L-carnosineCAS# 305-84-0 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 305-84-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 439224 | Appearance | Powder |
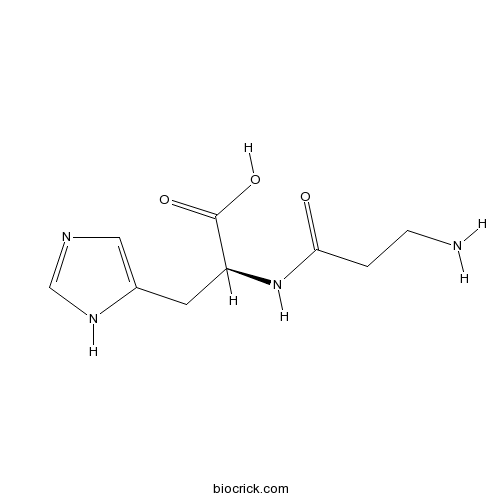
| Formula | C9H14N4O3 | M.Wt | 226.23 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | H2O : 125 mg/mL (552.54 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S)-2-(3-aminopropanoylamino)-3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)propanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1=C(NC=N1)CC(C(=O)O)NC(=O)CCN | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CQOVPNPJLQNMDC-ZETCQYMHSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C9H14N4O3/c10-2-1-8(14)13-7(9(15)16)3-6-4-11-5-12-6/h4-5,7H,1-3,10H2,(H,11,12)(H,13,14)(H,15,16)/t7-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | L-carnosine is an antioxidant naturally found in skeletal muscle, brain tissue, and the heart that protects cells against oxidative stress.L-carnosine plays an important role in inhibiting neuronal cell apoptosis through STAT3 signaling pathway after acute cerebral ischemia. L-carnosine may accelerate pressure ulcer healing during 4 weeks. |
| Targets | NO | STAT | Pim | Bcl-2/Bax | Caspase |
| In vivo | L-carnosine alters some hemorheologic and lipid peroxidation parameters in nephrectomized rats.[Pubmed: 24614724]Med Sci Monit. 2014 Mar 11;20:399-405.Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a major health problem worldwide. Oxidative stress is one of the mediators of this disease. Systemic complications of oxidative stress are involved in the pathogenesis of hypertension, endothelial dysfunction, shortened erythrocyte lifespan, deformability, and nitric oxide (NO) dysfunction. L-carnosine is known as an antioxidant. In this study, our aim was to investigate the effect of carnosine on hemorheologic and cardiovascular parameters in CKD-induced rats.
Β-alanine and l-histidine transport across the inner blood-retinal barrier: potential involvement in L-carnosine supply.[Pubmed: 23773890]Exp Eye Res. 2013 Aug;113:135-42.The supply of L-carnosine, a bioactive dipeptide of β-alanine and l-histidine, to the retina across the blood-retinal barrier (BRB) was studied. Effects of L-carnosine and its zinc complex (Polaprezinc) on pressure ulcer healing.[Pubmed: 23835365]Nutr Clin Pract. 2013 Oct;28(5):609-16.L-carnosine (CAR) is an endogenous dipeptide. We aimed to determine the effects of CAR and its zinc complex polaprezinc (PLZ) on pressure ulcer healing in institutionalized long-term care patients.
|
| Animal Research | The effect of L-carnosine on erythrocyte deformability and aggregation according to the cell age in young and aged rats.[Pubmed: 23909051]L-carnosine inhibits neuronal cell apoptosis through signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling pathway after acute focal cerebral ischemia.[Pubmed: 23454231]Brain Res. 2013 Apr 24;1507:125-33.Considerable studies have showed that L-carnosine provides anti-oxidative and anti-apoptotic roles in the animal models of global or focal cerebral ischemia. However, the anti-apoptotic mechanisms of L-carnosine in the focal cerebral ischemia model have yet to be elucidated. Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 2013;56(1):23-8.This study aimed to investigate alterations in hemorheology induced by L-carnosine, an anti- oxidant dipeptide, and to determine their relationship to oxidative stress in density-separated erythrocytes of aged and young rats. |

L-carnosine Dilution Calculator

L-carnosine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.4203 mL | 22.1014 mL | 44.2028 mL | 88.4056 mL | 110.507 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8841 mL | 4.4203 mL | 8.8406 mL | 17.6811 mL | 22.1014 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.442 mL | 2.2101 mL | 4.4203 mL | 8.8406 mL | 11.0507 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0884 mL | 0.442 mL | 0.8841 mL | 1.7681 mL | 2.2101 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0442 mL | 0.221 mL | 0.442 mL | 0.8841 mL | 1.1051 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Chlorambucil
Catalog No.:BCC5351
CAS No.:305-03-3
- 6,7-Dihydroxycoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN5905
CAS No.:305-01-1
- SANT-1
Catalog No.:BCC3941
CAS No.:304909-07-7
- AGK 2
Catalog No.:BCC7609
CAS No.:304896-28-4
- Alisol C
Catalog No.:BCN3458
CAS No.:30489-27-1
- Tanaproget
Catalog No.:BCC1984
CAS No.:304853-42-7
- Mearnsitrin
Catalog No.:BCN5220
CAS No.:30484-88-9
- Flunarizine 2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4398
CAS No.:30484-77-6
- S 24795
Catalog No.:BCC7700
CAS No.:304679-75-2
- Xerophilusin G
Catalog No.:BCN5219
CAS No.:304642-94-2
- Theaflavin 3,3'-di-O-gallate
Catalog No.:BCN5920
CAS No.:30462-35-2
- Theaflavin-3-gallate
Catalog No.:BCN2316
CAS No.:30462-34-1
- Licoricidin
Catalog No.:BCN6679
CAS No.:30508-27-1
- Zidovudine
Catalog No.:BCC5024
CAS No.:30516-87-1
- SL-327
Catalog No.:BCC1123
CAS No.:305350-87-2
- Caulilexin C
Catalog No.:BCN3960
CAS No.:30536-48-2
- 5'-Demethylaquillochin
Catalog No.:BCN5221
CAS No.:305364-91-4
- H-Cys(Bzl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2906
CAS No.:3054-01-1
- Etofenamate
Catalog No.:BCC1563
CAS No.:30544-47-9
- Bisabolangelone
Catalog No.:BCN8094
CAS No.:30557-81-4
- Stavudine (d4T)
Catalog No.:BCC5028
CAS No.:3056-17-5
- Acephate
Catalog No.:BCC7555
CAS No.:30560-19-1
- Geldanamycin
Catalog No.:BCC2125
CAS No.:30562-34-6
- H-Asp(OtBu)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2891
CAS No.:3057-74-7
The effect of L-carnosine on erythrocyte deformability and aggregation according to the cell age in young and aged rats.[Pubmed:23909051]
Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 2013;56(1):23-8.
This study aimed to investigate alterations in hemorheology induced by L-carnosine, an anti- oxidant dipeptide, and to determine their relationship to oxidative stress in density-separated erythrocytes of aged and young rats. 28 male Sprague Dawley rats were divided into 4 groups as aged (Aca), young (Yca) L-carnosine groups (250 mg/kg L-carnosine, i.p.) and aged (As), young (Ys) control groups (saline, i.p.). Density separation was further performed to these groups in order to separate erythrocytes according to their age. Blood samples were used for the determination of erythrocyte deformability, aggregation; and oxidative stress parameters. Erythrocyte deformability of Yca group measured at 0.53 Pa was lower than Aca group. Similarly, deformability of least-dense (young) erythrocytes of Yca group was decreased compared to least-dense erythrocytes of Aca groups. Total antioxidant capacity (TAC) of Aca group was higher and oxidative stress index (OSI) lower than As group. Although L-carnosine resulted in an enhancement in TAC of aged rats, this favorable effect was not observed in erythrocyte deformability and aggregation in the dose applied in this study.
L-carnosine alters some hemorheologic and lipid peroxidation parameters in nephrectomized rats.[Pubmed:24614724]
Med Sci Monit. 2014 Mar 11;20:399-405.
BACKGROUND: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a major health problem worldwide. Oxidative stress is one of the mediators of this disease. Systemic complications of oxidative stress are involved in the pathogenesis of hypertension, endothelial dysfunction, shortened erythrocyte lifespan, deformability, and nitric oxide (NO) dysfunction. L-carnosine is known as an antioxidant. In this study, our aim was to investigate the effect of carnosine on hemorheologic and cardiovascular parameters in CKD-induced rats. MATERIAL AND METHODS: We used 4-month-old male Sprague-Dawley rats divided into 4 groups of 6 rats each. Three days after subtotal nephrectomy and sham operations, the surviving rats were divided into the 4 groups; 1) Sham (S), 2) Sham+Carnosine (S-C), 3) Subtotal nephrectomy (Nx), and 4) Subtotal nephrectomy + Carnosine (N-C). Carnosine was injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) (50 mg/kg) for 15 days. The control group received the same volume of physiological saline. RESULTS: In CKD rats, malondialdehyde (MDA) levels were increased, and NO and RBC deformability were decreased compared to Sham. Carnosine treatment decreased MDA levels, improved RBC (red blood cell) ability to deform, and increased NO levels. However, carnosine did not affect blood pressure levels in these rats. CONCLUSIONS: We found that carnosine has beneficial effects on CKD in terms of lipid peroxidation and RBC deformability. Carnosine may have a healing effect in microcirculation level, but may not have any effect on systemic blood pressure in CKD-induced rats.
Effects of L-carnosine and its zinc complex (Polaprezinc) on pressure ulcer healing.[Pubmed:23835365]
Nutr Clin Pract. 2013 Oct;28(5):609-16.
BACKGROUND: L-carnosine (CAR) is an endogenous dipeptide. We aimed to determine the effects of CAR and its zinc complex polaprezinc (PLZ) on pressure ulcer healing in institutionalized long-term care patients. METHODS: This study was a nonrandomized controlled trial with a maximum 4-week follow-up. Forty-two patients with stage II-IV pressure ulcers for 4 or more weeks were allocated to 1 of 3 groups in order of recruitment: the control group (n = 14) was untreated, the PLZ group (n = 10) orally received 150 mg/d PLZ (containing 116 mg CAR and 34 mg zinc), and the CAR group (n = 18) orally received 116 mg/d CAR. Pressure ulcer severity was measured weekly using the Pressure Ulcer Scale for Healing (PUSH) score. RESULTS: At baseline, no significant differences were found among groups in demographic and nutrition parameters and pressure ulcer characteristics (severity, size, and staging). After 4 weeks, the rate of pressure ulcer healing, assessed by the mean weekly improvement in PUSH score, was significantly greater in the CAR (1.6 +/- 0.2, P = .02) and PLZ groups (1.8 +/- 0.2, P = .009) than in the control group (0.8 +/- 0.2). The difference between the CAR and PLZ groups was not significant (P = .73). Actual dietary intakes over this period did not differ significantly among groups. CONCLUSIONS: Our results suggest that CAR and PLZ may almost equally accelerate pressure ulcer healing during 4 weeks. The results need confirmation by randomized controlled trials with larger sample sizes.
Beta-alanine and l-histidine transport across the inner blood-retinal barrier: potential involvement in L-carnosine supply.[Pubmed:23773890]
Exp Eye Res. 2013 Aug;113:135-42.
The supply of L-carnosine, a bioactive dipeptide of beta-alanine and l-histidine, to the retina across the blood-retinal barrier (BRB) was studied. The in vivo and in vitro studies revealed low uptake activities for [(3)H]Gly-Sar, a representative dipeptide, suggesting that L-carnosine transport plays only a minor role at the BRB. The in vivo study using rats showed approximately 18- and 23-fold greater retinal uptake indexes (RUI) for [(3)H]beta-alanine and [(3)H]l-histidine compared with that of a paracellular marker, respectively. The RUI of [(3)H]beta-alanine was taurine- and gamma-aminobutyric acid-sensitive, and the in vitro uptake by TR-iBRB2 cells showed time- concentration- and temperature-dependent [(3)H]beta-alanine uptake, suggesting that a carrier-mediated process was involved in beta-alanine transport across the inner BRB. [(3)H]beta-Alanine uptake was inhibited by taurine and beta-guanidinopropionic acid, suggesting that taurine transporter (TAUT/SLC6A6) is responsible for the influx transport of beta-alanine across the inner BRB. Regarding l-histidine, the l-leucine-sensitive RUI of [(3)H]l-histidine was identified, and the in vitro [(3)H]l-histidine uptake by TR-iBRB2 cells suggested that a carrier-mediated process was involved in l-histidine transport across the inner BRB. The inhibition profile suggested that L-type amino acid transporter (LAT1/SLC7A5) is responsible for the influx transport of l-histidine across the inner BRB. These results show that the influx transports of beta-alanine and l-histidine across the inner BRB is carried out by TAUT and LAT1, respectively, suggesting that the retinal L-carnosine is supplied by enzymatic synthesis from two kinds of amino acids transported across the inner BRB.
L-carnosine inhibits neuronal cell apoptosis through signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling pathway after acute focal cerebral ischemia.[Pubmed:23454231]
Brain Res. 2013 Apr 24;1507:125-33.
Considerable studies have showed that L-carnosine provides anti-oxidative and anti-apoptotic roles in the animal models of global or focal cerebral ischemia. However, the anti-apoptotic mechanisms of L-carnosine in the focal cerebral ischemia model have yet to be elucidated. To investigate the molecular mechanisms, rat models of permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion (pMCAO) and sham operation were first established and then pMCAO and sham-operated rats were treated with L-carnosine or vehicle alone. After this treatment, neurological deficits were evaluated at 12, 24 and 72 h after operation and the infarct volume was measured at 72 h after treatment. In addition, we also detected the mRNA expression of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and Pim-1 and the protein expression of phosphorylated STAT3, Pim-1, bcl-2 and cleaved caspase-3 at 12, 24 and 72 h post-pMCAO. Our results showed that the L-carnosine-treated rats had milder neurological deficits and smaller infarct volume and showed up-regulated expression in mRNA levels of STAT3 and Pim-1 than vehicle-treated rats at 72 h after treatment. Meanwhile, compared with vehicle-treated rats, the L-carnosine-treated rats exhibited higher protein expressions of pSTAT3, Pim-1 and bcl-2 but lower expression of cleaved caspase-3 protein at 72 h following operation. These results indicate that L-carnosine plays an important role in inhibiting neuronal cell apoptosis through STAT3 signaling pathway after acute cerebral ischemia.


