GuaiacinCAS# 36531-08-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 36531-08-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11724027 | Appearance | Powder |
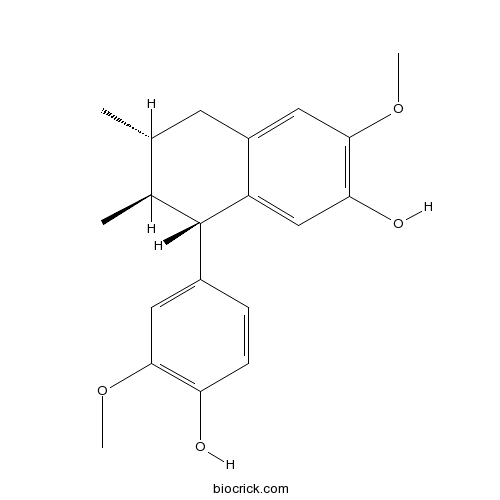
| Formula | C20H24O4 | M.Wt | 328.4 |
| Type of Compound | Lignans | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (6R,7S,8S)-8-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-3-methoxy-6,7-dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-ol | ||
| SMILES | CC1CC2=CC(=C(C=C2C(C1C)C3=CC(=C(C=C3)O)OC)O)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | TZAAYUCUPIYQBR-JGRMJRGVSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H24O4/c1-11-7-14-9-19(24-4)17(22)10-15(14)20(12(11)2)13-5-6-16(21)18(8-13)23-3/h5-6,8-12,20-22H,7H2,1-4H3/t11-,12+,20+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | (+)-Guaiacin has significant neuroprotective, and anti-inflammatory activities, it can inhibit cyclooxygenase (COX)-1 and COX-2. (+)-Guaiacin shows potent in vitro activities against the release of beta-glucuronidase in rat polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) induced by platelet-activating factor (PAF), with 42.5-75.6% inhibition at 10(-5) M. |
| Targets | PAFR | COX |
| In vitro | Biological Evaluation of Secondary Metabolites from the Root of Machilus obovatifolia.[Pubmed: 26172326]Chem Biodivers. 2015 Jul;12(7):1057-67.Bioassay-guided fractionation of the root of Machilus obovatifolia led to the isolation of four new lignans, epihenricine B (1), threo-(7'R,8'R) and threo-(7'S,8'S)-methylmachilusol D (2 and 3), and isofragransol A (4), along with 23 known compounds. Stimulatory activity of lignans from Machilus thunbergii on osteoblast differentiation.[Pubmed: 17409528]Biol Pharm Bull. 2007 Apr;30(4):814-7.Phytoestrogens are naturally occurring compounds exerting estrogenic activity, and include isoflavonoids, flavonoids and lignans. |
| Kinase Assay | Lipoperoxidation and cyclooxygenases 1 and 2 inhibitory compounds from Iryanthera juruensis.[Pubmed: 17335225 ]J. Agr. Food Chem., 2007, 55(7):2569-74.Plants from Iryanthera genus have been traditionally used as food supplements by South American Indians. |

Guaiacin Dilution Calculator

Guaiacin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0451 mL | 15.2253 mL | 30.4507 mL | 60.9013 mL | 76.1267 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.609 mL | 3.0451 mL | 6.0901 mL | 12.1803 mL | 15.2253 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3045 mL | 1.5225 mL | 3.0451 mL | 6.0901 mL | 7.6127 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0609 mL | 0.3045 mL | 0.609 mL | 1.218 mL | 1.5225 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0305 mL | 0.1523 mL | 0.3045 mL | 0.609 mL | 0.7613 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Serpentinine
Catalog No.:BCN5325
CAS No.:36519-42-3
- Emiline
Catalog No.:BCN2080
CAS No.:36506-99-7
- beta-Costic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5324
CAS No.:3650-43-9
- Agatholal
Catalog No.:BCN5323
CAS No.:3650-31-5
- Carnosic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5892
CAS No.:3650-09-7
- Methylsynephrine Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN3407
CAS No.:365-26-4
- Cinacalcet HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4408
CAS No.:364782-34-3
- Ginsenoside Rk3
Catalog No.:BCN3502
CAS No.:364779-15-7
- Ginsenoside Rk2
Catalog No.:BCN3721
CAS No.:364779-14-6
- Doripenem Hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC1160
CAS No.:364622-82-2
- Lucidenic acid SP1
Catalog No.:BCN7969
CAS No.:364622-33-3
- 6beta-Hydroxystigmast-4-en-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN5322
CAS No.:36450-02-9
- Cycloheterophyllin
Catalog No.:BCN4640
CAS No.:36545-53-6
- Ac-Tyr-OEt.H2O
Catalog No.:BCC3121
CAS No.:36546-50-6
- H-Arg-OEt.2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2860
CAS No.:36589-29-4
- Procarbazine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4452
CAS No.:366-70-1
- AY 9944 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC3940
CAS No.:366-93-8
- Mubritinib (TAK 165)
Catalog No.:BCC4513
CAS No.:366017-09-6
- 1,4-Benzodioxan-2-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8421
CAS No.:3663-80-7
- Semialactone
Catalog No.:BCN5422
CAS No.:366450-46-6
- 1-Hexadecanol
Catalog No.:BCC4616
CAS No.:36653-82-4
- Rivaroxaban
Catalog No.:BCC2292
CAS No.:366789-02-8
- Cussosaponin C
Catalog No.:BCN2895
CAS No.:366814-42-8
- Pulchinenoside E
Catalog No.:BCN8165
CAS No.:366814-43-9
Stimulatory activity of lignans from Machilus thunbergii on osteoblast differentiation.[Pubmed:17409528]
Biol Pharm Bull. 2007 Apr;30(4):814-7.
Phytoestrogens are naturally occurring compounds exerting estrogenic activity, and include isoflavonoids, flavonoids and lignans. In the present study, we evaluated the stimulating activity of six lignans, meso-dihydroguaiaretic acid, nordihydroguaiaretic acid, machilin A, Guaiacin, isoGuaiacin and isoGuaiacin dimethylether, from Machilus thunbergii, on osteoblast differentiation employing primary cultures of mouse osteoblast as an in vitro assay system. Among the six lignans tested, arylnaphthalene type lignans such as Guaiacin, isoGuaiacin and isoGuaiacin dimethylether significantly increased alkaline phosphatase activity, whereas bibenzylbutane type lignans such as meso-dihydroguaiaretic acid, nordihydroguaiaretic acid and machilin A showed little effects. IsoGuaiacin and isoGuaiacin dimethylether also increased collagen synthesis as well as calcium deposition. In addition, treatment of the mouse osteoblasts with tamoxifen markedly reduced ALP activity increased by isoGuaiacin or isoGuaiacin dimethylether, suggesting the involvement of estrogen receptor in the action of these lignans on osteoblast differentiation. Taken together, these results suggest that arylnaphthalene type lignans such as Guaiacin, isoGuaiacin and isoGuaiacin dimethylether significantly increase osteoblast differentiation.
Biological evaluation of secondary metabolites from the root of Machilus obovatifolia.[Pubmed:26172326]
Chem Biodivers. 2015 Jul;12(7):1057-67.
Bioassay-guided fractionation of the root of Machilus obovatifolia led to the isolation of four new lignans, epihenricine B (1), threo-(7'R,8'R) and threo-(7'S,8'S)-methylmachilusol D (2 and 3), and isofragransol A (4), along with 23 known compounds. The compounds were obtained as isomeric mixtures (i.e., 2/3 and 4/20, resp.). The structures were elucidated by spectral analyses. Among the isolates, 1, licarin A (12), Guaiacin (14), (+/-)-syringaresinol (21), and (-)-epicatechin (23) showed ABTS (=2,2'-azinobis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) cation radical-scavenging activity, with SC50 values of 11.7+/-0.5, 12.3+/-1.1, 11.0+/-0.1, 10.6+/-0.3, and 9.5+/-0.2 muM in 20 min, respectively. In addition, kachirachirol B (17) showed cytotoxicity against the NCI-H460 cell line with an IC50 value of 3.1 mug/ml.
Lipoperoxidation and cyclooxygenases 1 and 2 inhibitory compounds from Iryanthera juruensis.[Pubmed:17335225]
J Agric Food Chem. 2007 Apr 4;55(7):2569-74.
Plants from Iryanthera genus have been traditionally used as food supplements by South American Indians. The MeOH extract of leaves of Iryanthera juruensis, one of the plants endemic to the Amazon region and consumed in Brazil, and the hexane extract from its seeds inhibited lipid peroxidation (LPO) and cyclooxygenase (COX-1 and -2)) enzymes in in vitro assays. Further analyses of these extracts yielded 5-deoxyflavones (1-5) from the leaf extract and sargachromenol (6), sargaquinoic acid (7), a novel juruenolic acid (8), omega-arylalkanoic acids (9a-c), and the lignan Guaiacin (10) from the seed extract. Compounds 3-5 inhibited LPO by 86%, 77%, and 88% at 10 ppm, respectively, and compounds 6 and 9a-c showed inhibition at 76% and 78% at 100 ppm, respectively. However, compounds 7 and 8 were inactive and lignan 10 exhibited LPO inhibitory activity by 99% at 100 ppm compared to commercial antioxidants butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA), butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), and vitamin E. The flavones 1-5 also inhibited COX-1 and -2 enzymes by 50-65% at 100 ppm. Compound 6 showed high but nonselective inhibition of COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes, when compared to aspirin and Celebrex, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). Compounds 7 and 10 inhibited COX-1 by 60% and 65% and COX-2 by 37% and 18%, respectively, whereas compounds 8 and 9a-c showed little or no activity against these enzymes.


