IPA-3Non-ATP competitive Pak1 inhibitor CAS# 42521-82-4 |
- FRAX597
Catalog No.:BCC4172
CAS No.:1286739-19-2
- PF-3758309
Catalog No.:BCC1853
CAS No.:898044-15-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 42521-82-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 521106 | Appearance | Powder |
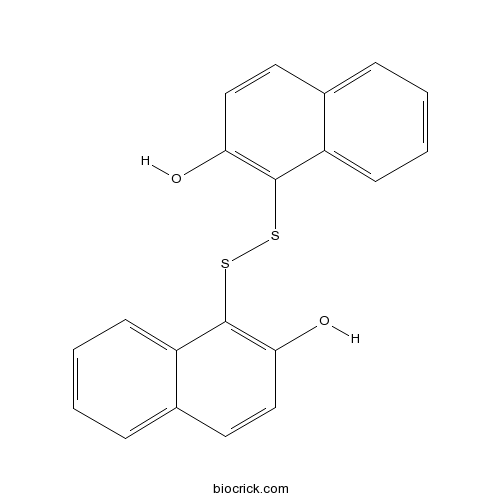
| Formula | C20H14O2S2 | M.Wt | 350.45 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (285.35 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | 1-[(2-hydroxynaphthalen-1-yl)disulfanyl]naphthalen-2-ol | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C2C(=C1)C=CC(=C2SSC3=C(C=CC4=CC=CC=C43)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | RFAXLXKIAKIUDT-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H14O2S2/c21-17-11-9-13-5-1-3-7-15(13)19(17)23-24-20-16-8-4-2-6-14(16)10-12-18(20)22/h1-12,21-22H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Group I p21-activated kinase (PAK) inhibitor (IC50 = 2.5 μM at PAK1). Targets the autoregulatory mechanism and promotes the inactive conformation of PAKs. Inhibits PAK1-mediated signaling in vivo; potential anti-tumor agent. Negative control PIR 3.5 available. |

IPA-3 Dilution Calculator

IPA-3 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8535 mL | 14.2674 mL | 28.5347 mL | 57.0695 mL | 71.3369 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5707 mL | 2.8535 mL | 5.7069 mL | 11.4139 mL | 14.2674 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2853 mL | 1.4267 mL | 2.8535 mL | 5.7069 mL | 7.1337 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0571 mL | 0.2853 mL | 0.5707 mL | 1.1414 mL | 1.4267 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0285 mL | 0.1427 mL | 0.2853 mL | 0.5707 mL | 0.7134 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
IPA-3 is an autoregulatory domain inhibitor of p21-activated kinase (Pak) with IC50 value of 2.5μM [1].
IPA-3 is a highly selective and non-ATP-competitive inhibitor that targets the autoregulatory mechanism of group I Paks. IPA-3 is screened out as an inhibitor of Pak1 by measuring ATP hydrolysis. In the in vitro assays, IPA-3 inhibits Pak1 autophosphorylation stimulated by Cdc42 or sphingosine. It shows an IC50 value of 2.5μM in the kinase assay. This inhibition of Pak1 is reported to be noncompetitive with ATP. Besides that, IPA-3 is found to remarkably inhibit the kinase activity of other group I Pak members, Pak2 and 3 at concentration of 10μM. Furthermore, 30μM IPA-3 can prevent both basal and PDGF-stimulated Pak activities in mouse embryonic fibroblasts [1].
References:
[1] Deacon S W, Beeser A, Fukui J A, et al. An isoform-selective, small-molecule inhibitor targets the autoregulatory mechanism of p21-activated kinase. Chemistry & biology, 2008, 15(4): 322-331.
- 23-Hydroxylongispinogenin
Catalog No.:BCN7830
CAS No.:42483-24-9
- Isobutyl 4-Hydroxybenzoate
Catalog No.:BCN8412
CAS No.:4247-02-3
- Flunixin Meglumin
Catalog No.:BCC4429
CAS No.:42461-84-7
- H-ß-Ala-OEt.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2852
CAS No.:4244-84-2
- Pinostilbene
Catalog No.:BCN5483
CAS No.:42438-89-1
- Pashanone
Catalog No.:BCN5482
CAS No.:42438-78-8
- 1-Benzylimidazole
Catalog No.:BCC8462
CAS No.:4238-71-5
- ML161
Catalog No.:BCC3642
CAS No.:423735-93-7
- Buxtamine
Catalog No.:BCC8135
CAS No.:4236-73-1
- (-)-Gallocatechin gallate
Catalog No.:BCN6328
CAS No.:4233-96-9
- SC 57461A
Catalog No.:BCC2348
CAS No.:423169-68-0
- PYZD-4409
Catalog No.:BCC4253
CAS No.:423148-78-1
- Semagacestat (LY450139)
Catalog No.:BCC3610
CAS No.:425386-60-3
- Crocin
Catalog No.:BCN2373
CAS No.:42553-65-1
- Sotrastaurin (AEB071)
Catalog No.:BCC3857
CAS No.:425637-18-9
- 8-Hydroxy-5-O-beta-D-glucopyranosylpsoralen
Catalog No.:BCN1443
CAS No.:425680-98-4
- Luteolin-6-C-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN4985
CAS No.:4261-42-1
- TAK-700 (Orteronel)
Catalog No.:BCC2280
CAS No.:426219-18-3
- TAK-700 salt
Catalog No.:BCC1979
CAS No.:426219-53-6
- 21,23-Dihydro-23-hydroxy-21-oxozapoterin
Catalog No.:BCN7230
CAS No.:426266-88-8
- Dehydrodiconiferyl alcohol
Catalog No.:BCN6878
CAS No.:4263-87-0
- Hemapolin
Catalog No.:BCC8994
CAS No.:4267-80-5
- 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl O-beta-D-6-O-syringate-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1442
CAS No.:426821-85-4
- NS 5806
Catalog No.:BCC7872
CAS No.:426834-69-7
Toxicity and anti-angiogenicity evaluation of Pak1 inhibitor IPA-3 using zebrafish embryo model.[Pubmed:27581547]
Cell Biol Toxicol. 2017 Feb;33(1):41-56.
p21-activated kinase 1 (Pak1)-a key node protein kinase regulating various cellular process including angiogenesis-has been recognised to be a therapeutic target for multitude of diseases, and hence, various small molecule inhibitors targeting its activity have been tested. However, the direct toxic and anti-angiogenic effects of these pharmacologic agents have not been examined. In this study, we evaluate the translational efficacy of Pak1 inhibitor IPA-3 using zebrafish toxicity model system to stratify its anti-angiogenic potential and off-target effects to streamline the compound for further therapeutic usage. The morphometric analysis has shown explicit delay in hatching, tail bending, pericardial sac oedema and abnormal angiogenesis. We provide novel evidence that Pak1 inhibitor could act as anti-angiogenic agents by impeding the development of sub-intestinal vessel (SIV) and intersegmental vessels (ISVs) by suppressing the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), VEGF receptor 2 (VEGFR2), neurophilin 1 (NRP1) and its downstream genes matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9. Knockdown studies using 2-O-methylated oligoribonucleotides targeting Pak1 also revealed similar phenotypes with inhibition of angiogenesis accompanied with deregulation of major angiogenic factor and cardiac-specific genes. Taken together, our findings indicate that Pak1 signalling facilitates enhanced angiogenesis and also advocated the design and use of small molecule inhibitors of Pak1 as potent anti-angiogenic agents and suggest their utility in combinatorial therapeutic approaches targeting anomalous angiogenesis.
Inhibition of p21-Activated Kinase 1 by IPA-3 Promotes Locomotor Recovery After Spinal Cord Injury in Mice.[Pubmed:26863260]
Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016 Jun;41(11):919-25.
STUDY DESIGN: Ninety-six male adult CD-1 mice were randomly divided into sham, spinal cord injury (SCI) + vehicle, and SCI + IPA-3 groups. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9, production of tumor necrosis factors (TNF)-alpha and interleukin (IL)-1beta, tissue edema, blood-spinal cord barrier penetrability, neural cell apoptosis, and neurological function recovery were measured. OBJECTIVE: The aim of the study was to evaluate the effect of specific inhibition of p21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1) by IPA-3 on SCI and the underlying mechanisms thereof. SUMMARY OF BACKGROUND DATA: SCI is a devastating clinical condition that may result in long-lasting and deteriorating functional deficits. The major goal of SCI treatment is to limit the development of secondary injury. IPA-3, a PAK1 inhibitor, exhibited neuroprotection against secondary damage after traumatic brain injury and subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). METHODS: MMP-2, MMP-9, and cleaved caspase-3 expression were assessed by Western blot. Inflammatory cytokines TNF-alpha and IL-1beta were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The blood-spinal cord barrier disruption was measured by water content and Evans blue extravasation of the spinal cord. Neuronal apoptosis was evaluated by Nissl staining and Terminal-deoxynucleoitidyl Transferase Mediated Nick End Labeling (TUNEL) assay. The locomotor behavior of hind limb was evaluated by Basso Mouse Scale (BMS) at 1, 3, 7, 14, and 28 days post-injury. RESULTS: Compared with SCI + vehicle mice, IPA-3 treatment showed decreased p-PAK1, MMP-2, MMP-9, cleaved caspase-3, TNF-alpha, and IL-1beta expression. Moreover, inhibition of PAK1 by IPA-3 reduced spinal cord water content and Evans blue extravasation, increased neuronal survival, and reduced TUNEL-positive cells at 24 hours after SCI. Furthermore, IPA-3 improved spinal cord functional recovery 7 days after SCI. CONCLUSION: Inhibition of PAK1 by IPA-3 promoted recovery of neurological function, possibly by downregulating the expression of MMP-2, MMP-9, TNF-alpha, and IL-1beta. Our data suggest that PAK1 may be a potential therapeutic target in patients with SCI. LEVEL OF EVIDENCE: 1.
Liposome-mediated delivery of the p21 activated kinase-1 (PAK-1) inhibitor IPA-3 limits prostate tumor growth in vivo.[Pubmed:26949163]
Nanomedicine. 2016 Jul;12(5):1231-1239.
P21 activated kinases-1 (PAK-1) is implicated in various diseases. It is inhibited by the small molecule 'inhibitor targeting PAK1 activation-3' (IPA-3), which is highly specific but metabolically unstable. To address this limitation we encapsulated IPA-3 in sterically stabilized liposomes (SSL). SSL-IPA-3 averaged 139nm in diameter, polydispersity index (PDI) of 0.05, and a zeta potential of -28.1, neither of which changed over 14days; however, the PDI increased to 0.139. Analysis of liposomal IPA-3 levels demonstrated good stability, with 70% of IPA-3 remaining after 7days. SSL-IPA-3 inhibited prostate cancer cell growth in vitro with comparable efficacy to free IPA-3. Excitingly, only a 2day/week dose of SSL-IPA-3 was needed to inhibit the growth of prostate xenografts in vivo, while a similar dose of free IPA-3 was ineffective. These data demonstrate the development and clinical utility of a novel liposomal formulation for the treatment of prostate cancer.
Inhibition of p21-activated kinase 1 by IPA-3 attenuates secondary injury after traumatic brain injury in mice.[Pubmed:25148711]
Brain Res. 2014 Oct 17;1585:13-22.
The p21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1) is up-regulated in the brain following traumatic brain injury (TBI). Inhibition of PAK1 has been found to alleviate brain edema in a rat model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Suppressing PAK1 activity might represent a novel therapeutics of attenuating secondary injury following TBI. Here we confirmed that the mRNA and protein levels of PAK1 and the protein level of p-PAK1 were significantly increased after inducing TBI in mice via M.A. Flierl's weight-drop model. A single intraperitoneal administration of IPA-3, a specific PAK1 inhibitor, immediately after TBI significantly reduced the protein level of p-PAK1, cleaved caspase-3 level, the number of apoptotic cells at the lesion sites of TBI mice. It also reduced brain water content and the blood-brain barrier permeability in TBI mice. Furthermore, the administration of IPA-3 significantly reduced the neurological severity score and increased the grip test score in TBI mice. Taken together, we demonstrate that PAK1 inhibition by IPA-3 may attenuate the secondary injury following TBI, suggesting it might be a promising neuroprotective strategy for preventing the development of secondary injury after TBI.
P21-Activated Kinase Inhibitors FRAX486 and IPA3: Inhibition of Prostate Stromal Cell Growth and Effects on Smooth Muscle Contraction in the Human Prostate.[Pubmed:27071060]
PLoS One. 2016 Apr 12;11(4):e0153312.
Prostate smooth muscle tone and hyperplastic growth are involved in the pathophysiology and treatment of male lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS). Available drugs are characterized by limited efficacy. Patients' adherence is particularly low to combination therapies of 5alpha-reductase inhibitors and alpha1-adrenoceptor antagonists, which are supposed to target contraction and growth simultaneously. Consequently, molecular etiology of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and new compounds interfering with smooth muscle contraction or growth in the prostate are of high interest. Here, we studied effects of p21-activated kinase (PAK) inhibitors (FRAX486, IPA3) in hyperplastic human prostate tissues, and in stromal cells (WPMY-1). In hyperplastic prostate tissues, PAK1, -2, -4, and -6 may be constitutively expressed in catecholaminergic neurons, while PAK1 was detected in smooth muscle and WPMY-1 cells. Neurogenic contractions of prostate strips by electric field stimulation were significantly inhibited by high concentrations of FRAX486 (30 muM) or IPA3 (300 muM), while noradrenaline- and phenylephrine-induced contractions were not affected. FRAX486 (30 muM) inhibited endothelin-1- and -2-induced contractions. In WPMY-1 cells, FRAX486 or IPA3 (24 h) induced concentration-dependent (1-10 muM) degeneration of actin filaments. This was paralleled by attenuation of proliferation rate, being observed from 1 to 10 muM FRAX486 or IPA3. Cytotoxicity of FRAX486 and IPA3 in WPMY-1 cells was time- and concentration-dependent. Stimulation of WPMY-1 cells with endothelin-1 or dihydrotestosterone, but not noradrenaline induced PAK phosphorylation, indicating PAK activation by endothelin-1. Thus, PAK inhibitors may inhibit neurogenic and endothelin-induced smooth muscle contractions in the hyperplastic human prostate, and growth of stromal cells. Targeting prostate smooth muscle contraction and stromal growth at once by a single compound is principally possible, at least under experimental conditions.
Membrane transport of WAVE2 and lamellipodia formation require Pak1 that mediates phosphorylation and recruitment of stathmin/Op18 to Pak1-WAVE2-kinesin complex.[Pubmed:19162178]
Cell Signal. 2009 May;21(5):695-703.
Membrane transport of WAVE2 that leads to lamellipodia formation requires a small GTPase Rac1, the motor protein kinesin, and microtubules. Here we explore the possibility of whether the Rac1-dependent and kinesin-mediated WAVE2 transport along microtubules is regulated by a p21-activated kinase Pak as a downstream effector of Rac1. We find that Pak1 constitutively binds to WAVE2 and is transported with WAVE2 to the leading edge by stimulation with hepatocyte growth factor (HGF). Concomitantly, phosphorylation of tubulin-bound stathmin/Op18 at serine 25 (Ser25) and Ser38, microtubule growth, and stathmin/Op18 binding to kinesin-WAVE2 complex were induced. The HGF-induced WAVE2 transport, lamellipodia formation, stathmin/Op18 phosphorylation at Ser38 and binding to kinesin-WAVE2 complex, but not stathmin/Op18 phosphorylation at Ser25 and microtubule growth, were abrogated by Pak1 inhibitor IPA-3 and Pak1 depletion with small interfering RNA (siRNA). Moreover, stathmin/Op18 depletion with siRNA caused significant inhibition of HGF-induced WAVE2 transport and lamellipodia formation, with HGF-independent promotion of microtubule growth. Collectively, it is suggested that Pak1 plays a critical role in HGF-induced WAVE2 transport and lamellipodia formation by directing Pak1-WAVE2-kinesin complex toward the ends of growing microtubules through phosphorylation and recruitment of tubulin-bound stathmin/Op18 to the complex.
An allosteric kinase inhibitor binds the p21-activated kinase autoregulatory domain covalently.[Pubmed:19723886]
Mol Cancer Ther. 2009 Sep;8(9):2559-65.
Kinases are important therapeutic targets in oncology due to their frequent deregulation in cancer. Typical ATP-competitive kinase inhibitors, however, also inhibit off-target kinases that could lead to drug toxicity. Allosteric inhibitors represent an alternative approach to achieve greater kinase selectivity, although examples of such compounds are few. Here, we elucidate the mechanism of action of IPA-3, an allosteric inhibitor of Pak kinase activation. We show that IPA-3 binds covalently to the Pak1 regulatory domain and prevents binding to the upstream activator Cdc42. Preactivated Pak1, however, is neither inhibited nor bound significantly by IPA-3, demonstrating exquisite conformational specificity of the interaction. Using radiolabeled IPA-3, we show that inhibitor binding is specific and reversible in reducing environments. Finally, cell experiments using IPA-3 implicate Pak1 in phorbol-ester-stimulated membrane ruffling. This study reveals a novel allosteric mechanism for kinase inhibition through covalent targeting of a regulatory domain.
An isoform-selective, small-molecule inhibitor targets the autoregulatory mechanism of p21-activated kinase.[Pubmed:18420139]
Chem Biol. 2008 Apr;15(4):322-31.
Autoregulatory domains found within kinases may provide more unique targets for chemical inhibitors than the conserved ATP-binding pocket targeted by most inhibitors. The kinase Pak1 contains an autoinhibitory domain that suppresses the catalytic activity of its kinase domain. Pak1 activators relieve this autoinhibition and initiate conformational rearrangements and autophosphorylation events leading to kinase activation. We developed a screen for allosteric inhibitors targeting Pak1 activation and identified the inhibitor IPA-3. Remarkably, preactivated Pak1 is resistant to IPA-3. IPA-3 also inhibits activation of related Pak isoforms regulated by autoinhibition, but not more distantly related Paks, nor >200 other kinases tested. Pak1 inhibition by IPA-3 in live cells supports a critical role for Pak in PDGF-stimulated Erk activation. These studies illustrate an alternative strategy for kinase inhibition and introduce a highly selective, cell-permeable chemical inhibitor of Pak.
p21-activated kinases in cancer.[Pubmed:16723992]
Nat Rev Cancer. 2006 Jun;6(6):459-71.
The pivotal role of kinases in signal transduction and cellular regulation has lent them considerable appeal as pharmacological targets across a broad spectrum of cancers. p21-activated kinases (Paks) are serine/threonine kinases that function as downstream nodes for various oncogenic signalling pathways. Paks are well-known regulators of cytoskeletal remodelling and cell motility, but have recently also been shown to promote cell proliferation, regulate apoptosis and accelerate mitotic abnormalities, which results in tumour formation and cell invasiveness. Alterations in Pak expression have been detected in human tumours, which makes them an attractive new therapeutic target.


