IsomenthoneCAS# 491-07-6 |
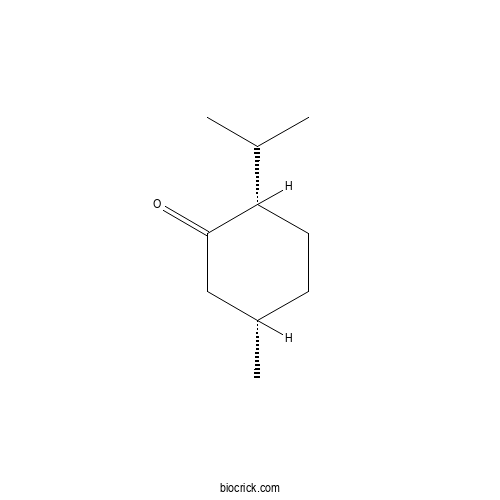
- p-Menthan-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN3850
CAS No.:10458-14-7
- (+)-Menthone
Catalog No.:BCC9239
CAS No.:89-80-5
- (-)-Menthone
Catalog No.:BCN9070
CAS No.:14073-97-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 491-07-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6432469 | Appearance | Colorless - yellowish liquid |
| Formula | C10H18O | M.Wt | 154.25 |
| Type of Compound | Isoprenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | cis-p-Menthan 3-one | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in acetone, chloroform, diethyl ether, ethanol and petroleum ether; insoluble in water | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S,5S)-5-methyl-2-propan-2-ylcyclohexan-1-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1CCC(C(=O)C1)C(C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NFLGAXVYCFJBMK-IUCAKERBSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C10H18O/c1-7(2)9-5-4-8(3)6-10(9)11/h7-9H,4-6H2,1-3H3/t8-,9-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Isomenthone Dilution Calculator

Isomenthone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.483 mL | 32.4149 mL | 64.8298 mL | 129.6596 mL | 162.0746 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.2966 mL | 6.483 mL | 12.966 mL | 25.9319 mL | 32.4149 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.6483 mL | 3.2415 mL | 6.483 mL | 12.966 mL | 16.2075 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1297 mL | 0.6483 mL | 1.2966 mL | 2.5932 mL | 3.2415 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0648 mL | 0.3241 mL | 0.6483 mL | 1.2966 mL | 1.6207 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Hyperforin (stable Dicyclohexylammonium salt)
Catalog No.:BCN0327
CAS No.:238074-03-8
- 3'-Hydroxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN0326
CAS No.:70460-18-3
- (Rac)-Hesperetin
Catalog No.:BCN0325
CAS No.:69097-99-0
- Grindelic acid
Catalog No.:BCN0324
CAS No.:1438-57-9
- Fukinolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN0323
CAS No.:50982-40-6
- trans-Ferulic acid
Catalog No.:BCN0322
CAS No.:537-98-4
- Euphorbol
Catalog No.:BCN0321
CAS No.:566-14-3
- Ethyl trans-caffeate
Catalog No.:BCN0320
CAS No.:66648-50-8
- (+/-)-Eriodictyol
Catalog No.:BCN0319
CAS No.:4049-38-1
- Echinatine N-oxide
Catalog No.:BCN0318
CAS No.:20267-93-0
- Diosmetin 7-glucuronide
Catalog No.:BCN0317
CAS No.:35110-20-4
- 2',6'-Dihydroxy 4',4-dimethoxychalcone
Catalog No.:BCN0316
CAS No.:94441-99-3
- Isoxanthohumol
Catalog No.:BCN0329
CAS No.:521-48-2
- Lactucin
Catalog No.:BCN0330
CAS No.:1891-29-8
- Lavandulol
Catalog No.:BCN0331
CAS No.:58461-27-1
- Lavandulyl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN0332
CAS No.:25905-14-0
- (+)-Lupanine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN0333
CAS No.:1025-39-4
- 6-Methoxytricin
Catalog No.:BCN0334
CAS No.:76015-42-4
- 16-O-Methylcafestol
Catalog No.:BCN0335
CAS No.:108214-28-4
- Naringenin chalcone
Catalog No.:BCN0336
CAS No.:25515-46-2
- Pinocembroside
Catalog No.:BCN0337
CAS No.:75829-43-5
- (S)-4',5,7-Trihydroxy-6-prenylflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN0338
CAS No.:68682-01-9
- Sophoraflavanone B
Catalog No.:BCN0339
CAS No.:68682-02-0
- Rebaudioside I
Catalog No.:BCN0340
CAS No.:1220616-34-1
Comparative investigation on aroma profiles of five different mint (Mentha) species using a combined sensory, spectroscopic and chemometric study.[Pubmed:34537605]
Food Chem. 2021 Sep 9;371:131104.
Mint is a widely used aromatic plant, and the aroma varies among different species. The aroma of five mint species, Mentha citrata L. (MC), Mentha piperita L. (MPI), Mentha spicata L. (MSP), Mentha persicaria L. (MPE), and Mentha suaveolens L. (MSU), were comparatively studied on the sensorial and molecular level. Quantitative descriptive analysis revealed that MC presented a pronounced lemon-like note, MSU is dominated by citrus and floral aromas, MPI has a prominent minty flavor, MSP and MPE have a similar scent, both of which are flavored with a spearmint-like note. Forty-one odorants with odor activity values (OAVs) >/=1 were characterized. Principal component analysis and orthogonal partial least squares discrimination analysis based on OAVs indicated that alpha-citral, menthofuran, Isomenthone, menthol, carvone, and linalool were potential odor-active markers for five mint species discrimination. This study herein will provide guidance for mint resources utilization and also aid mint breeding with better flavor.
Essential Oils of Four Virginia Mountain Mint (Pycnanthemum virginianum) Varieties Grown in North Alabama.[Pubmed:34371600]
Plants (Basel). 2021 Jul 8;10(7). pii: plants10071397.
Virginia mountain mint (Pycnanthemum virginianum) is a peppermint-flavored aromatic herb of the Lamiaceae and is mainly used for culinary, medicinal, aromatic, and ornamental purposes. North Alabama's climate is conducive to growing mint for essential oils used in culinary, confectionery, and medicinal purposes. There is, however, a need for varieties of P. virginianum that can be adapted and easily grown for production in North Alabama. Towards this end, four field-grown varieties with three harvesting times (M1H1, M1H2, M1H3; M2H1, M2H2, M2H3; M3H1, M3H2, M3H3, M4H1, M4H2, M4H3) were evaluated for relative differences in essential oil yield and composition. Thirty-day-old greenhouse-grown plants of the four varieties were transplanted on raised beds in the field at the Alabama A & M University Research Station in North Alabama. The plots were arranged in a randomized complete block with three replications. The study's objective was to compare the four varieties for essential oil yield and their composition at three harvest times, 135, 155, and 170 days after planting (DAP). Essential oils were obtained by hydrodistillation with continuous extraction with dichloromethane using a Likens-Nickerson apparatus and analyzed by gas chromatographic techniques. At the first harvest, the essential oil yield of the four varieties showed that M1H1 had a yield of 1.15%, higher than M2H1, M3H1, and M4H1 with 0.91, 0.76, and 1.03%, respectively. The Isomenthone concentrations increased dramatically through the season in M1 (M1H1, M1H2, M1H3) by 19.93, 54.7, and 69.31%, and M3 (M3H1, M3H2, M3H3) by 1.81, 48.02, and 65.83%, respectively. However, it increased only slightly in M2 and M4. The thymol concentration decreased slightly but not significantly in all four varieties; the thymol in M2 and M4 was very high compared with M1 and M3. The study showed that mountain mint offers potential for production in North Alabama. Two varieties, M1 and M3, merit further studies to determine yield stability, essential oil yield, composition, and cultivation development practices.
Cytosolic geraniol and citronellol biosynthesis require a Nudix hydrolase in rose-scented geranium (Pelargonium graveolens).[Pubmed:33949016]
Plant J. 2021 Jul;107(2):493-510.
Geraniol, citronellol and their esters are high-value acyclic monoterpenes used in food technology, perfumery and cosmetics. A major source of these compounds is the essential oil of rose-scented geraniums of the genus Pelargonium. We provide evidence that their biosynthesis mainly takes place in the cytosol of glandular trichomes via geranyl monophosphate (GP) through the action of a Nudix hydrolase. Protein preparations could convert geranyl diphosphate (GDP) to geraniol in in vitro assays, a process which could be blocked by inorganic phosphatase inhibitors, suggesting a two-step conversion of GDP to geraniol. Pelargonium graveolens chemotypes enriched in either geraniol or (-)-citronellol accumulate GP or citronellyl monophosphate (CP), respectively, the presumed precursors to their monoterpenoid end products. Geranyl monophosphate was highly enriched in isolated glandular trichomes of lines producing high amounts of geraniol. In contrast, (-)-Isomenthone-rich lines are depleted in these prenyl monophosphates and monoterpene alcohols and instead feature high levels of GDP, the precursor to plastidic p-menthane biosynthesis. A Nudix hydrolase cDNA from Pelargonium glandular trichomes, dubbed PgNdx1, encoded a cytosolic protein capable of hydrolyzing GDP to GP with a KM of about 750 nm but is only weakly active towards farnesyl diphosphate. In citronellol-rich lines, GDP, GP and CP were detected in nearly equimolar amounts, while citronellyl diphosphate was absent, suggesting that citronellol biosynthesis may proceed by reduction of GP to CP in this species. These findings highlight the cytosol as a compartment that supports monoterpene biosynthesis and expands the roles of Nudix hydrolases in the biosynthesis of plant volatiles.
Mentha pulegium L.: A Plant Underestimated for Its Toxicity to Be Recovered from the Perspective of the Circular Economy.[Pubmed:33918091]
Molecules. 2021 Apr 8;26(8). pii: molecules26082154.
The aim of the study was to investigate the micromorphology of Mentha pulegium leaves and flowers harvested in three different Sicilian (Italy) areas with peculiar pedo-climatic conditions, and to characterize the phytochemical profile, the phytotoxic activity, and the eco-compatibility of their essential oils (EOs) for potential use as safe bioherbicides. Light microscopy (LM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) highlighted that M. pulegium indumentum consists of non-glandular and glandular trichomes of different types. Peltate trichomes of plants from the different sites showed few significant differences in dimension and abundance, but they were characterized by a surprisingly high number of secretory cells both in leaves and flowers. Phytochemical analyses showed that oxygenated monoterpenes were the most abundant class in all the EOs investigated (92.2-97.7%), but two different chemotypes, pulegone/Isomenthone and piperitone/Isomenthone, were found. The complex of morphological and phytochemical data indicates that soil salinity strongly affects the expression of the toxic metabolite pulegone, rather than the EO yield. Phytotoxicity tests showed a moderate activity of EOs against the selected species as confirmed by alpha-amylase assay. Moreover, the low toxicity on brine shrimp provided a rationale for the possible use of investigated EOs as eco-friendly herbicides.
Spectrum-effect relationship between GC-QTOF-MS fingerprint and antioxidant, anti-inflammatory activities of Schizonepeta tenuifolia essential oil.[Pubmed:33638568]
Biomed Chromatogr. 2021 Jul;35(7):e5106.
Schizonepeta tenuifolia (Benth.) Briq, a traditional Chinese medicine, is an annual herbaceous plant that is widely distributed in China, Japan, and Korea. The essential oil (EO) of S. tenuifolia has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. However, the components contributing to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities remain unclear. This study was aimed at investigating the spectrum-effect relationship between GC-MS fingerprint and the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of S. tenuifolia EO. Here, the fingerprints of EO from 10 batches of S. tenuifolia from various sources were established using GC-MS, and the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory bioactivities were evaluated using 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl and nitric oxide inhibitory assays, respectively. Finally, 13 common peaks were identified from 10 batches of S. tenuifolia by searching against the standard mass spectra in NIST 14 and comparing the literature retention index. The different sources of S. tenuifolia EO exhibit mild antioxidant activities and significant anti-inflammatory effects. In particular, menthone (peak 3), Isomenthone (peak 4), pulegone (peak 7), piperitone (peak 8), and beta-caryophyllene (peak 11) might be the dominant constituents responsible for the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of S. tenuifolia EO. This method may provide a time-saving, convenient way to screen the potential effective components of S. tenuifolia EO.
Optical Investigation of Essential Oils Using Absorbance and Photoluminescence.[Pubmed:33464154]
Appl Spectrosc. 2021 Sep;75(9):1136-1145.
Essential oils are complex mixtures of organic substances with large commercial importance in the pharmaceutical, food, fragrance, and cosmetic industries due to their organoleptic and biological properties. Also, these materials are also luminescent what has taken several studies about its potential uses for the detection and quality control of essential oils, imaging, and for the investigation of the synergies of their constituents. Concerning this, the present work is dedicated to studying the optical properties of selected essential oils: citronella (Cymbopogon winterianus), Japanese mint (Mentha arvensis), clove bud (Syzygium aromaticum), and bergamot (Citrus bergamia). We carried out a comparative study of the photoluminescence and the ultraviolet-visible optical absorption (abs-UV-Vis) of these essential oils with their typical constituents. To inspect the effects of the intermolecular interactions on the optical response of these systems, mixtures between the essential oils constituents following the expected average percent mass fraction were also studied. From these experiments, the main results were bathochromic effects in the abs-UV-Vis spectra; excimer formation in citral, isopulegol, Isomenthone, eugenol, and eugenyl acetate; excimer emission enhancing and specific solvent effect in the essential oils photoluminescence spectra. These results contribute to the knowledge of essential oils' applications, especially in the evaluation of components' interactions through a simple abs-UV-Vis assay.
Heavy metals concentration, and antioxidant activity of the essential oil of the wild mint (Mentha longifolia L.) in the Egyptian watercourses.[Pubmed:33232173]
Int J Phytoremediation. 2021;23(6):641-651.
In the present study, we assessed seasonal variation in the accumulation potential of wild mint (Mentha longifolia) to heavy metals as well as the chemical composition and antioxidant activity of the essential oil of mint in polluted and unpolluted watercourses. The results indicated that the wild mint showed seasonal fluctuations in accumulation potential for heavy metals proved by bioaccumulation factor (BF) and translocation factor (TF). The all measured heavy metals, except Pb were retained in the underground parts. Summer plants accumulated the highest concentrations of Al, Cd, Cr and Fe in their root, while the lowest concentration of Ni in their shoot. The bioaccumulation factor for Cd, Cu, Mn, Ni, Zn and Co was greater than one, while the translocation factor of the investigated metals (except Pb) did not exceed one, indicating the potential of wild mint for phytostabilization of these metals in contaminated wetlands. The yield and composition of mint essential oil (MEO) were affected by harvesting season and heavy metals pollution. GC/MS showed that Isomenthone, cis-piperitenone oxide, menthone and pulegone, were the main oil constituents. Mint essential oil show promising antioxidant activity by 2,2'-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging assay under pollution stress. The maximum reducing power of MEO were obtained during autumn and summer seasons (polluted canals).In conclusion, summer is the ideal season for harvesting wild mint plants for the maximum plant biomass, oil yield, high radical scavenging activity of MEO and to monitor pollution in contaminated wetlands.
Chemical composition and selective BuChE inhibitory activity of the essential oils from aromatic plants used to prepare the traditional Ecuadorian beverage horchata lojana.[Pubmed:32736051]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Dec 5;263:113162.
ETHNOBOTANICAL AND ETHNOMEDICINAL RELEVANCE: In southern Ecuador, horchata lojana is a popular aromatic and refreshing beverage that is prepared from an aqueous infusion of different mixtures of local medicinal and aromatic plants. The drink is considered a traditional anti-inflammatory agent and brain tonic; due these properties, it has been drunk since Colonial Times. Several pharmacological studies have evaluated the effects of horchata aqueous infusion. However, the aromatic profile and the contribution of the volatile components to the biological activity of the drink have not been investigated so far. For these reasons, we have determined the chemical composition of the essential oils (EOs) distilled from five mixtures of aromatic plants commonly used for the preparation of this traditional drink. Moreover, to support the curative properties of the aromatic plants, the anticholinesterase activity of the EOs was examined. MATERIAL AND METHODS: Different bunches of fresh mixed medicinal and aromatic plants, called tongos, are sold at local markets in the province of Loja for the preparation of different types of horchata. In this research we have purchased plant bunches sold at five popular markets of Loja province. Subsequently, aromatic plants in each bunch were separated from medicinal plants and were then hydrodistilled to give the corresponding EOs. Subsequently, the chemical composition of each EO was determined by GC-MS/GC-FID techniques, whereas the cholinesterase inhibitory activity in vitro was determined against acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BuChE) enzymes. AIMS OF THE STUDY: i) to contribute to the chemical and pharmacological study of the aroma components of the traditional Ecuadorian drink horchata lojana; ii) to identify botanically the mixtures of aromatic plants used to make the drink; iii) to establish, on the basis of the chemical composition of the EOs, the compounds mainly responsible for the characteristic beverage flavor; iv) to establish the possible existence of an aromatic pattern characteristic of each horchata preparation; v) to test the anticholinesterase activity of the EOs against AChE and BuChE in order to support the traditional consume of the drink as an effective brain tonic. RESULTS: A total of 23 botanical families and 32 species of plants used for the preparation of five different variants of the traditional horchata lojana beverage, have been identified. Fourteen aromatic species were determined to be responsible for the characteristic flavor of the drink. All the analyzed EOs belong to the monoterpene type. A total of 88 compounds have been identified in the different EOs, twenty-four of which are common components of the oils. CONCLUSIONS: According to the main components of the EOs distilled from the five groups of horchata lojana plants, four aromatic profiles have been defined: (i) neral + geranial + carvone, (ii) neral + geranial + myrcene; (iii) geranial + methyl eugenol + Isomenthone + neral + citronellol; (iv) (E)-anethole + geranial + pulegone. Moreover, according to the literature, several aromatic plants and individual EOs components exhibit a wide range of biological activities. This finding as well as the significant BuChE inhibitory activity exhibited in vitro by the EOs give scientific support to the use of identified aromatic plants in the traditional preparation of horchata, that is considered a natural analgesic and anti-inflammatory remedy, and an effective brain tonic.
Composition and Antibacterial Effect of Mint Flavorings in Candies and Food Supplements.[Pubmed:32365392]
Planta Med. 2020 Oct;86(15):1089-1096.
Mint flavorings are widely used in confections, beverages, and dairy products. For the first time, mint flavoring composition of mint candies and food supplements (n = 45), originating from 16 countries, as well as their antibacterial properties, was analyzed. The flavorings were isolated by Marcusson's type micro-apparatus and analyzed by GC-MS. The total content of the mint flavoring hydrodistilled extracts was in the range of 0.01 - 0.9%. The most abundant compounds identified in the extracts were limonene, 1,8-cineole, menthone, menthofuran, Isomenthone, menthol and its isomers, menthyl acetate. The antimicrobial activity of 13 reference substances and 10 selected mint flavoring hydrodistilled extracts was tested on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus by broth dilution method. Linalool acetate and (-)-carvone, as most active against both bacteria, had the lowest MIC90 values. (+)-Menthyl acetate, (-)-menthyl acetate, and limonene showed no antimicrobial activity. Three of the tested extracts had antimicrobial activity against E. coli and 8 extracts against S. aureus. Their summary antimicrobial activity was not always in concordance with the activities of respective reference substances.
Studies on essential oil from rose-scented geranium, Pelargonium graveolens L'Herit. (Geraniaceae).[Pubmed:31679416]
Nat Prod Res. 2021 Aug;35(15):2593-2597.
Rose-scented geranium, Pelargonium graveolens L'Herit. (Geraniaceae), is an economically important plant. GC-MS analysis of the essential oil, prepared by hydro-distillation from this plant species, showed the presence of iso-menthone (15.71%), epi-alpha-cadinol (15.49%), iso-menthol (6.46%), geranyl formate (6.22%), geraniol (6.16%) and citronellol (5.53%). The composition of the absolute prepared by solvent extraction was compared to that of the essential oil. Change in citronellol to geraniol ratio in the absolute was monitored during leaf development. Estimation of the ratio of the two compounds was carried out using (1)H NMR spectroscopy. Geraniol content was highest in young leaves and citronellol content increased with increase in leaf age. Meta-analysis of the essential oil constituents reported from different countries was carried out. Menthone and Isomenthone as well as citronellol and geraniol were negatively correlated. A significantly positive correlation was found between geraniol and linalool.
Distinct metabolic pathways drive monoterpenoid biosynthesis in a natural population of Pelargonium graveolens.[Pubmed:31504760]
J Exp Bot. 2020 Jan 1;71(1):258-271.
Pelargonium graveolens is a wild predecessor to rose-scented geranium hybrids prized for their essential oils used as fragrances and flavorings. However, little is known about their biosynthesis. Here we present metabolic evidence that at least two distinct monoterpene biosynthetic pathways contribute to their volatile profiles, namely, cyclic p-menthanes such as (-)-Isomenthone and acyclic monoterpene alcohols such as geraniol and (-)-citronellol and their derivatives (referred to here as citronelloid monoterpenes). We established their common origin via the 2C-methyl-d-erythritol-4-phosphate pathway but found no indication these pathways share common intermediates beyond geranyl diphosphate. Untargeted volatile profiling of 22 seed-grown P. graveolens lines demonstrated distinct chemotypes that preferentially accumulate (-)-Isomenthone, geraniol, or (-)-citronellol along with approximately 85 minor volatile products. Whole plant 13CO2 isotopic labeling performed under physiological conditions permitted us to measure the in vivo rates of monoterpenoid accumulation in these lines and quantify differences in metabolic modes between chemotypes. We further determined that p-menthane monoterpenoids in Pelargonium are likely synthesized from (+)-limonene via (+)-piperitone rather than (+)-pulegone. Exploitation of this natural population enabled a detailed dissection of the relative rates of competing p-menthane and citronelloid pathways in this species, providing real time rates of monoterpene accumulation in glandular trichomes.
Heterogeneously Catalysed Oxidative Dehydrogenation of Menthol in a Fixed-Bed Reactor in the Gas Phase.[Pubmed:31406653]
ChemistryOpen. 2019 Jun 11;8(8):1066-1075.
For the first time, the oxidative dehydrogenation of (-)-menthol to (-)-menthone and (+)-Isomenthone in a marketable quality was carried out in a continuous gas phase reactor as a sustainable process using molecular oxygen as green oxidant and solid catalysts which do not contaminate the product mixture and which are easily to remove. The diastereomeric purity remained largely unchanged. Three types of catalysts were found to be very active and selective in the formation of menthone and Isomenthone: AgSr/SiO2, CuO distributed on a basic support and RuMnCe/CeO2, where Ru, Mn and Ce exist in an oxidized state. The best overall yield of menthon/Isomenthone obtained with an Ag-based catalyst was 58 % at 64 % selectivity, with a Cu-based catalyst 41 % at 51 % selectivity and with a Ru-based catalyst 68 % at 73 % selectivity. Reaction conditions were widely optimized.
Minor constituents of essential oils and aromatic extracts. Oximes derived from natural flavor and fragrance raw materials - Sensory evaluation, spectral and gas chromatographic characteristics.[Pubmed:31377615]
Food Chem. 2019 Dec 15;301:125283.
A small library of 57 low molecular weight oximes was prepared from fragrant aldehydes and ketones, and their olfactory profiles were determined. The most substantive and interesting in terms of the sensory impressions were (+)-Isomenthone oxime (fresh, musty, green) and cyclocitral oxime (earthy with patchouli, moss and leather notes). The linear retention indices (LRI) were determined for DB-1, DB-5 and DB-WAX columns, and E/Z isomers of 22 out of 57 compounds were resolved on the DB-5 column. Attempts were made to resolve enantiomers of the chosen oximes on chiral GC columns. The best results were obtained by using a Cyclosil B column, on which the enantiomers of camphor, menthone, piperitone and carvone oximes were fully resolved. NMR and MS spectra were acquired to characterize the synthesized library. Gas chromatography-olfactometry was used to assess odoriferous properties of both isomers of oximes. In most cases both isomers possessed similar profile and intensity.
Chemical Composition and Enzymatic Screening of Micromeria fruticosa serpyllifolia Volatile Oils Collected from Three Different Regions of West Bank, Palestine.[Pubmed:30410936]
Biomed Res Int. 2018 Oct 16;2018:6536919.
Introduction: Volatile oils (VOs) have been commonly used in cosmetics and food as fragrances, flavoring, and preservative agents or in alternative medicine for their therapeutic effects. This necessitates investigating those plants and their VOs. This study was conducted to investigate the chemical compositions of the VOs of Micromeria fruticosa serpyllifolia growing widely in three regions in Palestine (i.e., Hebron, Ramallah, and Nablus districts representing south, middle, and north of West Bank). Afterwards, VOs were subjected to in vitro screening and their enzymatic properties were compared. Methods: The analysis of chemical components of VOs was performed by gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The antilipase activity was evaluated using porcine pancreatic lipase and p-nitrophenyl butyrate. The antiamylase activity was assessed using porcine pancreatic alpha-amylase, starch, and 3,5-dinitrosalicylic. Results: Plant extracts yield range was 0.67 to 0.99 w/w%. GC-MS analysis showed the high percentages of oxygenated components in the range of 86.1-89.88% and nonoxygenated components in the range of 4.38-4.71%. Seven components were observed, pulegone was the most abundant component in the three samples in the range of 74.43-86.04%, and Isomenthone was the second most abundant component with the range of 3.16-14.41%. The sample collected from Nablus showed the most potent antilipase and antiamylase activity with IC50 values of 39.81 mug/mL and 3.31 mug/mL, respectively. Conclusions: The study showed that Micromeria fruticosa serpyllifolia volatile oils samples from different regions in Palestine contained different proportions of phytochemicals which provided different potential biological activities such as antiobesity and antidiabetes activities that were in line with traditional uses of the plant extracts. The plant extracts showed higher antilipase and antiamylase potency than that of the relative references and there were significant differences in these activities compared to each other.


