Indacaterolβ2-agonist CAS# 312753-06-3 |
- INCB3344
Catalog No.:BCC1648
CAS No.:1262238-11-8
- RS 504393
Catalog No.:BCC1910
CAS No.:300816-15-3
- MK-0812
Catalog No.:BCC1755
CAS No.:624733-88-6
- INCB 3284 dimesylate
Catalog No.:BCC1646
CAS No.:887401-93-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 312753-06-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6433117 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C24H28N2O3 | M.Wt | 392.49 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 83.33 mg/mL (212.31 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
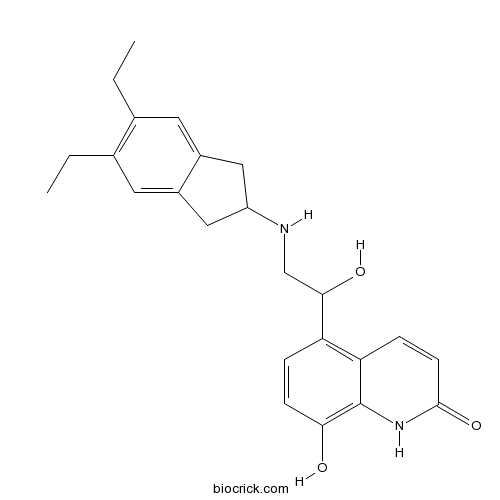
| Chemical Name | 5-[2-[(5,6-diethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-2-yl)amino]-1-hydroxyethyl]-8-hydroxy-1H-quinolin-2-one | ||
| SMILES | CCC1=C(C=C2CC(CC2=C1)NCC(C3=C4C=CC(=O)NC4=C(C=C3)O)O)CC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QZZUEBNBZAPZLX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C24H28N2O3/c1-3-14-9-16-11-18(12-17(16)10-15(14)4-2)25-13-22(28)19-5-7-21(27)24-20(19)6-8-23(29)26-24/h5-10,18,22,25,27-28H,3-4,11-13H2,1-2H3,(H,26,29) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Indacaterol Dilution Calculator

Indacaterol Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5478 mL | 12.7392 mL | 25.4784 mL | 50.9567 mL | 63.6959 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5096 mL | 2.5478 mL | 5.0957 mL | 10.1913 mL | 12.7392 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2548 mL | 1.2739 mL | 2.5478 mL | 5.0957 mL | 6.3696 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.051 mL | 0.2548 mL | 0.5096 mL | 1.0191 mL | 1.2739 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0255 mL | 0.1274 mL | 0.2548 mL | 0.5096 mL | 0.637 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Indacaterol is a novel, once-daily (o.d.) inhaled, long-acting β2-agonist in development for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- gamma-Mangostin
Catalog No.:BCN5228
CAS No.:31271-07-5
- THIQ
Catalog No.:BCC7539
CAS No.:312637-48-2
- SKI II
Catalog No.:BCC5029
CAS No.:312636-16-1
- Tetrahydrocannabivarin
Catalog No.:BCN6935
CAS No.:31262-37-0
- IQ 3
Catalog No.:BCC8093
CAS No.:312538-03-7
- Cimigenol-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN7430
CAS No.:31222-32-9
- Eucalyptin
Catalog No.:BCN5227
CAS No.:3122-88-1
- Sideroxylin
Catalog No.:BCN5226
CAS No.:3122-87-0
- H-D-Ser-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2676
CAS No.:312-84-5
- Methylionene
Catalog No.:BCN7120
CAS No.:31197-54-3
- Sudan II
Catalog No.:BCN8383
CAS No.:3118-97-6
- D-Xylose
Catalog No.:BCC8320
CAS No.:31178-70-8
- Hygromycin B
Catalog No.:BCC1204
CAS No.:31282-04-9
- Raucaffricine
Catalog No.:BCN4653
CAS No.:31282-07-2
- TCS JNK 5a
Catalog No.:BCC5148
CAS No.:312917-14-9
- LDN-27219
Catalog No.:BCC6236
CAS No.:312946-37-5
- Arjunic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5229
CAS No.:31298-06-3
- Estradiol Cypionate
Catalog No.:BCC4477
CAS No.:313-06-4
- Aristolochic acid A
Catalog No.:BCN6262
CAS No.:313-67-7
- ICA 121431
Catalog No.:BCC6358
CAS No.:313254-51-2
- Regadenoson
Catalog No.:BCC6438
CAS No.:313348-27-5
- Reversan
Catalog No.:BCC7764
CAS No.:313397-13-6
- VU 590 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7803
CAS No.:313505-85-0
- T0070907
Catalog No.:BCC2261
CAS No.:313516-66-4
Indacaterol/glycopyrronium versus salmeterol/fluticasone in Asian patients with COPD at a high risk of exacerbations: results from the FLAME study.[Pubmed:28176893]
Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2017 Jan 19;12:339-349.
BACKGROUND: The FLAME study demonstrated that Indacaterol/glycopyrronium (IND/GLY), the fixed-dose combination of a long-acting beta2-agonist (LABA, IND) and a long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA, GLY), was superior to salmeterol/fluticasone combination (SFC) in preventing exacerbations in COPD patients with a high risk of exacerbations. In this study, we report a prespecified analysis of the efficacy and safety of IND/GLY versus SFC in Asian patients from the FLAME study. PATIENTS AND METHODS: Patients from Asian centers with moderate-to-very severe COPD and >/=1 exacerbation in the previous year from the 52-week, randomized FLAME study were included. IND/GLY was compared versus SFC for effects on exacerbations, lung function (forced expiratory volume in 1 second [FEV1] and forced vital capacity [FVC]), health status (St George's Respiratory Questionnaire [SGRQ]), rescue medication use, and safety. RESULTS: A total of 510 Asian patients (IND/GLY, n=250 or SFC, n=260) were included. Compared to the overall FLAME population, the Asian cohort had more males, a shorter duration of COPD, fewer patients using inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) at screening, fewer current smokers, and more patients with very severe COPD. IND/GLY significantly reduced the rate of moderate/severe exacerbations (rate ratio: 0.75; 95% confidence interval: 0.58-0.97; P=0.027) and prolonged time to first moderate/severe exacerbation versus SFC (hazard ratio: 0.77; 95% confidence interval: 0.59-1.01; P=0.055). Predose trough FEV1 and FVC significantly improved in Asian patients (P<0.001). IND/GLY improved SGRQ for COPD (SGRQ-C score; P=0.006) and reduced rescue medication use (P=0.058) at week 52. Pneumonia incidence was 3.6% with IND/GLY and 7.7% with SFC (P=0.046). CONCLUSION: In exacerbating Asian COPD patients, IND/GLY was more effective than SFC.
Efficacy and safety of indacaterol/glycopyrronium fixed-dose combination in mild-to-moderate COPD patients symptomatic on tiotropium in Korea: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.[Pubmed:28228162]
Trials. 2017 Feb 22;18(1):80.
BACKGROUND: Long-acting bronchodilator monotherapy (long-acting beta2-agonist [LABA] or long-acting muscarinic antagonist [LAMA]) is extensively used for treatment of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) with mild-to-moderate airflow limitation. However, a substantial number of patients remain symptomatic despite treatment with a single bronchodilator, necessitating a change in therapy. METHODS: This 12-week, randomized, multicenter, open-label, phase IV study aims to show that the once-daily Indacaterol/glycopyrronium (IND/GLY) 110/50 mug fixed-dose LABA/LAMA combination results in an improved lung function in symptomatic patients with mild-to-moderate COPD who switch from once-daily tiotropium 18 mug. The study aims to enroll a total of 404 symptomatic patients in Korea with mild-to-moderate COPD who received tiotropium for at least 12 weeks prior to the study initiation. The primary objective of this study is to demonstrate the superiority of IND/GLY over tiotropium in terms of trough forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) following 12 weeks of treatment. Secondary endpoints include the pre-dose trough FEV1 after 4 weeks of treatment, transition dyspnea index (TDI) total score, COPD assessment test (CAT) total score, and rescue medication use following the 12-week treatment, and safety assessment over the 12-week treatment. DISCUSSION: This study intends to establish the use of LABA/LAMA combination therapy in symptomatic patients with mild-to-moderate COPD by demonstrating the superiority of IND/GLY over tiotropium monotherapy. TRIAL REGISTRATION: ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT02566031 . Registered on 10 August 2015.
Immediate salbutamol responsiveness does not predict long-term benefits of indacaterol in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.[Pubmed:28143447]
BMC Pulm Med. 2017 Jan 31;17(1):25.
BACKGROUND: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the correlation between immediate responsiveness with the short-acting beta2-agonist salbutamol and effects of treatment with the ultra-long-acting beta2-agonist Indacaterol in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). METHODS: The REVERBREZ study was a phase IV, multicentre, open-label study in which patients with moderate-to-severe COPD received Indacaterol 150 mug once-daily for 5 months. The primary endpoint was the correlation between immediate response of forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1) post-inhalation of salbutamol (400 mug) at study entry and the change from baseline in trough FEV1 after 1 month of Indacaterol. Secondary endpoints included dyspnoea measured by the modified Medical Research Council (mMRC) grade and health-related quality of life measured by the clinical COPD questionnaire (CCQ). RESULTS: Of the 602 patients enrolled from 177 centres in France, 543 patients received at least one Indacaterol dose, 512 patients completed 1 month of Indacaterol treatment (primary endpoint), and 400 patients completed 5 months of treatment. At study entry, mean FEV1 values before and after salbutamol inhalation were 1.54 +/- 0.50 L and 1.65 +/- 0.53 L, respectively. Based on the magnitude of an immediate response of FEV1 after salbutamol inhalation at study entry, patients were classified into reversible (Rv, >/=12% and >/=200 mL from pre-salbutamol value; n = 106) and non-reversible (NRv, <12% or <200 mL from pre-salbutamol value; n = 431) groups. After 1 month of Indacaterol treatment, mean absolute and relative difference in trough FEV1 were 100 mL and 9%, respectively. No significant correlation was found between the immediate FEV1 response to salbutamol at study entry and change from baseline in trough FEV1 after 1 month of Indacaterol treatment (correlation coefficient = 0.056 [95% CI;-0.032, 0.144] for absolute response and 0.028 [95% CI;-0.06, 0.116] for relative response). At all subsequent visits, mMRC and CCQ scores, and FEV1 improved from baseline with no significant difference between the Rv and NRv groups. CONCLUSIONS: Immediate FEV1 response to salbutamol did not predict the long-term benefits observed with Indacaterol treatment in patients with COPD. Patients considered reversible or non-reversible to salbutamol showed comparable improvements in lung function, dyspnoea and health-related quality of life. TRIAL REGISTRATION: ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT01272362 . Date: January 5, 2011.
Combination of glycopyrronium and indacaterol inhibits carbachol-induced ERK5 signal in fibrotic processes.[Pubmed:28284212]
Respir Res. 2017 Mar 11;18(1):46.
BACKGROUND: Airway fibrosis is one of the pathological features of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and recent studies revealed that acetylcholine plays an important role in the development of airway remodeling by stimulating proliferation and collagen synthesis of lung fibroblasts. This study was designed to examine the effects of a long-acting muscarinic receptor antagonist (LAMA) glycopyrronium and a long-acting beta2 adrenergic receptor agonist (LABA) Indacaterol on acetylcholine-mediated fibrotic responses in lung fibroblasts. METHODS: After carbachol (CCh) or transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) exposure, the response to glycopyrronium and Indacaterol was determined in vitro in fibroblasts isolated from mild-to-moderate COPD lung tissue. The ability of fibroblasts to mediate the contraction of collagen gels was assessed. The expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin (alpha-SMA) and the phosphorylation of extracellular-signal-regulated kinase 5 (ERK5) were determined by immunoblot. TGF-beta1 was quantified by ELISA and acetylcholine was quantified by liquid chromatography tandem-mass spectrometry. RESULTS: CCh stimulated fibroblast-mediated collagen gel contraction and alpha-SMA expression and TGF-beta1 release by fibroblasts. Blockade of autocrine TGF-beta1 attenuated CCh-mediated fibrotic responses, while TGF-beta1 did not stimulate acetylcholine release. Glycopyrronium plus Indacaterol significantly attenuated CCh- and TGF-beta1-mediated fibrotic responses through inhibition of ERK5 phosphorylation. Notably, the magnitudes of CCh- and TGF-beta1-stimulated gel contraction, CCh-induced TGF-beta1 release, and ERK5 phosphorylation were greater in fibroblasts isolated from COPD subjects than in those from non-smokers. CONCLUSIONS: CCh induced TGF-beta1 self-sustaining signaling loops by potentiating ERK5 signaling and promoted myofibroblast activity. This autocrine signaling mechanism may be an attractive therapeutic target to block the fibrotic response, which was modulated by the combination of glycopyrronium and Indacaterol.


