Gomisin DCAS# 60546-10-3 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 60546-10-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3085191 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C28H34O10 | M.Wt | 530.56 |
| Type of Compound | Lignans | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
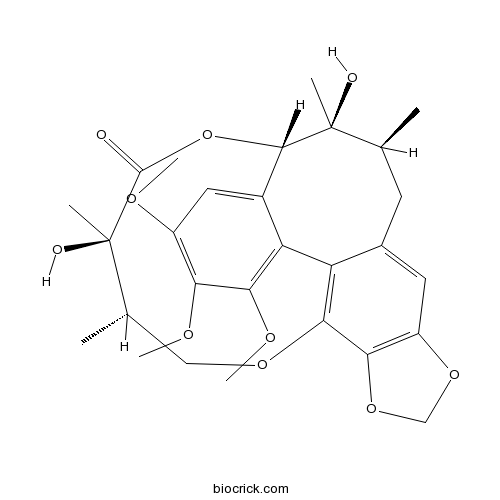
| SMILES | CC1CC2=CC3=C(C4=C2C5=C(C(=C(C=C5C(C1(C)O)OC(=O)C(C(CO4)C)(C)O)OC)OC)OC)OCO3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | VLLFEMVDMFTBHG-SMWGPYIJSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C28H34O10/c1-13-8-15-9-18-22(37-12-36-18)24-19(15)20-16(10-17(32-5)21(33-6)23(20)34-7)25(27(13,3)30)38-26(29)28(4,31)14(2)11-35-24/h9-10,13-14,25,30-31H,8,11-12H2,1-7H3/t13-,14-,25-,27-,28+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Gomisin D is a natural product from Schizandra chinensis. |
| In vitro | Evaluation of cytotoxic activity of Schisandra chinensis lignans.[Pubmed: 20458670]Planta Med. 2010 Oct;76(15):1672-7.
|
| Kinase Assay | Inhibition of UDP-Glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs) Activity by constituents of Schisandra chinensis.[Pubmed: 26084208]Phytother Res. 2015 Oct;29(10):1658-64.Structure-activity relationship for the inhibition of Schisandra chinensis's ingredients toward (Uridine-Diphosphate) UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs) activity was performed in the present study. |
| Structure Identification | Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2014 Aug;39(15):2900-6.Influlance of different drying methods on quality of Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus[Pubmed: 25423829]To study the influence of different drying methods on the quality of Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus and thus provide useful reference for its proper drying methods.
|

Gomisin D Dilution Calculator

Gomisin D Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8848 mL | 9.424 mL | 18.848 mL | 37.696 mL | 47.12 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.377 mL | 1.8848 mL | 3.7696 mL | 7.5392 mL | 9.424 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1885 mL | 0.9424 mL | 1.8848 mL | 3.7696 mL | 4.712 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0377 mL | 0.1885 mL | 0.377 mL | 0.7539 mL | 0.9424 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0188 mL | 0.0942 mL | 0.1885 mL | 0.377 mL | 0.4712 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Olsalazine Sodium
Catalog No.:BCC3829
CAS No.:6054-98-4
- Braylin
Catalog No.:BCN4118
CAS No.:6054-10-0
- Methyloleoside
Catalog No.:BCN8079
CAS No.:60539-23-3
- H-D-Thr-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2675
CAS No.:60538-15-0
- Zimelidine dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7173
CAS No.:60525-15-7
- 5,6-Dihydropyridin-2(1H)-one
Catalog No.:BCN4013
CAS No.:6052-73-9
- Serpentinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4616
CAS No.:605-14-1
- Pifithrin-β
Catalog No.:BCC5503
CAS No.:60477-34-1
- Cytisine Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN8133
CAS No.:6047-01-4
- Cauloside F
Catalog No.:BCN3848
CAS No.:60451-47-0
- Neopetasitenine
Catalog No.:BCN2114
CAS No.:60409-51-0
- Cucurbitacin A
Catalog No.:BCN2468
CAS No.:6040-19-3
- 1-Acetyltagitinin A
Catalog No.:BCN4119
CAS No.:60547-63-9
- P1075
Catalog No.:BCC7027
CAS No.:60559-98-0
- DCEBIO
Catalog No.:BCC7060
CAS No.:60563-36-2
- Tirandamycin B
Catalog No.:BCN1862
CAS No.:60587-14-6
- Pamabrom
Catalog No.:BCC1835
CAS No.:606-04-2
- 2,4'-Dihydroxybenzophenone
Catalog No.:BCN3358
CAS No.:606-12-2
- Toyocamycin
Catalog No.:BCC8047
CAS No.:606-58-6
- Cinnabarinic acid
Catalog No.:BCC7865
CAS No.:606-59-7
- Homopterocarpin
Catalog No.:BCN4615
CAS No.:606-91-7
- MK-0773
Catalog No.:BCC1754
CAS No.:606101-58-0
- Momor-cerebroside I
Catalog No.:BCN4120
CAS No.:606125-07-9
- AZD6244 (Selumetinib)
Catalog No.:BCC3624
CAS No.:606143-52-6
Evaluation of cytotoxic activity of Schisandra chinensis lignans.[Pubmed:20458670]
Planta Med. 2010 Oct;76(15):1672-7.
Using exhaustive chromatographic separation we have isolated (-)-tigloyl-deangeloyl-gomisin F as a novel dibenzocyclooctadiene lignan from schisandra chinensis. With the help of HPLC, we further isolated (+)-schisandrin, (+)-deoxyschisandrin, (+)-gamma-schisandrin, (-)-gomisin J, (+)-gomisin A, (-)-gomisin N, (-)-tigloyl-gomisin P, (-)-wuweizisu C, (-)-Gomisin D, rubrisandrin A, (-)-gomisin G, (+)-gomisin K (3) and (-)-schisantherin C. A full NMR description of (-)-schisantherin C was carried out with the aim to confirm previous reports of its structure. Compounds isolated were identified on the basis of UV, IR, (1)H- and (13)C-NMR and MS. The cytotoxicity of lignans was tested for the BY-2 cell line alone and as a synergistic effect with the cytotoxic agent camptothecin. Lignans showed various toxicity and synergistic and antagonistic effects on camptothecin-induced cytotoxicity. Cytotoxicity against colon cancer cell line LoVo was also tested.
[Influlance of different drying methods on quality of Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus].[Pubmed:25423829]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2014 Aug;39(15):2900-6.
OBJECTIVE: To study the influence of different drying methods on the quality of Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus and thus provide useful reference for its proper drying methods. METHOD: Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus was processed by eight drying methods including vacuum freeze drying, natural drying in the shade, drying in the sun, oven drying and vacuum drying under different temperature. The contents of the functional ingredients includes chisandrin, Gomisin D, gomisin J, schisandrol B, angeloylgomisin H, angeloylgomisin Q, gomisin G, schisantherin A, deoxyschisandrin, schisandrin B, schisandrin C, 5-HMF, total aids and total sugars. The main components change after drying were analyzed by HPLC, ultraviolet spectrophotometry and potentiometric titration. Principal component analysis (PCA) was carried out by SPSS software to evaluate the quality of different processed products from Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus. RESULT: All these results are in accordance with the requirements of Chinese Pharmacopoeia published in 2010, the contents of schisandrin and total eleven lignans were the highest using vacuum drying, and 5-HMF were the lower, oven drying made little difference but with lower schisandrin and higher 5-HMF as the heat increased. CONCLUSION: Different drying methods have significant influence on the quality of Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus. Oven drying under 5 degrees C should be adopted to substitute drying in the sun according to the China Pharmacopoeia published in 2010 for Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus by comprehensive analysis of the cost, content and practicality.
Inhibition of UDP-Glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs) Activity by constituents of Schisandra chinensis.[Pubmed:26084208]
Phytother Res. 2015 Oct;29(10):1658-64.
Structure-activity relationship for the inhibition of Schisandra chinensis's ingredients toward (Uridine-Diphosphate) UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs) activity was performed in the present study. In vitro incubation system was employed to screen the inhibition capability of S. chinensis's ingredients, and in silico molecular docking method was carried out to explain possible mechanisms. At 100 muM of compounds, the activity of UGTs was inhibited by less than 90% by schisandrol A, schisandrol B, schisandrin, schisandrin C, schisantherin A, Gomisin D, and gomisin G. Schisandrin A exerted strong inhibition toward UGT1A1 and UGT1A3, with the residual activity to be 7.9% and 0% of control activity. Schisanhenol exhibited strong inhibition toward UGT2B7, with the residual activity to be 7.9% of control activity. Gomisin J of 100 muM inhibited 91.8% and 93.1% of activity of UGT1A1 and UGT1A9, respectively. Molecular docking prediction indicated different hydrogen bonds interaction resulted in the different inhibition potential induced by subtle structure alteration among schisandrin A, schisandrin, and schisandrin C toward UGT1A1 and UGT1A3: schisandrin A > schisandrin > schisandrin C. The detailed inhibition kinetic evaluation showed the strong inhibition of gomisin J toward UGT1A9 with the inhibition kinetic parameter (Ki ) to be 0.7 muM. Based on the concentrations of gomisin J in the plasma of the rats given with S. chinensis, high herb-drug interaction existed between S. chinensis and drugs mainly undergoing UGT1A9-mediated metabolism. In conclusion, in silico-in vitro method was used to give the inhibition information and possible inhibition mechanism for S. chinensis's components toward UGTs, which guide the clinical application of S. chinensis.


