Dihydrooroxylin ACAS# 18956-18-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 18956-18-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 177032 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C16H14O5 | M.Wt | 286.3 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
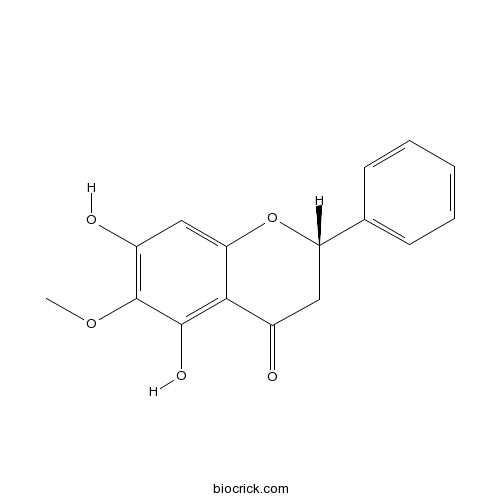
| Chemical Name | (2S)-5,7-dihydroxy-6-methoxy-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydrochromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C=C2C(=C1O)C(=O)CC(O2)C3=CC=CC=C3)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QUAPPCXFYKSDSV-LBPRGKRZSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C16H14O5/c1-20-16-11(18)8-13-14(15(16)19)10(17)7-12(21-13)9-5-3-2-4-6-9/h2-6,8,12,18-19H,7H2,1H3/t12-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Dihydrooroxylin A has significant antifeeding activity. |

Dihydrooroxylin A Dilution Calculator

Dihydrooroxylin A Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4928 mL | 17.4642 mL | 34.9284 mL | 69.8568 mL | 87.321 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6986 mL | 3.4928 mL | 6.9857 mL | 13.9714 mL | 17.4642 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3493 mL | 1.7464 mL | 3.4928 mL | 6.9857 mL | 8.7321 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0699 mL | 0.3493 mL | 0.6986 mL | 1.3971 mL | 1.7464 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0349 mL | 0.1746 mL | 0.3493 mL | 0.6986 mL | 0.8732 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 6'-Hydroxy-7'-ethoxybergamottin
Catalog No.:BCC8306
CAS No.:
- Pinostrobin chalcone
Catalog No.:BCN1173
CAS No.:18956-15-5
- Ginsenoside F5
Catalog No.:BCN6419
CAS No.:189513-26-6
- Epothilone D
Catalog No.:BCC1554
CAS No.:189453-10-9
- Boc-Ser(tBu)-OH.DCHA
Catalog No.:BCC3445
CAS No.:18942-50-2
- Boc-D-Phe-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3433
CAS No.:18942-49-9
- Boc-Cys(pMeOBzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3378
CAS No.:18942-46-6
- Chebulinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3263
CAS No.:18942-26-2
- Triptinin B
Catalog No.:BCN6785
CAS No.:189389-05-7
- Endomorphin-1
Catalog No.:BCC1008
CAS No.:189388-22-5
- Corchoionol C
Catalog No.:BCN1172
CAS No.:189351-15-3
- Fmoc-Thr(tBu)-ol
Catalog No.:BCC2576
CAS No.:189337-28-8
- trans-4-phenylbut-3-en-2-one
Catalog No.:BCN3805
CAS No.:1896-62-4
- 6,4'-Dihydroxy-7-methoxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN7797
CAS No.:189689-32-5
- Akuammiline
Catalog No.:BCN4772
CAS No.:1897-26-3
- Ro 10-5824 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7330
CAS No.:189744-94-3
- 8-Amino-2-methylquinoline
Catalog No.:BCC8782
CAS No.:18978-78-4
- 3-O-Feruloylquinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3353
CAS No.:1899-29-2
- Palmitoylisopropylamide
Catalog No.:BCC7187
CAS No.:189939-61-5
- Mesopram
Catalog No.:BCC7549
CAS No.:189940-24-7
- Firocoxib
Catalog No.:BCC5498
CAS No.:189954-96-9
- N-Acetyl-O-phosphono-Tyr-Glu Dipentylamide
Catalog No.:BCC5855
CAS No.:190078-50-3
- 7-Hydroxy-2,2-dimethylchromene
Catalog No.:BCN7784
CAS No.:19012-97-6
- Eupatoriochromene
Catalog No.:BCN1174
CAS No.:19013-03-7
Insect antifeedant compounds from Nothofagus dombeyi and N. pumilio.[Pubmed:15279992]
Phytochemistry. 2004 Jul;65(14):2173-6.
A bioassay-guided purification of the extracts of Nothofagus dombeyi and N. pumilio leaves yielded several triterpenes and flavonoids including 2-O-acetylmaslinic acid, 3-O-acetyl 20,24,25-trihydroxydammarane, and 3,20,24,25-tetrahydroxydammarane as new natural products. All the isolated compounds were assessed for antifeeding activity against the 5th instar larvae of Ctenopsteustis obliquana. 12-Hydroxyoleanolic lactone and pectolinarigenin from N. dombeyi and Dihydrooroxylin A from N. pumilio, showed significant antifeeding activity.
Characteristics of delayed excretion of flavonoids in human urine after administration of Shosaiko-to, a herbal medicine.[Pubmed:9881633]
Biol Pharm Bull. 1998 Dec;21(12):1251-7.
There has been little explanation of herbal medicines by modern medical sciences, including pharmacokinetics, whereas physicians follow empirical indications written in classical literature. Recent reports of herb-induced adverse reactions compelled us to proceed the investigation of a herbal medicine Shosaiko-to (TJ-9) from a pharmacokinetic point of view. To five healthy volunteers, a single 5 g dose of TJ-9, consisting of 7 herbs, was administered. We conducted HPLC analysis of the timed-urine specimens to disclose the type and amount of compounds excreted. Excretion rate-time curves were analyzed individually. Four flavonoids, liquiritigenin, baicalein, wogonin and oroxylin A, were found both in the urine and TJ-9. The glycosides in TJ-9 were absorbed after microflora hydrolysis. Davidigenin, which was not found in TJ-9, was an intestinal metabolite of liquiritigenin. Also, two flavanones, S-dihydrowogonin and S-Dihydrooroxylin A, were identified as the metabolites of wogonin and oroxylin A, respectively. Excretion rate-time curves of the flavonoids were divided into three types of structure-dependent absorption, i.e. (1) the fast absorption of herbal-origin aglycons, (2) the moderately-delayed absorption of aglycons derived from herbal glycosides, and (3) markedly-delayed absorption after the molecular transformation of herbal compounds. Individual excretion profiles seemed to depend on microflora activities. Two types of flavanones, S-dihydrowogonin and S-Dihydrooroxylin A, were found in a half of the volunteers, suggesting there might be two kinds of volunteers, namely, rapid and poor metabolizers of flavonoids.


