Pubmed:24354202]
Nat Prod Commun. 2013 Oct;8(10):1463-6.
Glucosinolates (GLs) were characterized in the seed and root of Aurinia leucadea (Guss.) C. Koch and A. sinuata (L.) Griseb., and quantified according to the ISO 9167-1 official method based on the HPLC analysis of desulfo-GLs. Glucoalyssin (GAL, 1), glucobrassicanapin (GBN, 2) and Glucoberteroin (GBE, 3) were the major GLs identified in A. leucadea and A. sinuata. GC/MS analysis of the volatile fractions obtained after enzyme hydrolysis showed that they mostly contain isothiocyanates (ITCs) originating from the parent GLs. On this basis and from previous reports, C-5 alkyl GLs 1, 2, and 3 can be considered as chemotaxonomic markers of the Aurinia genus.
Glucosinolate profiling and antimicrobial screening of Aurinia leucadea (Brassicaceae).[Pubmed:22162169]
Chem Biodivers. 2011 Dec;8(12):2310-21.
Glucosinolates (GLs) were characterized in various aerial parts (stems, leaves, and flowers) of Aurinia leucadea (Guss.) C. Koch and quantified according to the ISO 9167-1 official method based on the HPLC analysis of desulfoglucosinolates. Eight GLs, i.e., glucoraphanin (GRA), glucoalyssin (GAL; 1), gluconapin (GNA; 2), glucocochlearin (GCC), glucobrassicanapin (GBN; 3), glucotropaeolin (GTL), glucoerucin (GER), and Glucoberteroin (GBE) were identified. The total GL contents were 57.1, 37.8, and 81.3 mumol/g dry weight in the stems, leaves, and flowers, respectively. The major GL detected in all parts of the plant was 2, followed by 1 and 3. GC/MS Analysis of the volatile fractions extracted from the aerial parts of fresh plant material either by hydrodistillation or CH(2) Cl(2) extraction showed that these fractions mostly contained isothiocyanates (ITCs). The main ITCs were but-3-enyl- (55.6-71.8%), pent-4-enyl- (7.6-15.3%), and 5-(methylsulfinyl)pentyl ITC (0-9.5%), originating from the corresponding GLs 2, 3, and 1, respectively. The antimicrobial activity of the volatile samples was investigated by determining inhibition zones with the disk-diffusion method and minimal inhibitory concentrations (MIC) with the microdilution method. They were found to inhibit a wide range of bacteria and fungi, with MIC values of 2.0-32.0 mug/ml, indicating their promising antimicrobial potential, especially against the fungi Candida albicans and Rhizopus stolonifer as well as against the clinically important pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Glucosinolate distribution in aerial parts of Degenia velebitica.[Pubmed:22083920]
Chem Biodivers. 2011 Nov;8(11):2090-6.
The glucosinolates present in the leaf, stem, and seed extracts of Degenia velebitica (Degen) Hayek were characterized and quantified according to the ISO 9167-1 method, which is based on the HPLC analysis of desulfoglucosinolates. The stems contained glucoalyssin (3a) as the major compound as well as Glucoberteroin (1a) and glucoaubrietin (4a). The leaves contained three glucosinolates, the major one being 3a, followed by glucobrassicanapin (2a) and 1a. Glucoberteroin (1a) was the major glucosinolate in the seeds, along with the two minor glucosinolates 3a and glucoerucin (5a). The content of 1a in the whole, non-defatted seeds amounted to 4% (w/w). The compound was characterized as its desulfo counterpart by spectroscopic techniques.
Metabolic responses of Thellungiella halophila/salsuginea to biotic and abiotic stresses: metabolite profiles and quantitative analyses.[Pubmed:20122704]
Phytochemistry. 2010 Apr;71(5-6):581-9.
The metabolite profiles of the model crucifer Thellungiella salsuginea (salt cress) ecotype Shandong subjected to various biotic and abiotic stresses were analyzed using HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS. Two different cruciferous microbial pathogens, Albugo candida, a biotrophic oomycete, and Leptosphaeria maculans, a necrotrophic fungus, elicited formation of the phytoalexins wasalexins A and B without causing visual damage on inoculated leaves. Analyses of non-polar and polar metabolites led to elucidation of the chemical structures of five metabolites: 4'-O-(E)-sinapoyl-7-methoxyisovitexin-2''-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside, 4'-O-(E)-sinapoylisovitexin-2''-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside, 4-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-7-hydroxymatairesinol, 5'-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyldihydroneoascorbigen and 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosylthiane. 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosylthiane, an unique metabolite for which we suggest the name glucosalsuginin, is proposed to derive from the glucosinolate Glucoberteroin. In addition, the identification of a broad range of polar metabolites identical to those of other crucifers was carried out. Quantification of several metabolites over a period of eight days showed that concentrations of the polar phytoanticipin 4-methoxyglucobrassicin increased substantially in leaves irradiated with UV light (lambda(max) 254 nm) relative to control leaves, but not in leaves subjected to other stresses.
Updated glucosinolate profile of Dithyrea wislizenii.[Pubmed:19334740]
J Nat Prod. 2009 May 22;72(5):889-93.
Fruit extracts of Dithyrea wislizenii were analyzed for desulfoglucosinolates and intact glucosinolates using HPLC-APCI-MS and HPLC-ESI-MS, respectively. 2-Propenylglucosinolate (sinigrin) was shown to be present in the extracts. 6-Methylsulfanylhexyl- (glucolesquerellin 9), 6-methylsulfinylhexyl- (glucohesperin 10), 7-methylsulfanylheptyl- (11), and 5-methylsulfanylpentylglucosinolate (Glucoberteroin 12) were isolated from the extracts and characterized by NMR and MS data. 7-Methoxyglucobrassicin was not detected in D. wislizenii extracts.


