Epothilone DNatural polyketide compound CAS# 189453-10-9 |
- Docetaxel
Catalog No.:BCN5342
CAS No.:114977-28-5
- ABT-751 (E7010)
Catalog No.:BCC1085
CAS No.:141430-65-1
- Epothilone A
Catalog No.:BCC1091
CAS No.:152044-53-6
- Vincristine
Catalog No.:BCN5411
CAS No.:57-22-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 189453-10-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 447865 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C27H41NO5S | M.Wt | 491.68 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 12,13-Desoxyepothilone B; Desoxyepothilone B; KOS 862 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (203.38 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
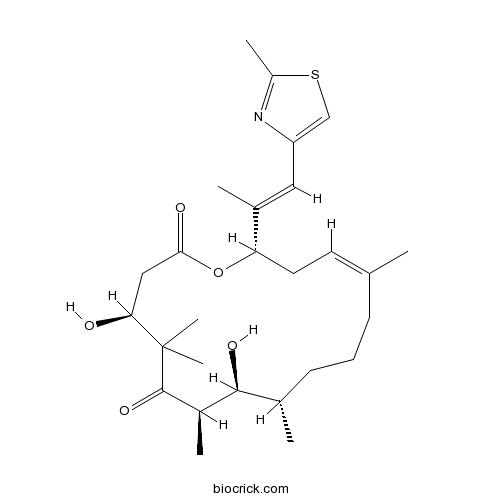
| Chemical Name | (4S,7R,8S,9S,13Z,16S)-4,8-dihydroxy-5,5,7,9,13-pentamethyl-16-[(E)-1-(2-methyl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)prop-1-en-2-yl]-1-oxacyclohexadec-13-ene-2,6-dione | ||
| SMILES | CC1CCCC(=CCC(OC(=O)CC(C(C(=O)C(C1O)C)(C)C)O)C(=CC2=CSC(=N2)C)C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | XOZIUKBZLSUILX-GIQCAXHBSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C27H41NO5S/c1-16-9-8-10-17(2)25(31)19(4)26(32)27(6,7)23(29)14-24(30)33-22(12-11-16)18(3)13-21-15-34-20(5)28-21/h11,13,15,17,19,22-23,25,29,31H,8-10,12,14H2,1-7H3/b16-11-,18-13+/t17-,19+,22-,23-,25-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Epothilone B is a Taxol-like microtubule-stabilizing agent with an EC0.01 value of 1.8 μM. | |||||
| Targets | Tubulin | |||||
| IC50 | 1.8 μM(EC0.01) | |||||

Epothilone D Dilution Calculator

Epothilone D Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0338 mL | 10.1692 mL | 20.3384 mL | 40.6769 mL | 50.8461 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4068 mL | 2.0338 mL | 4.0677 mL | 8.1354 mL | 10.1692 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2034 mL | 1.0169 mL | 2.0338 mL | 4.0677 mL | 5.0846 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0407 mL | 0.2034 mL | 0.4068 mL | 0.8135 mL | 1.0169 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0203 mL | 0.1017 mL | 0.2034 mL | 0.4068 mL | 0.5085 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
IC50: 2.9 nM for MCF-7 cell line; 2.7 nM for KB-31 cell line; 9.5 nM for CCRF-CEM cell line
Drugs targeting tubulin are active in human malignant disease and are an essential component of medical treatment of these diseases. As a result, pharmaceutical research on compounds that interfere with tubulin function has concentrated on agents which might have enhanced efficacy or reduced toxicity. Epothilone D is a more potent microtubule stabilizer.
In vitro: Epothilone D is a more potent microtubule stabilizer in vitro than epothilone A or B. In vitro, Epothilone D showed potent cytotoxicity in a panel of human tumor cell lines, with similar potency to paclitaxel. It also showed definite advantage over paclitaxel in drug-resistant cell lines, and retained its cytotoxicity against a multidrug resistant cell line over-expressing P-glycoprotein [1].
In vivo: In vivo, antitumor efficacy of Epothilone D has been observed in both paclitaxel sensitive and resistant xenografts, as well as certain multidrug resistant xenografts including a doxorubinresistant CCRF-CEM leukemic cell xenograft [1].
Clinical trial: Epothilone D was well tolerated with manageable toxicity, favorable PK profile, and clinical activity. The maximum tolerated dose was determined to be 100 mg/m2 weekly 3-on/1-off. MTBF can be demonstrated in PBMCs of patients exposed to Epothilone D [1].
Reference:
[1] Konner J, Grisham RN, Park J, O'Connor OA, Cropp G, Johnson R, Hannah AL, Hensley ML, Sabbatini P, Mironov S, Danishefsky S, Hyman D, Spriggs DR, Dupont J, Aghajanian C. Phase I clinical, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic study of KOS-862 (Epothilone D) in patients with advanced solid tumors and lymphoma. Invest New Drugs. 2012 Dec;30(6):2294-302. doi: 10.1007/s10637-011-9765-7.
- Boc-Ser(tBu)-OH.DCHA
Catalog No.:BCC3445
CAS No.:18942-50-2
- Boc-D-Phe-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3433
CAS No.:18942-49-9
- Boc-Cys(pMeOBzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3378
CAS No.:18942-46-6
- Chebulinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3263
CAS No.:18942-26-2
- Triptinin B
Catalog No.:BCN6785
CAS No.:189389-05-7
- Endomorphin-1
Catalog No.:BCC1008
CAS No.:189388-22-5
- Corchoionol C
Catalog No.:BCN1172
CAS No.:189351-15-3
- Fmoc-Thr(tBu)-ol
Catalog No.:BCC2576
CAS No.:189337-28-8
- 3'-Methoxyrocaglamide
Catalog No.:BCN1171
CAS No.:189322-69-8
- 3'-Hydroxyrocaglamide
Catalog No.:BCN1170
CAS No.:189322-67-6
- Xanthohumol B
Catalog No.:BCN8018
CAS No.:189308-10-9
- Danshenol B
Catalog No.:BCN2616
CAS No.:189308-09-6
- Ginsenoside F5
Catalog No.:BCN6419
CAS No.:189513-26-6
- Pinostrobin chalcone
Catalog No.:BCN1173
CAS No.:18956-15-5
- 6'-Hydroxy-7'-ethoxybergamottin
Catalog No.:BCC8306
CAS No.:
- Dihydrooroxylin A
Catalog No.:BCN3500
CAS No.:18956-18-8
- trans-4-phenylbut-3-en-2-one
Catalog No.:BCN3805
CAS No.:1896-62-4
- 6,4'-Dihydroxy-7-methoxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN7797
CAS No.:189689-32-5
- Akuammiline
Catalog No.:BCN4772
CAS No.:1897-26-3
- Ro 10-5824 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7330
CAS No.:189744-94-3
- 8-Amino-2-methylquinoline
Catalog No.:BCC8782
CAS No.:18978-78-4
- 3-O-Feruloylquinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3353
CAS No.:1899-29-2
- Palmitoylisopropylamide
Catalog No.:BCC7187
CAS No.:189939-61-5
- Mesopram
Catalog No.:BCC7549
CAS No.:189940-24-7
Stabilized Polymer Micelles for the Development of IT-147, an Epothilone D Drug-Loaded Formulation.[Pubmed:28044108]
J Drug Deliv. 2016;2016:8046739.
Epothilones have demonstrated promising potential for oncology applications but suffer from a narrow therapeutic window. Epothilone D stabilizes microtubules leading to apoptosis, is active against multidrug-resistant cells, and is efficacious in animal tumor models despite lack of stability in rodent plasma. Clinical development was terminated in phase II due to dose limiting toxicities near the efficacious dose. Taken together, this made Epothilone D attractive for encapsulation in a stabilized polymer micelle for improved safety and efficacy. We have designed a library of triblock copolymers to develop IT-147, a lead formulation of Epothilone D that extends plasma circulation for accumulation in the tumor environment, and potentially decrease systemic exposure to reduce dose limiting toxicities. The drug loading efficiency for IT-147 exceeds 90%, is 75 nm in diameter, and demonstrates pH-dependent release of Epothilone D without chemical conjugation or enzymatic activation. Administration of IT-147 at 20 mg/kg increases exposure of Epothilone D to the plasma compartment over 6-fold compared to free drug. At the same dose, 20 mg/kg Epothilone D from IT-147 is considered the no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL) but is the maximum tolerated dose for free drug. Consequently, IT-147 is positioned to be a safer, more effective means to deliver Epothilone D.
The Total Synthesis of Epothilone D as a Yardstick for Probing New Methodologies.[Pubmed:27792853]
Chemistry. 2017 Jan 12;23(3):541-545.
Here, a concise and highly convergent synthesis of Epothilone D was investigated, relying on fragments of equal complexity that could be prepared in gram scale quantities. The strategy to construct the fragments includes the use of a previously reported enantiospecific zinc-catalyzed cross-coupling of an alpha-hydroxy ester triflate with a Grignard reagent, the application of a hydroboration/boron-magnesium exchange sequence for the rapid construction of the Z-substituted trisubstituted double bond present in the natural product, and a Noyori-type hydrogenation to install the beta-hydroxy ester moiety of the southern part. The key to success is the diastereoselective head-to-tail macrolactonization by an intramolecular addition of the corresponding omega-alkynyl-substituted carboxylic acids to construct a new stereocenter in the macrocyclic core structure in one single step.
Abeta-mediated spine changes in the hippocampus are microtubule-dependent and can be reversed by a subnanomolar concentration of the microtubule-stabilizing agent epothilone D.[Pubmed:26772969]
Neuropharmacology. 2016 Jun;105:84-95.
Dendritic spines represent the major postsynaptic input of excitatory synapses. Loss of spines and changes in their morphology correlate with cognitive impairment in Alzheimer's disease (AD) and are thought to occur early during pathology. Therapeutic intervention at a preclinical stage of AD to modify spine changes might thus be warranted. To follow the development and to potentially interfere with spine changes over time, we established a long term ex vivo model from organotypic cultures of the hippocampus from APP transgenic and control mice. The cultures exhibit spine loss in principal hippocampal neurons, which closely resembles the changes occurring in vivo, and spine morphology progressively changes from mushroom-shaped to stubby. We demonstrate that spine changes are completely reversed within few days after blocking amyloid-beta (Abeta) production with the gamma-secretase inhibitor DAPT. We show that the microtubule disrupting drug nocodazole leads to spine loss similar to Abeta expressing cultures and suppresses DAPT-mediated spine recovery in slices from APP transgenic mice. Finally, we report that Epothilone D (EpoD) at a subnanomolar concentration, which slightly stabilizes microtubules in model neurons, completely reverses Abeta-induced spine loss and increases thin spine density. Taken together the data indicate that Abeta causes spine changes by microtubule destabilization and that spine recovery requires microtubule polymerization. Moreover, our results suggest that a low, subtoxic concentration of EpoD is sufficient to reduce spine loss during the preclinical stage of AD.
Epothilone D prevents binge methamphetamine-mediated loss of striatal dopaminergic markers.[Pubmed:26465779]
J Neurochem. 2016 Feb;136(3):510-25.
Exposure to binge methamphetamine (METH) can result in a permanent or transient loss of dopaminergic (DAergic) markers such as dopamine (DA), dopamine transporter, and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) in the striatum. We hypothesized that the METH-induced loss of striatal DAergic markers was, in part, due to a destabilization of microtubules (MTs) in the nigrostriatal DA pathway that ultimately impedes anterograde axonal transport of these markers. To test this hypothesis, adult male Sprague-Dawley rats were treated with binge METH or saline in the presence or absence of Epothilone D (EpoD), a MT-stabilizing compound, and assessed 3 days after the treatments for the levels of several DAergic markers as well as for the levels of tubulins and their post-translational modifications (PMTs). Binge METH induced a loss of stable long-lived MTs within the striatum but not within the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc). Treatment with a low dose of EpoD increased the levels of markers of stable MTs and prevented METH-mediated deficits in several DAergic markers in the striatum. In contrast, administration of a high dose of EpoD appeared to destabilize MTs and potentiated the METH-induced deficits in several DAergic markers. The low-dose EpoD also prevented the METH-induced increase in striatal DA turnover and increased behavioral stereotypy during METH treatment. Together, these results demonstrate that MT dynamics plays a role in the development of METH-induced losses of several DAergic markers in the striatum and may mediate METH-induced degeneration of terminals in the nigrostriatal DA pathway. Our study also demonstrates that MT-stabilizing drugs such as EpoD have a potential to serve as useful therapeutic agents to restore function of DAergic nerve terminals following METH exposure when administered at low doses. Administration of binge methamphetamine (METH) negatively impacts neurotransmission in the nigrostriatal dopamine (DA) system. The effects of METH include decreasing the levels of DAergic markers in the striatum. We have determined that high-dose METH destabilizes microtubules in this pathway, which is manifested by decreased levels of acetylated (Acetyl) and detyrosinated (Detyr) alpha-tubulin (I). A microtubule stabilizing agent Epothilone D protects striatal microtubules form the METH-induced loss of DAergic markers (II). These findings provide a new strategy for protection form METH - restoration of proper axonal transport.


