HarmalineCAS# 304-21-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 304-21-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5280951 | Appearance | White powder |
| Formula | C13H14N2O | M.Wt | 214.3 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 3,4-Dihydroharmine; Harmidine | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in chloroform and methanol; slightly soluble in water | ||
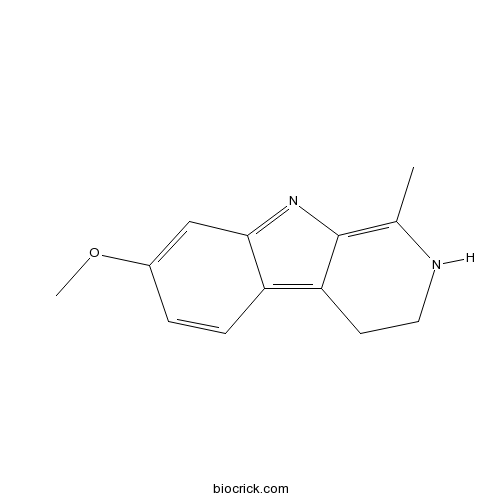
| Chemical Name | 7-methoxy-1-methyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C2C(=C3C=CC(=CC3=N2)OC)CCN1 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QJOZJXNKVMFAET-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C13H14N2O/c1-8-13-11(5-6-14-8)10-4-3-9(16-2)7-12(10)15-13/h3-4,7,14H,5-6H2,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Harmaline is a central nervous system stimulant and an acetylcholinesterase (AChR) inhibitor; also inhibits histamine N-methyltransferase. Harmaline has antileishmanial, bioinsecticidal, and vasorelaxant effects. It has antagonist effects on alpha1-adrenorecepteors in non-competitive manner, it also exerts an antioxidant activity by scavenging the free radical generated by DPPH.Harmaline may prevent dopamine-induced mitochondrial damage and PC12 cell death through a scavenging action on reactive oxygen species and inhibition of monoamine oxidase and thiol oxidation. |
| Targets | NOS | cAMP | Calcium Channel | PKC | Antifection | AChR | alpha1-adrenorecepteor |
| In vitro | In vitro activity of the beta-carboline alkaloids harmane, harmine, and harmaline toward parasites of the species Leishmania infantum.[Pubmed: 15172213 ]Exp Parasitol. 2004 Mar-Apr;106(3-4):67-74.Harmane, harmine, and Harmaline were investigated for their in vitro antileishmanial activity toward parasites of the species Leishmania infantum.
|
| In vivo | Bioinsecticidal effect of harmaline on Plodia interpunctella development (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae).[Reference: WebLink]Pesticide Biochemistry & Physiology, 2007, 89(2):137-145.We have investigated the effects of Harmaline, a plant secondary metabolic compound belonging to β-carboline alkaloids, on the 4th instar larvae of Plodia interpunctella (Lepidoptera).
Protective effect of harmalol and harmaline on MPTP neurotoxicity in the mouse and dopamine-induced damage of brain mitochondria and PC12 cells.[Pubmed: 10899927]J Neurochem. 2000 Aug;75(2):521-31.The present study elucidated the protective effect of beta-carbolines (Harmaline, harmalol, and harmine) on oxidative neuronal damage.
|
| Kinase Assay | Vasorelaxant effects of harmine and harmaline extracted from Peganum harmala L. seeds in isolated rat aorta.[Pubmed: 16750635 ]Pharmacol Res. 2006 Aug;54(2):150-7.The present work describes the mechanisms involved in the vasorelaxant effect of harmine and Harmaline.
|
| Animal Research | Rhythmic activity induced by harmaline in the olivo-cerebello-bulbar system of the cat.[Reference: WebLink]Harmaline-induced tremor as a potential preclinical screening method for essential tremor medications.[Pubmed: 15580562]Mov Disord. 2005 Mar;20(3):298-305.No preclinical method to evaluate potential new medications for essential tremor (ET) is available currently. Although Harmaline tremor is a well known animal model of ET, it has not found utility as a preclinical drug screen and has not been validated with anti-ET medications.
Brain Res., 1973, 53(1):81-95.
|

Harmaline Dilution Calculator

Harmaline Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.6664 mL | 23.3318 mL | 46.6636 mL | 93.3271 mL | 116.6589 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.9333 mL | 4.6664 mL | 9.3327 mL | 18.6654 mL | 23.3318 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4666 mL | 2.3332 mL | 4.6664 mL | 9.3327 mL | 11.6659 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0933 mL | 0.4666 mL | 0.9333 mL | 1.8665 mL | 2.3332 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0467 mL | 0.2333 mL | 0.4666 mL | 0.9333 mL | 1.1666 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Hydralazine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4911
CAS No.:304-20-1
- Reutericyclin
Catalog No.:BCN1855
CAS No.:303957-69-9
- U 18666A
Catalog No.:BCC7136
CAS No.:3039-71-2
- L-779,450
Catalog No.:BCC7593
CAS No.:303727-31-3
- Dalbergioidin
Catalog No.:BCN4801
CAS No.:30368-42-4
- Centrolobol
Catalog No.:BCN5216
CAS No.:30359-01-4
- TAK-715
Catalog No.:BCC3968
CAS No.:303162-79-0
- Picrasin B acetate
Catalog No.:BCN5215
CAS No.:30315-04-9
- Pandamarilactonine B
Catalog No.:BCN5214
CAS No.:303008-81-3
- Pandamarilactonine A
Catalog No.:BCN5213
CAS No.:303008-80-2
- Coenzyme Q10
Catalog No.:BCN5954
CAS No.:303-98-0
- Ochratoxin A
Catalog No.:BCC7008
CAS No.:303-47-9
- LU AA33810
Catalog No.:BCC7708
CAS No.:304008-29-5
- Corydalmine
Catalog No.:BCN5217
CAS No.:30413-84-4
- Pelirine
Catalog No.:BCN4077
CAS No.:30435-26-8
- Toxicarolisoflavone
Catalog No.:BCN6468
CAS No.:3044-60-8
- Dynasore
Catalog No.:BCC1088
CAS No.:304448-55-3
- AVE 0991
Catalog No.:BCC4032
CAS No.:304462-19-9
- Cyclomusalenone
Catalog No.:BCN4654
CAS No.:30452-60-9
- Theaflavin-3-gallate
Catalog No.:BCN2316
CAS No.:30462-34-1
- Theaflavin 3,3'-di-O-gallate
Catalog No.:BCN5920
CAS No.:30462-35-2
- Xerophilusin G
Catalog No.:BCN5219
CAS No.:304642-94-2
- S 24795
Catalog No.:BCC7700
CAS No.:304679-75-2
- Flunarizine 2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4398
CAS No.:30484-77-6
Vasorelaxant effects of harmine and harmaline extracted from Peganum harmala L. seeds in isolated rat aorta.[Pubmed:16750635]
Pharmacol Res. 2006 Aug;54(2):150-7.
The present work describes the mechanisms involved in the vasorelaxant effect of harmine and Harmaline. These alkaloids induce in a dose-dependent manner the relaxation in the aorta precontracted with noradrenaline or KCl. However, the removal of endothelium or pre-treatment of intact aortic ring with L-NAME (inhibitor of NOSe synthetase) or with indomethacin (non-specific inhibitor of cyclo-oxygenase), reduces significantly the vasorelaxant response of Harmaline but not harmine. According to their IC50 values, prazosin (inhibitor of alpha-adrenorecepteors) reduces the vasorelaxant effect only of Harmaline, whereas, pre-treatment with IBMX (non-specific inhibitor of phosphodiesterase) affects both the Harmaline and harmine-responses. Inhibitions of L-type voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels (VOCs) in endothelium-intact aortic rings with diltiazem depress the relaxation evoked by Harmaline as well as by harmine. Pre-treatment with Harmaline or harmine (3, 10 or 30 microM) shifted the phenylephrine-induced dose response curves to the right and the maximum response was attenuated indicating that the antagonist effect of both alkaloids on alpha1-adrenorecepteors was non-competitive. These two alkaloids also exert an antioxidant activity by scavenging the free radical generated by DPPH. Therefore, the present results suggest that the vasorelaxant effect of Harmaline but not harmine is related to its action on the prostacyclin pathway and on the endothelial cells to release NO. However, both alkaloids can act as blockers VOCs, as inhibitors of phosphodiesterase resulting in an increase of the second messenger (cAMP and cGMP) levels and finally reduce the levels of free radicals in tissues.
Protective effect of harmalol and harmaline on MPTP neurotoxicity in the mouse and dopamine-induced damage of brain mitochondria and PC12 cells.[Pubmed:10899927]
J Neurochem. 2000 Aug;75(2):521-31.
The present study elucidated the protective effect of beta-carbolines (Harmaline, harmalol, and harmine) on oxidative neuronal damage. MPTP treatment increased activities of total superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase and levels of malondialdehyde and carbonyls in the basal ganglia, diencephalon plus midbrain of brain compared with control mouse brain. Coadministration of harmalol (48 mg/kg) attenuated the MPTP effect on the enzyme activities and formation of tissue peroxidation products. Harmaline, harmalol, and harmine attenuated both the 500 microM MPP(+)-induced inhibition of electron flow and membrane potential formation and the 100 microM dopamine-induced thiol oxidation and carbonyl formation in mitochondria. The scavenging action of beta-carbolines on hydroxyl radicals was represented by inhibition of 2-deoxy-D-ribose degradation. Harmaline and harmalol (100 microM) attenuated 200 microM dopamine-induced viability loss in PC12 cells. The beta-carbolines (50 microM) attenuated 50 microM dopamine-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells. The compounds alone did not exhibit significant cytotoxic effects. The results indicate that beta-carbolines attenuate brain damage in mice treated with MPTP and MPP(+)-induced mitochondrial damage. The compounds may prevent dopamine-induced mitochondrial damage and PC12 cell death through a scavenging action on reactive oxygen species and inhibition of monoamine oxidase and thiol oxidation.
Harmaline-induced tremor as a potential preclinical screening method for essential tremor medications.[Pubmed:15580562]
Mov Disord. 2005 Mar;20(3):298-305.
No preclinical method to evaluate potential new medications for essential tremor (ET) is available currently. Although Harmaline tremor is a well known animal model of ET, it has not found utility as a preclinical drug screen and has not been validated with anti-ET medications. We measured Harmaline tremor in rats (10 mg/kg s.c.) and mice (20 mg/kg s.c.) with a load sensor under the cage floor and performed spectral analysis on 20-minute epochs. The motion power over the tremor frequency bandwidth (8-12 Hz in rats; 10-16 Hz in mice) was divided by the motion power over the full motion frequency range (0-15 Hz in rats; 0-34 Hz in mice). The use of these measures greatly reduced data variability, permitting experiments with small sample sizes. Three drugs that suppress ET (propranolol, ethanol, and octanol) all significantly suppressed Harmaline-induced tremor. We propose that, with this methodology, Harmaline-induced tremor may be useful as a preclinical method to identify potential medications for ET.
In vitro activity of the beta-carboline alkaloids harmane, harmine, and harmaline toward parasites of the species Leishmania infantum.[Pubmed:15172213]
Exp Parasitol. 2004 Mar-Apr;106(3-4):67-74.
Harmane, harmine, and Harmaline were investigated for their in vitro antileishmanial activity toward parasites of the species Leishmania infantum. Harmane and Harmine displayed a moderate antiproliferative activity toward human monocytes and exerted a weak antileishmanial activity toward both the promastigote and the amastigote forms of the parasite. Their mechanism of action on the promastigote form of the parasite involved interactions with DNA metabolism leading to an accumulation of parasites in the S-G(2)M phases of the cell-cycle. Harmaline, at the contrary, was deprived from toxicity toward human cells and Leishmania promastigotes, however it exerted a strong antileishmanial activity toward the intracellular amastigote form of the parasite. This property was shown to partly result from the capacity of the molecule to prevent parasite internalization within macrophages by inhibiting Leishmania PKC activity.


