S 24795CAS# 304679-75-2 |
- I-BET-762
Catalog No.:BCC4474
CAS No.:1260907-17-2
- Bromodomain Inhibitor, (+)-JQ1
Catalog No.:BCC1132
CAS No.:1268524-70-4
- I-BET151 (GSK1210151A)
Catalog No.:BCC4476
CAS No.:1300031-49-5
- GSK1324726A
Catalog No.:BCC4038
CAS No.:1300031-52-0
- PFI-1 (PF-6405761)
Catalog No.:BCC2225
CAS No.:1403764-72-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 304679-75-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9888248 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C14H13BrINO | M.Wt | 418.07 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 10 mM in water with gentle warming and to 100 mM in DMSO | ||
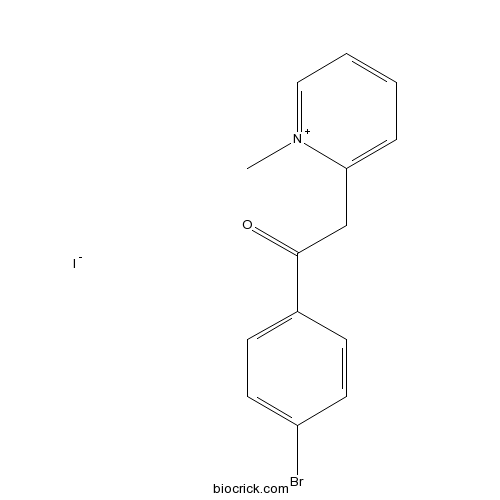
| Chemical Name | 1-(4-bromophenyl)-2-(1-methylpyridin-1-ium-2-yl)ethanone;iodide | ||
| SMILES | C[N+]1=CC=CC=C1CC(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)Br.[I-] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | LERUHBBUGAOYOD-UHFFFAOYSA-M | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H13BrNO.HI/c1-16-9-3-2-4-13(16)10-14(17)11-5-7-12(15)8-6-11;/h2-9H,10H2,1H3;1H/q+1;/p-1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Partial agonist of α7 nAChR. Improves mnemonic function in aged mice for the treatment of aging-related memory disturbances. Displays more efficient memory-enhancing effects than memantine in Alzheimer's disease mouse models. |

S 24795 Dilution Calculator

S 24795 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3919 mL | 11.9597 mL | 23.9194 mL | 47.8389 mL | 59.7986 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4784 mL | 2.3919 mL | 4.7839 mL | 9.5678 mL | 11.9597 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2392 mL | 1.196 mL | 2.3919 mL | 4.7839 mL | 5.9799 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0478 mL | 0.2392 mL | 0.4784 mL | 0.9568 mL | 1.196 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0239 mL | 0.1196 mL | 0.2392 mL | 0.4784 mL | 0.598 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Xerophilusin G
Catalog No.:BCN5219
CAS No.:304642-94-2
- Theaflavin 3,3'-di-O-gallate
Catalog No.:BCN5920
CAS No.:30462-35-2
- Theaflavin-3-gallate
Catalog No.:BCN2316
CAS No.:30462-34-1
- Cyclomusalenone
Catalog No.:BCN4654
CAS No.:30452-60-9
- AVE 0991
Catalog No.:BCC4032
CAS No.:304462-19-9
- Dynasore
Catalog No.:BCC1088
CAS No.:304448-55-3
- Toxicarolisoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN6468
CAS No.:3044-60-8
- Pelirine
Catalog No.:BCN4077
CAS No.:30435-26-8
- Corydalmine
Catalog No.:BCN5217
CAS No.:30413-84-4
- LU AA33810
Catalog No.:BCC7708
CAS No.:304008-29-5
- Harmaline
Catalog No.:BCN5218
CAS No.:304-21-2
- Hydralazine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4911
CAS No.:304-20-1
- Flunarizine 2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4398
CAS No.:30484-77-6
- Mearnsitrin
Catalog No.:BCN5220
CAS No.:30484-88-9
- Tanaproget
Catalog No.:BCC1984
CAS No.:304853-42-7
- Alisol C
Catalog No.:BCN3458
CAS No.:30489-27-1
- AGK 2
Catalog No.:BCC7609
CAS No.:304896-28-4
- SANT-1
Catalog No.:BCC3941
CAS No.:304909-07-7
- 6,7-Dihydroxycoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN5905
CAS No.:305-01-1
- Chlorambucil
Catalog No.:BCC5351
CAS No.:305-03-3
- L-carnosine
Catalog No.:BCN3803
CAS No.:305-84-0
- Licoricidin
Catalog No.:BCN6679
CAS No.:30508-27-1
- Zidovudine
Catalog No.:BCC5024
CAS No.:30516-87-1
- SL-327
Catalog No.:BCC1123
CAS No.:305350-87-2
Dissociating beta-amyloid from alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor by a novel therapeutic agent, S 24795, normalizes alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine and NMDA receptor function in Alzheimer's disease brain.[Pubmed:19726654]
J Neurosci. 2009 Sep 2;29(35):10961-73.
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is characterized by synaptic dysfunction and cardinal neuropathological features including amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. Soluble amyloid-beta (Abeta) can suppress synaptic activities by interacting with alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (alpha7nAChRs). Here, we show that alpha7nAChR and NMDA glutamatergic receptor (NMDAR) activities are severely compromised in synaptosomes prepared from AD and Abeta(1-42) (Abeta42)-exposed control frontal cortex slices from postmortem tissue. Whereas Abeta(12-28) prevents Abeta42 from binding to alpha7nAChRs, 2-[2-(4-bromophenyl)-2-oxoethyl]-1-methyl pyridinium (S 24795), a novel alpha7nAChR partial agonist, facilitates release of Abeta42 from Abeta42-alpha7nAChR and -Abeta42 complexes. S 24795 interacts with alpha7nAChR and Abeta(15-20) region of the Abeta42 to enable partial recovery of the alpha7nAChR and NMDAR channel function. These findings suggest that the Abeta-alpha7nAChR interaction may be an upstream pathogenic event in AD and demonstrate that some recovery of neuronal channel activities may be achieved in AD brains by removing Abeta from alpha7nAChRs.
Positive modulation of alpha7 nAChR responses in rat hippocampal interneurons to full agonists and the alpha7-selective partial agonists, 4OH-GTS-21 and S 24795.[Pubmed:19705574]
Neuropharmacology. 2009 Mar;56(4):821-30.
One approach for the identification of therapeutic agents for Alzheimer's disease has focused on the research of alpha7 nAChR-selective agonists such as the partial agonists 3-(4-hydroxy,2-methoxybenzylidene)anabaseine (4OH-GTS-21) and, more recently, 2-[2-(4-bromophenyl)-2-oxoethyl]-1-methyl pyridinium (S 24795). An alternative approach for targeting alpha7 nAChR has been the development of positive modulators for this receptor. In this study we examined the interactions between full or partial agonists and positive modulators of alpha7 nAChRs in situ in brain tissue. Three positive modulators were used, 5-hydroxyindole (5-HI), 1-(5-chloro-2,4-dimethoxy-phenyl)-3-(5-methyl-isoxanol-3-yl)-urea (PNU-120596), and genistein. Whole-cell recordings were performed in stratum radiatum interneurons from rat brain slices. Hippocampal interneurons were stimulated by ACh, choline, S 24795, or 4OH-GTS-21, before and after bath perfusion with the positive modulators. 5-HI was not effective at potentiating 200 microM 4OH-GTS-21-evoked responses, however 5-HI induced a sustained potentiation of responses evoked by 30 microM 4OH-GTS-21. When 1 mM ACh and 200 microM 4OH-GTS-21 were applied alternately alpha7-mediated responses to both agonists were reduced, suggesting that high concentration of 4OH-GTS-21 produces residual inhibition or desensitization and that 5-HI is not effective at overcoming receptor desensitization. Similar results were obtained with alpha7 receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Interestingly, responses evoked by S 24795 were potentiated by 5-HI but not by genistein. Additionally, PNU-120596 was able to potentiate alpha7-mediated responses, regardless of the nature of the agonist. We demonstrated that the potentiation of alpha7 nAChR response would depend on the nature and the effective concentration of the agonist involved and its particular interaction with the positive modulator.
Comparative effects of the alpha7 nicotinic partial agonist, S 24795, and the cholinesterase inhibitor, donepezil, against aging-related deficits in declarative and working memory in mice.[Pubmed:18265960]
Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008 Apr;197(3):499-508.
INTRODUCTION: The comparative effects of a newly described specific alpha7 nAChR partial agonist, S 24795, and a cholinesterase inhibitor, donepezil, currently used as a symptomatic Alzheimer's disease treatment were studied in two mouse models of aging-related memory deficits. MATERIALS AND METHODS: We employed radial arm-maze paradigms assessing short-term working memory (STWM, experiment A) and mnemonic flexibility, a cardinal property of long-term declarative (LTDM, experiment B). Both compounds were administered daily at 0.3 and 1 mg/kg subcutaneously (~3 weeks). RESULTS: In the STWM experiment, vehicle-treated aged mice displayed a severe and persistent deficit in the retention of successive arm visits in comparison to younger controls. S 24795 at 1 mg/kg (trends at 0.3 mg/kg) and donepezil at 0.3 mg/kg (but not 1 mg/kg) exerted beneficial effects on this deficit: The performance of aged mice treated with these drugs remarkably increased across the testing days and almost reached young adult performance level. In the critical test trials of memory flexibility (i.e., LTDM), in experiment B, S 24795 at 1 mg/kg (trends at 0.3 mg/kg) and donepezil at the dose of 1 mg/kg (but not 0.3 mg/kg) improved aged mice performance. CONCLUSION: This preclinical demonstration that S 24795 restored specific age-related memory deficits with as much efficacy as donepezil adds to recent literature in highlighting the potential interest of an alpha7 nAChR drug as a symptomatic AD therapeutic.
S 24795 limits beta-amyloid-alpha7 nicotinic receptor interaction and reduces Alzheimer's disease-like pathologies.[Pubmed:19932469]
Biol Psychiatry. 2010 Mar 15;67(6):522-30.
BACKGROUND: Beta-amyloid (Abeta) enables Alzheimer's disease (AD) plaque and neurofibrillary pathogenesis. Soluble Abeta promotes intraneuronal Abeta aggregates and tau phosphorylation by interacting with alpha7 nicotinic receptors (alpha7nAChRs). The current study assessed whether the novel alpha7nAChR partial agonist 2-(2-(4-bromophenyl)-2-oxoethyl)-1-methyl pyridinium (S 24795) could reduce AD-like pathologies by interfering with Abeta-alpha7nAChR interaction. METHODS: We compared the in vitro effect of S 24795, memantine, galantamine, and Abeta(12-28) on Abeta(42)-alpha7nAChR interaction in rat hippocampal synaptosomes. We further evaluated the effect of S 24795 on Abeta(42)-induced tau phosphorylation with rat hippocampal synaptosomes in vitro. Effects of S 24795 on Abeta(42) immunostaining, Abeta(42)-alpha7nAChR interaction, and/or Abeta(42)-mediated reduction of calcium (Ca(2+)) influx through alpha7nAChR and N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) were assessed in Abeta(42)-incubated organotypic brain slices and intracerebroventricularly (ICV) Abeta(42)-injected mouse brain. RESULTS: Preincubation with S 24795 in vitro reduces Abeta(42)-alpha7nAChR interaction and Abeta(42)-induced tau phosphorylation. In organotypic brain slice cultures and in an ICV Abeta(42) injection in vivo model, S 24795 reduces Abeta(42)-alpha7nAChR association and Abeta(42) immunostaining. S 24795 also normalizes Ca(2+) fluxes through both alpha7nAChR and NMDAR channels in Abeta(42)-infused mouse brains and Abeta(42)-exposed organotypic cortical slices. Unlike S 24795 and Abeta(12-28), galantamine or memantine minimally affect Abeta(42)-alpha7nAChR coupling and Abeta(42)-mediated reduction of alpha7nAChR- and NMDAR-mediated Ca(2+) influx. INTERPRETATION: Drugs like S 24795 that disrupt Abeta(42)-alpha7nAChR interaction might alleviate Abeta(42)-mediated synaptic dysfunction and block AD-like pathologies.
Improvement of contextual memory by S 24795 in aged mice: comparison with memantine.[Pubmed:18034231]
Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008 Mar;196(4):555-64.
RESULTS: In comparison with 5-month-old mice, 18- to 19-month-old mice exhibited a severe and specific memory impairment in a contextual serial discrimination (CSD) task involving the learning and remembering of two successive spatial discriminations carried out on two distinct floors. This impairment was specific, as spatial memory, simultaneously tested on a simple discrimination (SD) task, was not affected in these aged mice. This deficit was completely reversed by 9-day per os administration of S 24795, a partial agonist of alpha 7 nicotinic receptors, at either 0.3 or 1.0 mg/kg. Memantine, an NMDA receptor antagonist, also had a memory-enhancing effect at a dose of 3.0 mg/kg, but not at 0.3 mg/kg. CONCLUSIONS: The memory-enhancing effect of S 24795 was due to a strong enhancement of contextual memory as indicated by a decrease in interference rate, whereas memantine enhanced spatial/semantic memory. S 24795 was more effective than memantine and also appears to be more specific to flexible forms of memory, one of the first cognitive domains (i.e. episodic memory) affected in Alzheimer's disease.
The partial alpha7 nicotine acetylcholine receptor agonist S 24795 enhances long-term potentiation at CA3-CA1 synapses in the adult mouse hippocampus.[Pubmed:18187166]
Neuropharmacology. 2008 Mar;54(4):676-85.
The effects of S 24795, a newly developed partial agonist at alpha7 nAChRs, were tested on synaptic transmission and plasticity using extracellular field excitatory postsynaptic potentials (fEPSPs) evoked in the CA1 region by Schaffer collateral stimulation in hippocampal slices obtained from adult mice. S 24795 reduced the amplitude of the fEPSPs in a concentration-dependent manner with an IC(50) of 127 microM and a Hill coefficient of 1.1. The reduction in amplitude of the fEPSPs started at S 24795 concentrations higher than 3muM and reached 71% of controls at 300 microM. This effect was mediated by alpha7 nAChRs since it was blocked by nAChR antagonists and was not observed in alpha7 -/- mice. This effect was probably due to a reduction in glutamate release from presynaptic terminals since it was associated with a significant increase in the paired pulse ratio. In addition, S 24795 (100 microM) significantly reduced the frequency, but not the amplitude of spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents, recorded in the whole cell configuration of the patch clamp technique (in voltage clamp mode), further supporting a presynaptic site of action of S 24795. In addition, S 24795 at 3 microM, a concentration that did not affect basic synaptic transmission, potentiated LTP. This effect was mediated by alpha7 nAChRs since it was prevented by MLA (10 nM) and was absent in alpha7 -/- mice. Galantamine an allosteric modulator of nAChRs, at the concentrations of 0.3-3 microM, failed to potentiate LTP. In view of its powerful effect on LTP and on cognitive function, S 24795 can be considered a novel useful tool for the treatment of AD patients and other senile forms of dementia.


