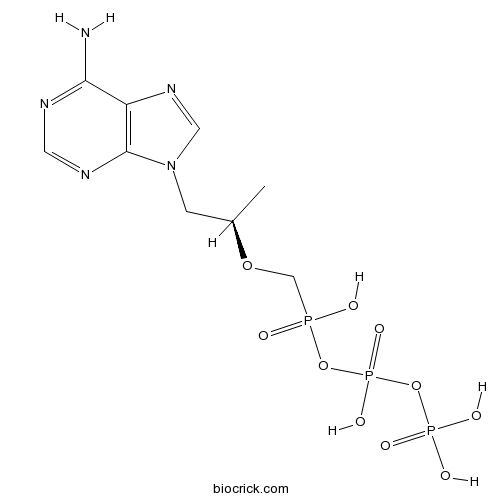
tenofovir diphosphateOral prodrug of Tenofovir CAS# 166403-66-3 |
- Adefovir Dipivoxil
Catalog No.:BCC5025
CAS No.:142340-99-6
- Merimepodib
Catalog No.:BCC4128
CAS No.:198821-22-6
- Telbivudine
Catalog No.:BCC3862
CAS No.:3424-98-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 166403-66-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5481180 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C9H16N5O10P3 | M.Wt | 447.17 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | [(2R)-1-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)propan-2-yl]oxymethyl-[hydroxy(phosphonooxy)phosphoryl]oxyphosphinic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(CN1C=NC2=C1N=CN=C2N)OCP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)OP(=O)(O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | IACQCQDWSIQSRP-ZCFIWIBFSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C9H16N5O10P3/c1-6(2-14-4-13-7-8(10)11-3-12-9(7)14)22-5-25(15,16)23-27(20,21)24-26(17,18)19/h3-4,6H,2,5H2,1H3,(H,15,16)(H,20,21)(H2,10,11,12)(H2,17,18,19)/t6-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

tenofovir diphosphate Dilution Calculator

tenofovir diphosphate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2363 mL | 11.1814 mL | 22.3629 mL | 44.7257 mL | 55.9071 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4473 mL | 2.2363 mL | 4.4726 mL | 8.9451 mL | 11.1814 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2236 mL | 1.1181 mL | 2.2363 mL | 4.4726 mL | 5.5907 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0447 mL | 0.2236 mL | 0.4473 mL | 0.8945 mL | 1.1181 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0224 mL | 0.1118 mL | 0.2236 mL | 0.4473 mL | 0.5591 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Tenofovir Alafenamide Fumarate
Catalog No.:BCC8067
CAS No.:379270-38-9
- Tenofovir alafenamide
Catalog No.:BCC8066
CAS No.:379270-37-8
- Saracatinib (AZD0530)
Catalog No.:BCC1166
CAS No.:379231-04-6
- Cimifugin
Catalog No.:BCN5433
CAS No.:37921-38-3
- Jolkinolide B
Catalog No.:BCN2391
CAS No.:37905-08-1
- Jolkinolide A
Catalog No.:BCN3771
CAS No.:37905-07-0
- Scarlet 808
Catalog No.:BCC9139
CAS No.:3789-75-1
- Ro 08-2750
Catalog No.:BCC7307
CAS No.:37854-59-4
- Nepodin
Catalog No.:BCN6894
CAS No.:3785-24-8
- Germacrene D
Catalog No.:BCN3851
CAS No.:37839-63-7
- Phaseollidin
Catalog No.:BCN5432
CAS No.:37831-70-2
- ACDPP hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7302
CAS No.:37804-11-8
- Geranylacetone
Catalog No.:BCN7567
CAS No.:3796-70-1
- LM 22A4
Catalog No.:BCC6239
CAS No.:37988-18-4
- 2-Amino-4'-fluorobenzophenone
Catalog No.:BCC8530
CAS No.:3800-06-4
- Sulfamonomethoxine sodium
Catalog No.:BCC9157
CAS No.:38006-08-5
- Tenovin-1
Catalog No.:BCC2239
CAS No.:380315-80-0
- (+)-columbianetin
Catalog No.:BCN2331
CAS No.:3804-70-4
- NBMPR
Catalog No.:BCC7516
CAS No.:38048-32-7
- alpha-Epoxydihydroartemisinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5434
CAS No.:380487-65-0
- 187-1, N-WASP inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC5866
CAS No.:380488-27-7
- DQP 1105
Catalog No.:BCC6205
CAS No.:380560-89-4
- CMPDA
Catalog No.:BCC6151
CAS No.:380607-77-2
- [(pF)Phe4]Nociceptin(1-13)NH2
Catalog No.:BCC5778
CAS No.:380620-88-2
Decreased tenofovir diphosphate concentrations in a transgender female cohort: Implications for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP).[Pubmed:30963179]
Clin Infect Dis. 2019 Apr 9. pii: 5432320.
Feminizing hormone therapy (FHT) may interact with HIV PrEP. We found transgender women taking FHT exhibited a 7-fold lower rectal tissue ratio of PrEP's active metabolites vs competing deoxynucleotides compared to cisgender women and men (p=0.03) that inversely correlated with estradiol (rho=-0.79; p<0.05). Thus FHT may negatively impact PrEP efficacy.
Predictive value of tenofovir diphosphate in dried blood spots for future viremia in persons living with HIV.[Pubmed:30942881]
J Infect Dis. 2019 Apr 3. pii: 5426853.
BACKGROUND: tenofovir diphosphate (TFV-DP) in dried blood spots (DBS) is associated with viral suppression in persons living with HIV (PLWH) taking tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF). However, its value as a predictor of future viremia remains unknown. METHODS: Blood for plasma HIV viral load (VL) and TFV-DP in DBS were prospectively collected (up to 3 visits within 48 weeks) in PLWH on TDF. TFV-DP cut points were selected using logistic prediction models maximizing the area under the receiver operation characteristic curve, and the estimated adjusted odds ratio (aOR) of future viremia (>/=20 copies/mL) were compared to the highest TFV-DP category. RESULTS: Among 451 participants included in the analysis, the aOR of future viremia for participants with TFV-DP <800 and 800 to <1650 fmol/punch were 4.7 (95% CI 2.6, 8.7; p<0.0001) and 2.1 (95% CI 1.3, 3.3; p=0.002) vs. >/=1650 fmol/punch, respectively. These remained significant for participants who were virologically-suppressed at the time of the study visit (4.2, 95% CI 1.5, 12.0; p=0.007 and 2.2, 95% CI 1.2, 4,0; p=0.01). CONCLUSIONS: TFV-DP in DBS predicts future viremia in PLWH on TDF, even in those who are virologically-suppressed. This highlights the utility of this biomarker to inform about adherence beyond HIV VL.
Predictors of Long Term HIV Pre Exposure Prophylaxis Adherence after Study Participation in Men who have Sex with Men.[Pubmed:30865175]
J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2019 Feb 21.
BACKGROUND: Efficacy of HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) among men who have sex with men (MSM) is well documented in randomized trials. Following trial completion, participants are challenged with acquiring PrEP on their own, and remaining adherent. METHODS: This was a follow-up study of the TAPIR randomized controlled multi-center PrEP trial. Participants were contacted after their last TAPIR visit (i.e., after study provided PrEP was discontinued) to attend observational post-trial visits 24 and 48 weeks later. Adherence during TAPIR and post-trial visits was estimated by dried blood spot (DBS) intracellular tenofovir diphosphate (TFV-DP) levels (adequate adherence defined as TFV-DP levels >719 fmol/punch). Binary logistic regression analysis assessed predictors of completing post-trial visits and PrEP adherence among participants completing >/= 1 visit. RESULTS: Of 395 TAPIR participants who were on PrEP as part of the TAPIR trial for a median of 597 days (range 3-757 days), 122 (31%) completed >/= 1 post-trial visit (57% of UCSD participants completed post-trial visits, while this was 13% or lower for other study sites). Among participants who completed >/= 1 post-trial visit, 57% had adequate adherence post-trial. Significant predictors of adequate adherence post-trial were less problematic substance use, higher risk behavior, and adequate adherence in year 1 of TAPIR. CONCLUSION: More than half of PrEP users followed after trial completion had successfully acquired PrEP and showed adequate adherence. Additional adherence monitoring and interventions measures may be needed for those with low PrEP adherence and problematic substance use during the first year of trial.
Rifampicin effect on intracellular and plasma pharmacokinetics of tenofovir alafenamide.[Pubmed:30815689]
J Antimicrob Chemother. 2019 Feb 27. pii: 5366220.
OBJECTIVES: Tenofovir alafenamide produces lower plasma tenofovir and higher intracellular tenofovir diphosphate (DP) concentrations than tenofovir disoproxil fumarate but it is likely a victim of interactions with rifampicin. We aimed to investigate the pharmacokinetics of tenofovir alafenamide/emtricitabine with rifampicin. PATIENTS AND METHODS: Healthy volunteers received tenofovir alafenamide/emtricitabine at 25/200 mg once daily, followed by tenofovir alafenamide/emtricitabine + rifampicin daily followed by tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. Plasma tenofovir alafenamide, tenofovir, emtricitabine and intracellular tenofovir-DP and emtricitabine triphosphate pharmacokinetics and genetic polymorphisms were assessed. RESULTS: Tenofovir alafenamide exposure decreased when tenofovir alafenamide/emtricitabine+rifampicin was used compared with tenofovir alafenamide/emtricitabine [geometric mean ratio (GMR) (90% CI): 0.45 (0.33-0.60)]. Plasma tenofovir and intracellular tenofovir-DP concentrations decreased with rifampicin [GMR (90% CI): 0.46 (0.40-0.52) and 0.64 (0.54-0.75), respectively]. GMR (90% CI) of intracellular tenofovir-DP AUC0-24 for tenofovir alafenamide/emtricitabine + rifampicin versus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate was 4.21 (2.98-5.95). Rifampicin did not affect emtricitabine pharmacokinetics. CYP3A4*22 rs35599367 was associated with higher plasma tenofovir alafenamide AUC0-24 at day 56. CONCLUSIONS: Following tenofovir alafenamide/emtricitabine administration with rifampicin, intracellular tenofovir-DP concentrations were still 4.21-fold higher than those achieved by tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, supporting further study during HIV/TB co-infection.
Emtricitabine triphosphate in dried blood spots is a predictor of viral suppression in HIV infection and reflects short-term adherence to antiretroviral therapy.[Pubmed:30668713]
J Antimicrob Chemother. 2019 Jan 18. pii: 5296288.
Background: Emtricitabine triphosphate (FTC-TP), the phosphorylated anabolite of emtricitabine, can be quantified in dried blood spots (DBS). We evaluated FTC-TP in DBS as a predictor of viral suppression and evaluated self-reported adherence as a predictor of FTC-TP. Methods: Persons living with HIV (PLWH) on an FTC-containing regimen were prospectively recruited. A DBS and HIV viral load were obtained during routine clinical visits. Self-reported adherence for 3 days, 30 days and 3 months was captured. Generalized estimating equations were used to estimate the adjusted odds ratio (aOR) of viral suppression for quantifiable FTC-TP versus below the limit of quantification (BLQ). The utility of self-reported adherence to predict quantifiable FTC-TP was assessed by calculating the area under receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Results: One thousand one hundred and fifty-four person-visits from 514 participants who had DBS assayed for FTC-TP were included in the analysis. After adjusting for age, gender, race, BMI, ART class, ART duration, estimated glomerular filtration rate and CD4+ T cell count, the aOR (95% CI) for viral suppression for quantifiable FTC-TP versus BLQ was 7.2 (4.3-12.0; P < 0.0001). After further adjusting for tenofovir diphosphate, the aOR was 2.1 (1.2-4.0; P < 0.015). The area under the ROC curve for 3 day self-reported adherence was 0.82 (95% CI 0.75-0.88) compared with 0.70 (95% CI 0.62-0.77, P = 0.004) and 0.79 (95% CI 0.71-0.86, P = 0.32) for 3 month and 30 day self-reported adherence, respectively. Conclusions: In PLWH, FTC-TP from DBS is a strong predictor of viral suppression, even after adjusting for tenofovir diphosphate, and was best predicted by 3 day self-reported adherence.
Brief Report: Role of Sociobehavioral Factors in Subprotective TFV-DP Levels Among YMSM Enrolled in 2 PrEP Trials.[Pubmed:30640203]
J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2019 Feb 1;80(2):160-165.
BACKGROUND: Young men who have sex with men (YMSM) experience disparities in HIV acquisition more than any other group. Daily oral pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) with tenofovir/emtricitabine has been shown to effectively prevent HIV transmission in YMSM; however, recent studies suggest that young Black men who have sex with men experience subprotective levels of tenofovir diphosphate more frequently than other groups. SETTING: Combined data from Adolescent Medicine Trials Network for HIV/AIDS Interventions (ATN) 110/113, 2 open-label PrEP studies that provided PrEP and evidence-based behavioral interventions to YMSM aged 15-22 years. METHODS: Bivariate and logistic regression analyses were used to examine sociodemographic and behavioral factors associated with protective tenofovir diphosphate levels (defined as >/=700 fmol/punch) in ATN 110/113 data. RESULTS: In bivariate analysis, self-identified Black participants, residential displacement due to sexual orientation, low perceived risk, and stigma with the medication were associated with subprotective levels. Hispanic ethnicity was associated with protective levels. In the final models, Black males were less likely to have subprotective levels than non-Black males at 4, 8, and 12 weeks. Self-reported displacement due to sexual orientation was associated with subprotective levels, whereas older age was as associated with protective levels. CONCLUSIONS: These findings highlight how future behavioral research and biomedical prevention efforts in YMSM will need to address PrEP disparities that may occur in young Black men who have sex with men, perception of risk, and lack of key supportive housing during this period that may be critical factors that contribute to HIV acquisition.
Self-initiated continuation of and adherence to HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) after PrEP demonstration project roll-off in men who have sex with men: associations with risky decision making, impulsivity/disinhibition, and sensation seeking.[Pubmed:30617849]
J Neurovirol. 2019 Jan 7. pii: 10.1007/s13365-018-0716-3.
The objective of this study was to examine differences in the levels of risky decision making and other frontal system behavior constructs in relation to self-initiated continuance of HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) and PrEP adherence outcomes among men who have sex with men (MSM) following completion of a clinical PrEP trial. At the last PrEP trial visit, study provided PrEP was discontinued and participants were navigated to the community for PrEP continuation. In this cross-sectional analysis, 84/187 (45%) MSM who completed a prospective observational post-PrEP trial follow-up visit at the University of California San Diego were included. PrEP adherence was measured using dried blood spot tenofovir diphosphate (TFV-DP) levels. Risky decision making was assessed using the Iowa Gambling Task (IGT) and the Balloon Analogue Risk Task (BART), while impulsivity/disinhibition, sensation seeking, and substance use were assessed via standardized self-report questionnaires. A total of 58/84 (69%) of MSM who completed the 12-month post-study visit continued PrEP. Of those, n = 46 (79%) reached TFV-DP levels associated with adequate adherence. Individuals who elected to continue PrEP 12 months post-trial had riskier decision making on BART, but less impulsivity/disinhibition compared to individuals who did not continue PrEP. Neither risky decision making nor impulsivity/disinhibition/sensation seeking nor substance use correlated with PrEP adherence. Our findings suggest that those with risky decision making may have greater insight into their HIV risks, and therefore be more likely to continue to use PrEP. However, elevated impulsivity/disinhibition, indicative of greater neurobehavioral alterations, was negatively associated with PrEP continuance and is a potential target for future interventions to help people link to PrEP.
Acquisition of tenofovir-susceptible, emtricitabine-resistant HIV despite high adherence to daily pre-exposure prophylaxis: a case report.[Pubmed:30503324]
Lancet HIV. 2018 Nov 29. pii: S2352-3018(18)30288-1.
BACKGROUND: Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) with emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is highly protective against HIV infection. We report a case of tenofovir-susceptible, emtricitabine-resistant HIV acquisition despite high adherence to daily PrEP. METHODS: Adherence to PrEP was assessed by measuring concentrations of emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate or their metabolites in plasma, dried blood spots, and hair. After seroconversion, genotypic and phenotypic resistance of the acquired virus was determined by standard clinical tests and by single-genome sequencing of proviral genomes. HIV partner services identified the likely transmission partner. FINDINGS: A 21-year-old Latino man tested positive for HIV infection 13 months after PrEP initiation. He had a negative HIV antibody test, but detectable HIV RNA with 559 copies per mL. He reported good adherence to daily PrEP. He was linked to care and immediately started antiretroviral therapy, at which point his RNA was 1544 copies per mL and his HIV antibody test was positive. The HIV genotype revealed Met184Val, Leu74Val, Leu100Ile, and Lys103Asn mutations in reverse transcriptase, and the phenotype showed susceptibility to tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and resistance to emtricitabine. Segmental hair analysis of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate concentrations measured in 1 cm segments of hair from the scalp indicated consistently high adherence to PrEP in each of the 6 months before HIV diagnosis (0.0672-0.0889 ng/mg). Concentrations of tenofovir diphosphate (1012 fmol per punch) and emtricitabine triphosphate (0.266 fmol per punch) in a dried blood spot indicated high adherence over the preceding 6 weeks. Concentrations of emtricitabine (870.5 ng/mL) and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (188.2 ng/mL) measured in plasma 3 months before HIV seroconversion confirmed adherence in the days preceding that visit. The likely transmission partner was not engaged in HIV primary care and had a similar viral genotype. INTERPRETATION: Acquisition of HIV virus that is susceptible to tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, but resistant to emtricitabine can occur despite high adherence to PrEP. Quarterly screening for HIV and sexually transmitted diseases facilitates early diagnosis in people on PrEP; when combined with prompt linkage to care and partner services this can prevent onward transmission of HIV. FUNDING: US National Institutes of Health.
Substance Use and Adherence to HIV Preexposure Prophylaxis for Men Who Have Sex with Men(1).[Pubmed:30457536]
Emerg Infect Dis. 2018 Dec;24(12).
The effectiveness of oral HIV preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) strongly depends on maintaining adherence. We investigated the association between substance use and PrEP adherence, as well as incident sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in a high-risk cohort of 394 participants (391 men who have sex with men and 3 transgender women) who were enrolled in a PrEP demonstration project. We assessed baseline and ongoing substance use over a 48-week period for stimulants and nonstimulant substances and for each substance separately. We measured PrEP adherence by using dried blood spots to obtain levels of tenofovir diphosphate. No differences in these levels were found between substance users and nonsubstance users. Baseline stimulant use was strongly associated (odds ratio 3.4; p<0.001) with incident STIs during the study. Thus, PrEP adherence was not decreased by substance use. Because substance users had increased rates of STIs, indicating higher-risk behavior, they might be excellent candidates for PrEP.
The role of socio-behavioral factors in sub-protective tenofovir diphosphate (TFV-DP) levels among YMSM enrolled in two PrEP trials.[Pubmed:30399038]
J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2018 Oct 26.
BACKGROUND: Young men who have sex with men (YMSM) experience disparities in HIV acquisition more than any other group. Daily oral pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) with tenofovir/embricitabine (TDF/FTC) has been shown to effectively prevent HIV transmission in YMSM; however, recent studies suggest that young Black men who have sex with men (YBMSM) experience sub-protective levels of tenofovir diphosphate (TFV-DP) more frequently than other groups. SETTING: Combined data from Adolescent Medicine Trials Network for HIV/AIDS Interventions (ATN) 110/113, two open label PrEP studies that provided PrEP and evidence-based behavioral interventions to young MSM (YMSM) age 15 to 22 years old. METHODS: Bivariate and logistic regression analysis were used to examine sociodemographic and behavioral factors associated with protective TVF-DP levels (defined as >/=700 fmol/punch) in ATN 110/113 data. RESULTS: In bivariate analysis, self-identified Black participants, residential displacement due to sexual orientation, low perceived risk, and stigma with the medication were associated with sub-protective levels. Hispanic ethnicity was associated with protective levels. In the final models, Black males were less likely to have sub-protective levels than non-Black males at 4, 8, 12 weeks. Self-reported displacement due to sexual orientation was associated with sub-protective levels while older age was as associated with protective levels. CONCLUSION: These findings highlight how future behavioral research and biomedical prevention efforts in YMSM will need to address PrEP disparities that may occur in YBMSM, perception of risk and lack of key supportive housing during this period that may be critical factors that contribute to HIV acquisition.


