Hydroxychloroquine SulfateAutophagy inhibitor; also TLR9 inhibitor CAS# 747-36-4 |
- DAPT (GSI-IX)
Catalog No.:BCC3618
CAS No.:208255-80-5
- Semagacestat (LY450139)
Catalog No.:BCC3610
CAS No.:425386-60-3
- AR-A014418
Catalog No.:BCC1366
CAS No.:487021-52-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 747-36-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 12947 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H28ClN3O5S | M.Wt | 433.95 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | H2O : 110 mg/mL (253.49 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) | ||
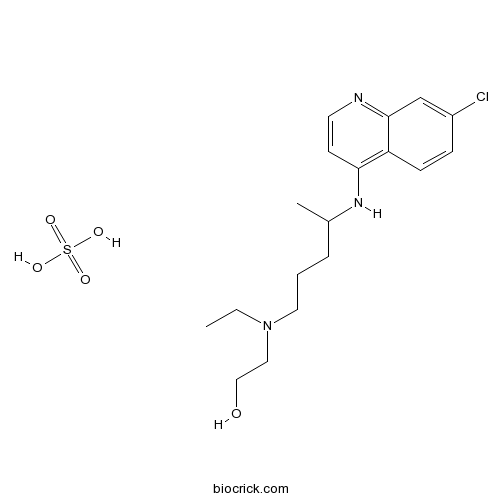
| Chemical Name | 2-[4-[(7-chloroquinolin-4-yl)amino]pentyl-ethylamino]ethanol;sulfuric acid | ||
| SMILES | CCN(CCCC(C)NC1=C2C=CC(=CC2=NC=C1)Cl)CCO.OS(=O)(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | JCBIVZZPXRZKTI-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H26ClN3O.H2O4S/c1-3-22(11-12-23)10-4-5-14(2)21-17-8-9-20-18-13-15(19)6-7-16(17)18;1-5(2,3)4/h6-9,13-14,23H,3-5,10-12H2,1-2H3,(H,20,21);(H2,1,2,3,4) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Autophagy inhibitor. Inhibits growth and induces apoptosis of renal cancer cells in vitro. Also inhibits TLR9. |

Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate Dilution Calculator

Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3044 mL | 11.5221 mL | 23.0441 mL | 46.0883 mL | 57.6103 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4609 mL | 2.3044 mL | 4.6088 mL | 9.2177 mL | 11.5221 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2304 mL | 1.1522 mL | 2.3044 mL | 4.6088 mL | 5.761 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0461 mL | 0.2304 mL | 0.4609 mL | 0.9218 mL | 1.1522 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.023 mL | 0.1152 mL | 0.2304 mL | 0.4609 mL | 0.5761 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Vibsanin C
Catalog No.:BCN4590
CAS No.:74690-89-4
- 1-Methoxycarbonyl-beta-carboline-N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN8205
CAS No.:74690-74-7
- 4-hydroxy-1-methoxycarbonyl-beta-carboline
Catalog No.:BCN7909
CAS No.:74690-72-5
- 3-Methoxy-4,5-methylenedioxycinnamaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCN1364
CAS No.:74683-19-5
- Nuclear yellow
Catalog No.:BCC1810
CAS No.:74681-68-8
- 1,3,9-Trimethyluric acid
Catalog No.:BCN7393
CAS No.:7464-93-9
- Liquiritin Apioside
Catalog No.:BCC8334
CAS No.:74639-14-8
- 11-Hydroxydrim-7-en-6-one
Catalog No.:BCN7770
CAS No.:74635-87-3
- ent-3Beta-Angeloyloxykaur-16-en-19-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1365
CAS No.:74635-61-3
- Tylosin tartrate
Catalog No.:BCC4875
CAS No.:74610-55-2
- Tetrahydrocoptisine
Catalog No.:BCN2558
CAS No.:7461-02-1
- Rubiadin 1-methyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN4298
CAS No.:7460-43-7
- 5-Hydroxyxanthotoxin
Catalog No.:BCC8107
CAS No.:7471-73-0
- Zaltoprofen
Catalog No.:BCC4442
CAS No.:74711-43-6
- Secoxyloganin methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN4299
CAS No.:74713-15-8
- Pterolactone A
Catalog No.:BCN6513
CAS No.:74730-10-2
- AUY922 (NVP-AUY922)
Catalog No.:BCC2123
CAS No.:747412-49-3
- VER-50589
Catalog No.:BCC5296
CAS No.:747413-08-7
- Ciglitazone
Catalog No.:BCC7014
CAS No.:74772-77-3
- Methylophiopogonone B
Catalog No.:BCN8182
CAS No.:74805-89-3
- Methylophiopogonone A
Catalog No.:BCN2841
CAS No.:74805-90-6
- Methylophiopogonanone B
Catalog No.:BCN5418
CAS No.:74805-91-7
- Methylophiopogonanone A
Catalog No.:BCN5417
CAS No.:74805-92-8
- Zalcitabine
Catalog No.:BCC5026
CAS No.:7481-89-2
A parallel design study to assess the bioequivalence of generic and branded hydroxychloroquine sulfate tablets in healthy volunteers.[Pubmed:23138518]
Arzneimittelforschung. 2012 Dec;62(12):644-9.
Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) is a racemic 4-aminoquinoline derivative that was first introduced as an antimalarial, and subsequently applied to the treatment of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Information on the pharmacokinetics of HCQ in healthy volunteers, especially in a Chinese population is limited, and this study was conducted to provide support for a generic product to obtain marketing authorization in China.The aim of the present study was to compare the pharmacokinetics and assess bioequivalence of a new generic test and the branded reference Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate tablets in healthy volunteers.This was a parallel, open-label, randomized, single-dose, 1-period fasting study. 54 healthy subjects were randomly assigned (1:1) to receive 200 mg Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate tablets of the test or the reference formulation. 15 blood samples were collected and whole blood concentrations of HCQ were determined by a validated liquid chromatography-isotopic dilution mass spectrometry method. Log-transformed Cmax and AUC0-24 values were used to test for bioequivalence. The 2 formulations were considered bioequivalent if 90% confidence intervals (CIs) for the log-transformed ratios of Cmax and AUC0-24 were within the predetermined bioequivalence range of 80-125%. Tolerability was evaluated throughout the study by vital signs, physical examinations, clinical laboratory tests, 12-lead electrocardiograms, and interviews with the subjects about adverse events.54 healthy subjects were enrolled and completed the study (mean [SD] age, height, body weight, and BMI were 23.9 [2.4] years, 168.9 [5.0] cm, 61.3 [5.4] kg, and 21.5 [1.7] kg/m2), 27 subjects per group. No formulation or sequence effects were observed. The mean values of Cmax and AUC0-24 for the test and reference formulations of HCQ (197.6 and 199.0 ng/mL, 2460.1 and 2468.3 ng/mL/h) were not significantly different. The 90% CIs of the ratios of Cmax and AUC0-24 were 99.3% (98.1-102.1%), 99.7% (98.9-101.4%), respectively. 4 subjects (7.41%) experienced a total of 4 mild AEs (headache and microscopic hematuria, 1 each; and increase in plasma triglycerides, 2).The results of this study suggest that the test and reference Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate tablets are bioequivalent. Both formulations were generally well tolerated.
Comparable efficacy of standardized Ayurveda formulation and hydroxychloroquine sulfate (HCQS) in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA): a randomized investigator-blind controlled study.[Pubmed:21773714]
Clin Rheumatol. 2012 Feb;31(2):259-69.
Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate (HCQS) is a popular disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) despite modest efficacy and toxicity. Ayurveda (ancient India medicinal system) physicians treat rheumatoid arthritis (RA) with allegedly safer herbal formulations. We report a head-to-head comparison in an exploratory drug trial. The objective is to compare standardized Ayurvedic formulations and HCQS in the treatment of RA. One hundred twenty-one patients with active moderately severe RA (ACR 1988 classified) were randomized into a 24-week investigator-blind, parallel efficacy, three-arm (two Ayurvedic and HCQS) multicenter drug trial study; polyherb (Tinospora cordifolia and Zingiber officinale based) and monoherb (Semecarpus anacardium). Study measures included joint counts (pain/tenderness and swelling), pain visual analogue scale, global disease assessments, and health assessment questionnaire. Oral meloxicam (fixed-dosage schedule) was prescribed to all patients during the initial 16 weeks. Patients on prednisolone could continue a fixed stable dose (<7.5 mg daily). Rescue oral use of paracetamol was permitted and monitored. All groups matched well at baseline. An intent-to-treat analysis (ANOVA, significance P < 0.05) did not show significant differences by treatment groups. In the polyherb, monoherb, and HCQS arms, 44%, 36%, and 51%, respectively, showed ACR 20 index improvement. Several efficacy measures improved significantly in the HCQS and polyherb groups with no difference between the groups (corrected P). However, the latter was individually superior to monoherb. Only mild adverse events (gut and skin, and none withdrew) were reported with no differences between the groups. Forty-two patients dropped out. This preliminary drug trial controlled for HCQS demonstrated a standardized Ayurvedic polyherb drug to be effective and safe in controlling active RA. A better-designed study with a longer evaluation period is recommended.
[Analysis of the clinical efficacy of yiqi fumai injection combined hydroxychloroquine sulfate tablet for treating Sjogren's syndrome].[Pubmed:23469599]
Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2012 Dec;32(12):1621-3.
OBJECTIVE: To observe the clinical efficacy of Yiqi Fumai Injection (YFI) combined Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate tablet in the treatment of Sjogren's syndrome patients. METHODS: Eighty patients were randomly assigned to three groups. Forty patients in Group A were treated with YFI alone, 2. 6 g YFI added in 250 mL normal saline for intravenous dripping, once daily. Twenty patients in Group B took Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate alone, 0. 2 g each time, twice daily. Twenty patients in Group C were treated with YFI and Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate tablet (with the same dose and dosage as Group A and B). Fifteen days was taken as one course of treatment. The scores for dry mouth and dry eyes, the efficacy on salivary flow rate, Schirmer test, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-reactive protein (CRP), and IgG, and so on were compared among the three groups before and after treatment. RESULTS: There was no significant difference in the laboratory parameters and clinical symptoms among the three groups before treatment. After treatment obvious improvement of the scores for dry mouth, the salivary flow rate, Schirmer test, ESR, CRP, and IgG was shown in all the 3 groups (P<0.05). Besides, the optimal effect was shown in Group C. Its total effective rate was 85% (17/20), better than that of Group A [80% (32/40)] and Group B [75% (15/20)], with no statistical difference (chi2 = 0.736 and 0. 695, P>0.05). CONCLUSION: YFU combined Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate tablet showed better effects in treating Sjogren's syndrome patients than using Chinese medicine or Western medicine alone.
Pharmacokinetics and Bioequivalence Study of Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate Tablets in Chinese Healthy Volunteers by LC-MS/MS.[Pubmed:27747530]
Rheumatol Ther. 2015 Dec;2(2):183-195.
INTRODUCTION: Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), 4-aminoquinoline, is an antimalarial drug and has become a basic therapy for rheumatic disease treatment. It can stabilize the condition of SLE patients and reduce the chances of patient relapse through its immunosuppressive function and antiinflammatory effects. This drug was absorbed completely and rapidly by oral administration, but has a prolonged half-life for elimination. The objective of this study was to evaluate the pharmacokinetic parameters and relative bioequivalence of a new generic (test) formulation with the branded (reference) formulation of HCQ in healthy Chinese male volunteers. This study was designed to acquire regulatory approval for the test formulation. METHODS: This study was conducted with a randomized, single-dose, two-period, and crossover design. The male subjects were randomly assigned to two groups at a 1:1 ratio to receive 0.2 g Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate tablets (0.1 g/piece) of the two formulations after a 3-month washout period then administered the alternate formulation. Study drugs were administered after overnight fasting (over 10 h). Plasma concentrations of hydroxychloroquine were measured by a validated LC-MS/MS method. The following pharmacokinetic properties were determined by a noncompartmental pharmacokinetic method: C max, T max, AUC0-t , AUC0- proportional, variant, and t 1/2. The bioequivalence between the test and reference products was assessed based on the following parameters: C max, AUC0-60d, and AUC0- proportional, variant using the ANOVA method. If the 90% CI for AUC0-t was within 80-125% and for C max was within 70-143% of the statistical interval proposed by the SFDA, the two formulations were assumed bioequivalent. Concerning the main pharmacokinetic charateristics of hydroxychloroquine, a long half-life drug, the pharmacokinetic parameters of 0-72 h were determined according to the FDA. Furthermore, a comparison was made between the parameters at 0-60 days and 0-72 h to evaluate whether a truncated AUC method can be applied to estimate the relative bioavailability of HCQ. Tolerability was assessed by monitoring vital signs and laboratory tests and by questioning subjects about adverse events. RESULTS: The 90% CI of C max for HCQ is 103.8-142.3%; the AUC0-60 is 100-114.2% and AUC0- proportional, variant 100-115.5%. Both met the criteria according to the SFDA's guidelines for bioequivalence. The relative bioavailability was 109.5% (according to AUC0-60d) and 110.7% (according to AUC0- proportional, variant). No serious or unexpected adverse events were observed. CONCLUSIONS: In this study, the pharmacokinetic studies and results were conducted so that the test and reference formulations of HCQ met the Chinese criteria for assuming bioequivalence. Both formulations were well tolerated in the population studies.
Hydroxychloroquine Destabilizes Phospho-S6 in Human Renal Carcinoma Cells.[Pubmed:26134285]
PLoS One. 2015 Jul 2;10(7):e0131464.
mTOR inhibitors are used to treat metastatic renal cell cancer (RCC), but most patients eventually become resistant. One possible mechanism for resistance is upregulation of autophagy, a pathway that helps recycle intracellular proteins and promotes cell survival. Hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), a potent autophagy inhibitor used to treat malaria and autoimmune disorders, is currently being studied in the context of cancer treatment. Here, we have investigated the effects of HCQ on three different renal carcinoma derived cell lines. We found that HCQ treatment inhibits RCC cell growth, promotes apoptosis, inhibits mitochondrial oxygen consumption, and increases rates of glycolysis. To understand the molecular mechanism behind these effects, we examined various nodes in the mTOR pathway and compared the effects of HCQ with the effects of the mTOR inhibitor RAD001. A key downstream readout of the pathway, phospho-S6 protein, was inhibited by both HCQ and RAD001. However, the upstream kinase, P70S6K was only inhibited by RAD001 and not HCQ, suggesting that the block by HCQ was downstream of P70S6K. Treatment with the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib restored phospho-S6 levels, suggesting that the reduction of phospho-S6 is caused by increased degradation of phospho-S6, but not total S6. Surprisingly, treatment with other autophagy inhibitors did not exhibit the same effects. Our findings suggest that HCQ causes the down-regulation of phospho-S6 in RCC cell lines via a novel mechanism that is not shared with other autophagy inhibitors.
Novel small molecule inhibitors of TLR7 and TLR9: mechanism of action and efficacy in vivo.[Pubmed:24342772]
Mol Pharmacol. 2014 Mar;85(3):429-40.
The discovery that circulating nucleic acid-containing complexes in the serum of autoimmune lupus patients can stimulate B cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells via Toll-like receptors 7 and 9 suggested that agents that block these receptors might be useful therapeutics. We identified two compounds, AT791 {3-[4-(6-(3-(dimethylamino)propoxy)benzo[d]oxazol-2-yl)phenoxy]-N,N-dimethylpropa n-1-amine} and E6446 {6-[3-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)propoxy)-2-(4-(3-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)propoxy)phenyl]benzo[d]o xazole}, that inhibit Toll-like receptor (TLR)7 and 9 signaling in a variety of human and mouse cell types and inhibit DNA-TLR9 interaction in vitro. When administered to mice, these compounds suppress responses to challenge doses of cytidine-phosphate-guanidine (CpG)-containing DNA, which stimulates TLR9. When given chronically in spontaneous mouse lupus models, E6446 slowed development of circulating antinuclear antibodies and had a modest effect on anti-double-stranded DNA titers but showed no observable impact on proteinuria or mortality. We discovered that the ability of AT791 and E6446 to inhibit TLR7 and 9 signaling depends on two properties: weak interaction with nucleic acids and high accumulation in the intracellular acidic compartments where TLR7 and 9 reside. Binding of the compounds to DNA prevents DNA-TLR9 interaction in vitro and modulates signaling in vivo. Our data also confirm an earlier report that this same mechanism may explain inhibition of TLR7 and 9 signaling by hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil; Sanofi-Aventis, Bridgewater, NJ), a drug commonly prescribed to treat lupus. Thus, very different structural classes of molecules can inhibit endosomal TLRs by essentially identical mechanisms of action, suggesting a general mechanism for targeting this group of TLRs.


