LM 22A4Potent TrkB agonist CAS# 37988-18-4 |
- CX-6258
Catalog No.:BCC1504
CAS No.:1202916-90-2
- AZD1208
Catalog No.:BCC2079
CAS No.:1204144-28-4
- CX-6258 hydrochloride hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1505
CAS No.:1353858-99-7
- SMI-4a
Catalog No.:BCC2233
CAS No.:438190-29-5
- TCS PIM-1 1
Catalog No.:BCC2447
CAS No.:491871-58-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 37988-18-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 2054170 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C15H21N3O6 | M.Wt | 339.34 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | H2O : ≥ 50 mg/mL (147.34 mM) DMSO : ≥ 29 mg/mL (85.46 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
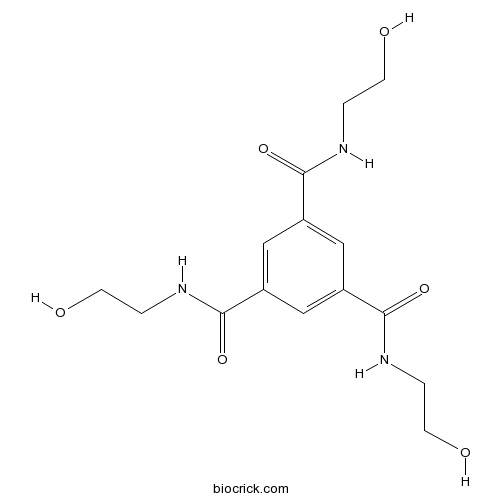
| Chemical Name | 1-N,3-N,5-N-tris(2-hydroxyethyl)benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxamide | ||
| SMILES | C1=C(C=C(C=C1C(=O)NCCO)C(=O)NCCO)C(=O)NCCO | ||
| Standard InChIKey | RGWJKANXFYJKHN-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H21N3O6/c19-4-1-16-13(22)10-7-11(14(23)17-2-5-20)9-12(8-10)15(24)18-3-6-21/h7-9,19-21H,1-6H2,(H,16,22)(H,17,23)(H,18,24) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent tropomyosin-related kinase B (TrkB) agonist. Induces activation of Trk, Akt and ERK in mouse hippocampus and striatum and exhibits neurotrophic activity. Reverses deficits in motor task learning in mice following traumatic brain injury; restores respiratory function in a rat model of Rett syndrome. |

LM 22A4 Dilution Calculator

LM 22A4 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9469 mL | 14.7345 mL | 29.469 mL | 58.9379 mL | 73.6724 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5894 mL | 2.9469 mL | 5.8938 mL | 11.7876 mL | 14.7345 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2947 mL | 1.4734 mL | 2.9469 mL | 5.8938 mL | 7.3672 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0589 mL | 0.2947 mL | 0.5894 mL | 1.1788 mL | 1.4734 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0295 mL | 0.1473 mL | 0.2947 mL | 0.5894 mL | 0.7367 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
LM22A-4 is a specific agonist of tyrosine kinase receptor B, used for neurological disease research.
In Vitro:LM22A-4 significantly up-regulates OPN and ALPase mRNA expression in a dose-dependent manner and OC mRNA level is significantly increased by 5 μM of LM22A-4. LM22A-4 significantly increases OPN, ALPase and OC mRNA expression in a time-dependent manner. LM22A-4 stimulated OPN and OC mRNA expression in HCEM cells cultured with mineralizing media[2].
In Vivo:LM22A-4 (10 mg/kg, i.p.) significantly reduces the degree of tissue injury and apoptosis (TUNEL staining and caspase-3 and Bcl-2 expression) compared with vehicle treated group. LM22A-4 also significantly ameliorates the recovery of limb function. LM22A-4 (10 mg/kg) treatment results in a significant increase in neuron number. LM22A-4 administration (10 mg/kg) significantly improves the neurological scores compared with those of the solvent-treated animals[1].
References:
[1]. Yu G, et al. Protective effects of LM22A-4 on injured spinal cord nerves. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jun 1;8(6):6526-32. eCollection 2015.
[2]. Kajiya M, et al. BDNF mimetic compound LM22A-4 regulates cementoblast differentiation via the TrkB-ERK/Akt signaling cascade. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 Apr;19(2):245-52.
- Geranylacetone
Catalog No.:BCN7567
CAS No.:3796-70-1
- tenofovir diphosphate
Catalog No.:BCC6447
CAS No.:166403-66-3
- Tenofovir Alafenamide Fumarate
Catalog No.:BCC8067
CAS No.:379270-38-9
- Tenofovir alafenamide
Catalog No.:BCC8066
CAS No.:379270-37-8
- Saracatinib (AZD0530)
Catalog No.:BCC1166
CAS No.:379231-04-6
- Cimifugin
Catalog No.:BCN5433
CAS No.:37921-38-3
- Jolkinolide B
Catalog No.:BCN2391
CAS No.:37905-08-1
- Jolkinolide A
Catalog No.:BCN3771
CAS No.:37905-07-0
- Scarlet 808
Catalog No.:BCC9139
CAS No.:3789-75-1
- Ro 08-2750
Catalog No.:BCC7307
CAS No.:37854-59-4
- Nepodin
Catalog No.:BCN6894
CAS No.:3785-24-8
- Germacrene D
Catalog No.:BCN3851
CAS No.:37839-63-7
- 2-Amino-4'-fluorobenzophenone
Catalog No.:BCC8530
CAS No.:3800-06-4
- Sulfamonomethoxine sodium
Catalog No.:BCC9157
CAS No.:38006-08-5
- Tenovin-1
Catalog No.:BCC2239
CAS No.:380315-80-0
- (+)-columbianetin
Catalog No.:BCN2331
CAS No.:3804-70-4
- NBMPR
Catalog No.:BCC7516
CAS No.:38048-32-7
- alpha-Epoxydihydroartemisinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5434
CAS No.:380487-65-0
- 187-1, N-WASP inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC5866
CAS No.:380488-27-7
- DQP 1105
Catalog No.:BCC6205
CAS No.:380560-89-4
- CMPDA
Catalog No.:BCC6151
CAS No.:380607-77-2
- [(pF)Phe4]Nociceptin(1-13)NH2
Catalog No.:BCC5778
CAS No.:380620-88-2
- Pterolactam
Catalog No.:BCN5435
CAS No.:38072-88-7
- Bosutinib (SKI-606)
Catalog No.:BCC1167
CAS No.:380843-75-4
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor enhances cholinergic contraction of longitudinal muscle of rabbit intestine via activation of phospholipase C.[Pubmed:24356881]
Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014 Feb 15;306(4):G328-37.
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) belongs to the neurotrophin family of proteins best known for its role in neuronal survival, differentiation, migration, and synaptic plasticity in central and peripheral neurons. BDNF is also widely expressed in nonneuronal tissues including the gastrointestinal tract. The role of BDNF in intestinal smooth muscle contractility is not well defined. The aim of this study was to identify the role of BDNF in carbachol (CCh)- and substance P (SP)-induced contraction of intestinal longitudinal smooth muscle. BDNF, selective tropomyosin-related kinase B (TrkB) receptor agonists, and pharmacological inhibitors of signaling pathways were examined for their effects on contraction of rabbit intestinal longitudinal muscle strips induced by CCh and SP. BDNF activation of intracellular signaling pathways was examined by Western blot in homogenates of muscle strips and isolated muscle cells. One-hour preincubation with BDNF enhanced intestinal muscle contraction induced by CCh but not by SP. The selective synthetic TrkB agonists LM 22A4 and 7,8-dihydroxyflavone produced similar effects to BDNF. The Trk antagonist K-252a, a TrkB antibody but not p75NTR antibody, blocked the effect of BDNF. The enhancement of CCh-induced contraction by BDNF was blocked by the phospholipase C (PLC) antagonist U73122, but not by ERK1/2 or Akt antagonists. Direct measurement in muscle strips and isolated muscle cells showed that BDNF caused phosphorylation of TrkB receptors and PLC-gamma, but not ERK1/2 or Akt. We conclude that exogenous BDNF augments the CCh-induced contraction of longitudinal muscle from rabbit intestine by activating TrkB receptors and subsequent PLC activation.
A TrkB small molecule partial agonist rescues TrkB phosphorylation deficits and improves respiratory function in a mouse model of Rett syndrome.[Pubmed:22302819]
J Neurosci. 2012 Feb 1;32(5):1803-10.
Rett syndrome (RTT) results from loss-of-function mutations in the gene encoding the methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MeCP2) and is characterized by abnormal motor, respiratory and autonomic control, cognitive impairment, autistic-like behaviors and increased risk of seizures. RTT patients and Mecp2-null mice exhibit reduced expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which has been linked in mice to increased respiratory frequency, a hallmark of RTT. The present study was undertaken to test the hypotheses that BDNF deficits in Mecp2 mutants are associated with reduced activation of the BDNF receptor, TrkB, and that pharmacologic activation of TrkB would improve respiratory function. We characterized BDNF protein expression, TrkB activation and respiration in heterozygous female Mecp2 mutant mice (Het), a model that recapitulates the somatic mosaicism for mutant MECP2 found in typical RTT patients, and evaluated the ability of a small molecule TrkB agonist, LM22A-4, to ameliorate biochemical and functional abnormalities in these animals. We found that Het mice exhibit (1) reduced BDNF expression and TrkB activation in the medulla and pons and (2) breathing dysfunction, characterized by increased frequency due to periods of tachypnea, and increased apneas, as in RTT patients. Treatment of Het mice with LM22A-4 for 4 weeks rescued wild-type levels of TrkB phosphorylation in the medulla and pons and restored wild-type breathing frequency. These data provide new insight into the role of BDNF signaling deficits in the pathophysiology of RTT and highlight TrkB as a possible therapeutic target in this disease.
Small molecule BDNF mimetics activate TrkB signaling and prevent neuronal degeneration in rodents.[Pubmed:20407211]
J Clin Invest. 2010 May;120(5):1774-85.
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) activates the receptor tropomyosin-related kinase B (TrkB) with high potency and specificity, promoting neuronal survival, differentiation, and synaptic function. Correlations between altered BDNF expression and/or function and mechanism(s) underlying numerous neurodegenerative conditions, including Alzheimer disease and traumatic brain injury, suggest that TrkB agonists might have therapeutic potential. Using in silico screening with a BDNF loop-domain pharmacophore, followed by low-throughput in vitro screening in mouse fetal hippocampal neurons, we have efficiently identified small molecules with nanomolar neurotrophic activity specific to TrkB versus other Trk family members. Neurotrophic activity was dependent on TrkB and its downstream targets, although compound-induced signaling activation kinetics differed from those triggered by BDNF. A selected prototype compound demonstrated binding specificity to the extracellular domain of TrkB. In in vitro models of neurodegenerative disease, it prevented neuronal degeneration with efficacy equal to that of BDNF, and when administered in vivo, it caused hippocampal and striatal TrkB activation in mice and improved motor learning after traumatic brain injury in rats. These studies demonstrate the utility of loop modeling in drug discovery and reveal what we believe to be the first reported small molecules derived from a targeted BDNF domain that specifically activate TrkB.We propose that these compounds constitute a novel group of tools for the study of TrkB signaling and may provide leads for developing new therapeutic agents for neurodegenerative diseases.


