LentinanCAS# 37339-90-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 37339-90-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 21868678.0 | Appearance | Powder |
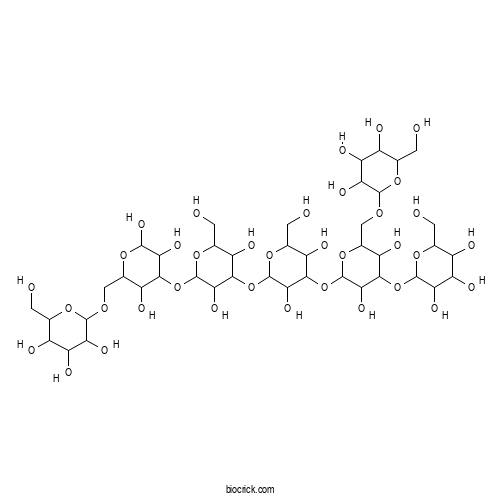
| Formula | C42H72O36 | M.Wt | 1153.0 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-[[4-[4-[4-[3,5-dihydroxy-4-[3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-6-[[3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxymethyl]oxan-2-yl]oxy-3,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-3,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-3,5,6-trihydroxyoxan-2-yl]methoxy]-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol | ||
| SMILES | C(C1C(C(C(C(O1)OCC2C(C(C(C(O2)O)O)OC3C(C(C(C(O3)CO)O)OC4C(C(C(C(O4)CO)O)OC5C(C(C(C(O5)COC6C(C(C(C(O6)CO)O)O)O)O)OC7C(C(C(C(O7)CO)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MAXBMUKIXLNXGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C42H72O36/c43-1-8-15(48)22(55)25(58)37(69-8)66-6-13-20(53)32(28(61)36(65)68-13)75-40-29(62)33(18(51)11(4-46)72-40)77-41-30(63)34(19(52)12(5-47)73-41)78-42-31(64)35(76-39-27(60)24(57)17(50)10(3-45)71-39)21(54)14(74-42)7-67-38-26(59)23(56)16(49)9(2-44)70-38/h8-65H,1-7H2 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Lentinan Dilution Calculator

Lentinan Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.8673 mL | 4.3365 mL | 8.673 mL | 17.3461 mL | 21.6826 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.1735 mL | 0.8673 mL | 1.7346 mL | 3.4692 mL | 4.3365 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.0867 mL | 0.4337 mL | 0.8673 mL | 1.7346 mL | 2.1683 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0173 mL | 0.0867 mL | 0.1735 mL | 0.3469 mL | 0.4337 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0087 mL | 0.0434 mL | 0.0867 mL | 0.1735 mL | 0.2168 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 6-Methoxyldihydrochelerythrine
Catalog No.:BCX0739
CAS No.:21080-31-9
- (-)-Myrtenal
Catalog No.:BCX0738
CAS No.:18486-69-6
- Fructo-oligosaccharide DP13/GF12
Catalog No.:BCX0737
CAS No.:137405-37-9
- Fructo-oligosaccharide DP9/GF8
Catalog No.:BCX0736
CAS No.:143625-74-5
- Glucosinalbin
Catalog No.:BCX0735
CAS No.:19253-84-0
- Fructo-oligosaccharide DP10/GF9
Catalog No.:BCX0734
CAS No.:118150-64-4
- (9Z,12Z,15Z)-N-[(3-Methoxyphenyl)methyl]-9,12,15-octadecatrienamide
Catalog No.:BCX0733
CAS No.:883715-23-9
- Fructo-oligosaccharide DP14/GF13
Catalog No.:BCX0732
CAS No.:137405-38-0
- Maltoheptaose
Catalog No.:BCX0731
CAS No.:34620-78-5
- 6,7-Dimethoxy-2-[2-(4'-methoxyphenyl)ethyl]chromone
Catalog No.:BCX0730
CAS No.:117596-92-6
- 3'-Hydroxypterostilbene
Catalog No.:BCX0729
CAS No.:475231-21-1
- Melezitose
Catalog No.:BCX0728
CAS No.:597-12-6
- Edgeworoside C
Catalog No.:BCX0741
CAS No.:126221-40-7
- Taxifolin 7-O-β-D-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX0742
CAS No.:14292-40-1
- Yuanhuacine
Catalog No.:BCX0743
CAS No.:60195-70-2
- Astragenol
Catalog No.:BCX0744
CAS No.:86541-79-9
- Saikosaponin K
Catalog No.:BCX0745
CAS No.:405229-61-0
- guan-fu base H
Catalog No.:BCX0746
CAS No.:4758-99-0
- Kuwanon B
Catalog No.:BCX0747
CAS No.:62949-78-4
- Yuanhuadine
Catalog No.:BCX0748
CAS No.:76402-66-9
- Emetine
Catalog No.:BCX0749
CAS No.:483-18-1
- Epipinoresinol-4-O-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCX0750
CAS No.:24404-49-7
- Cyaonoside A
Catalog No.:BCX0751
CAS No.:110081-91-9
- Epimedin I
Catalog No.:BCX0752
CAS No.:205445-00-7
Immune-enhancing activity of compound polysaccharide on the inactivated influenza vaccine.[Pubmed:38670772]
Carbohydr Polym. 2024 Jul 15;336:122080.
Traditional Chinese medicine polysaccharides have numerous biological activities with broad applications in the biomedical industries. However, a clear understanding of the pharmacological activities of compound polysaccharides with multi-component structures remain challenging. This study aimed to investigate the immune boosting effect of compound polysaccharides on the influenza vaccine and assess the preliminary structure-activity relationship. The compound polysaccharide (CP) was isolated from the combined Chinese herbs Lentinan, pachymaran and tremellan, and purified by gradient ethanol precipitation to obtain its subcomponents of CP-20, CP-40, CP-60, and CP-80 with decreasing molecular weights. These polysaccharides were mainly composed of glucans with different linkage patterns, including alpha-(1 --> 3)-glucan, alpha-(1 --> 4)-glucan and beta-(1 --> 6)-glucan. A significant improvement was observed in the survival of mice vaccinated with inactivated (IAV) vaccine and the isolated polysaccharides as adjuvants. A reduction in the pulmonary virus titer and weight loss were also observed. Moreover, CP-40 and CP-60, as well as the original CP, significantly enhanced the serum anti-IAV antibody titers and interleukin IL-2, IL-5, and IL-6 concentrations. These preliminary results indicate the immune boosting effect of the compound polysaccharides is highly relevant to the specific structural properties of the subcomponent, and CP-40 is worthy of further exploration as a glycan adjuvant for the IAV vaccine.
Rapid Selenoprotein Activation by Selenium Nanoparticles to Suppresses Osteoclastogenesis and Pathological Bone Loss.[Pubmed:38621414]
Adv Mater. 2024 Apr 15:e2401620.
Osteoclast hyperactivation stands as a significant pathological factor contributing to the emergence of bone disorders driven by heightened oxidative stress levels. The modulation of the redox balance to scavenge reactive oxygen species emerges as a viable approach to addressing this concern. Selenoproteins, characterized by selenocysteine (SeCys(2)) as the active center, are crucial for selenium-based antioxidative stress therapy for inflammatory diseases. This study reveals that surface-active elemental selenium (Se) nanoparticles, particularly Lentinan-Se (LNT-Se), exhibit enhanced cellular accumulation and accelerated metabolism to SeCys(2), the primary active Se form in biological systems. Consequently, LNT-Se demonstrates significant inhibition of osteoclastogenesis. Furthermore, in vivo studies underscore the superior therapeutic efficacy of LNT-Se over SeCys(2), potentially attributable to the enhanced stability and safety profile of LNT-Se. Specifically, LNT-Se effectively modulates the expression of the selenoprotein GPx1, thereby exerting regulatory control over osteoclastogenesis inhibition, and the prevention of osteolysis. In summary, these results suggest that the prompt activation of selenoproteins by Se nanoparticles serves to suppress osteoclastogenesis and pathological bone loss by upregulating GPx1. Moreover, the utilization of bioactive Se species presents a promising avenue for effectively managing bone disorders.
Lentinan inhibits cell invasion via M2 polarization of tumor-associated macrophages and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in non-small cell lung cancer.[Pubmed:38538070]
Chem Biol Drug Des. 2024 Mar;103(3):e14507.
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is an aggressive and devastating cancer due to its metastasis induced by increased invasion. Lentinan is a polysaccharide exerting antitumor roles in multiple cancers, including lung cancer. However, the influence of Lentinan on cell invasion in NSCLC remains unclear. Cell invasion was detected by transwell analysis. Matrix metallopeptidase 9 (MMP9) levels were measured through immunofluorescence staining. The markers arginase-1 (Arg-1), CD206 and interleukin (IL)-10 (IL-10) of M2 macrophages, Wnt3a, and beta-catenin levels were measured by western blot or enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. Lentinan did not affect cell viability and proliferation in NSCLC cells. Lentinan suppressed cell invasion and reduced the expression and secretion of MMP9. Lentinan attenuated also M2 polarization of tumor-associated macrophages. Moreover, Lentinan mitigated the M2 macrophage conditioned medium-mediated cell invasion and MMP9 alterations in NSCLC cells. Lentinan inhibited the activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in NSCLC cells. The activated Wnt/beta-catenin pathway reversed the suppressive effects of Lentinan on cell invasion and MMP9 level in NSCLC cells. In conclusion, Lentinan reduces cell invasion in NSCLC cells by inhibiting the M2 polarization of tumor-associated macrophages and the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling.
Lentinan-loaded GelMA hydrogel accelerates diabetic wound healing through enhanced angiogenesis and immune microenvironment modulation.[Pubmed:38458275]
Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Apr;264(Pt 2):130716.
Diabetic wound healing is a substantial clinical challenge, characterized by delayed angiogenesis and unresolved inflammation. Lentinan, a polysaccharide extracted from shiitake mushrooms, has the potential to regulate both macrophage polarization and angiogenesis, though this aspect remains inadequately explored. To facilitate Lentinan's clinical utility, we have developed a GelMA hydrogel encapsulated with Lentinan (10 muM), offering a controlled release mechanism for sustained Lentinan delivery at the wound site. Application of the Lentinan-encapsulated delivery system topically significantly expedites wound closure compared to control groups. Furthermore, histological examination demonstrates enhanced neovascularization and reduced inflammation in Lentinan-treated wounds, as evidenced by increased M2 macrophage infiltration. Moreover, our results indicated that Lentinan-induced AMPK activation promotes DAF16 expression, enhancing the resistance of macrophages and HUVECs to oxidative stress in high-glucose environments, thereby promoting M2 macrophage polarization and angiogenesis. All these findings underscore Lentinan's capacity to modulate macrophage polarization and angiogenesis via the AMPK/DAF16 pathway, ultimately facilitating the healing of diabetic wounds.
The effect of lentinan on dexamethasone-induced immunosuppression in mice.[Pubmed:38447834]
Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Apr;264(Pt 2):130621.
The immune system acts as a vital defense barrier against pathogenic invasions, and its stable operation is crucial for maintaining body health. Nevertheless, various natural or artificial factors can compromise the body's immune function, leading to immunosuppression, which may interfere with the efficacy of vaccination and increase the susceptibility of the body to disease-causing pathogens. In an effort to ensure successful vaccinations and improve overall physical well-being, the search for appropriate immune regulators to enhance immunity is of paramount importance. Lentinan (LNT) has a significant role in immune regulation and vaccine adjuvants. In the present study, we constructed an immunosuppressive model using dexamethasone (DEX) and demonstrated that LNT could significantly improved antibody levels in immunosuppressive mice and stimulated T-lymphocyte proliferation and differentiation in intestinal Peyer's patches. LNT also increased the production of secretory immunoglobulin A (sIgA) in the duodenal fluid, the number of goblet cells, and the proportion of mucin area. Moreover, LNT modulated the intestinal microbiota and increased the production of short-chain fatty acids. Additionally, LNT promoted the proliferation, differentiation, and pro-inflammatory cytokines production of DEX-treated splenic T lymphocytes in vitro. Thus, the present study highlights the potential of LNT in reversing immunosuppression and avoiding the failure of vaccination.
Medicinal Mushrooms as Multicomponent Mixtures-Demonstrated with the Example of Lentinula edodes.[Pubmed:38392825]
J Fungi (Basel). 2024 Feb 15;10(2):153.
Medicinal mushrooms are multicomponent mixtures (MOCSs). They consist of a large number of individual compounds, each with different chemical structures, functions, and possible pharmacological activities. In contrast to the activity of an isolated pure substance, the effects of the individual substances in a mushroom or its extracts can influence each other; they can strengthen, weaken, or complement each other. This results in both advantages and disadvantages for the use of either a pure substance or a multicomponent mixture. The review describes the differences and challenges in the preparation, characterization, and application of complex mixtures compared to pure substances, both obtained from the same species. As an example, we use the medicinal and culinary mushroom Lentinula edodes, shiitake, and some of its isolated compounds, mainly Lentinan and eritadenine.
Methods of study on conformation of polysaccharides from natural products: A review.[Pubmed:38373563]
Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Apr;263(Pt 1):130275.
Polysaccharides from natural products play multiple roles and have extensive bioactivities in life process. Bioactivities of polysaccharides (e.g., Lentinan, Schizophyllan, Scleroglucan, Curdlan, Cinerean) have a close relation to their chain conformation. Compared to other types of polysaccharides, the conformation of beta-glucan has been studied more. The major research methods of conformation of polysaccharides from natural products (Congo red experiment, circular dichroism spectrum, viscosity method, light scattering method, size exclusion chromatography, atomic force microscope), corresponding experimental schemes, and the external factors affecting polysaccharide conformation were reviewed in this paper. These research methods of conformation have been widely used, among which Congo red experiment and viscosity method are the most convenient ones to study the morphological changes of polysaccharide chains.
A novel method for detecting conformation-dependent beta-glucans-single, double, and triple-helical from Shiitake mushroom.[Pubmed:38270464]
Nat Prod Res. 2024 Jan 25:1-4.
This pioneering study explores the structural intricacies of therapeutic beta-glucan in Shiitake (Lentinula edodes), i.e. Lentinan (LNT). Lentinan, a neutral polysaccharide [beta-(1,3; 1,6) glucan], exists in three forms; single, double, and triple-helical, but conformation-dependent bioactivity studies are lacking. In this context, we meticulously assessed indigenous Shiitake accessions from Northeast India, unveiling the conformational spectrum of LNT through an innovative pipeline. The experiment approached the simultaneous estimation of total glucan (TG), triple helical glucan (THG), and single-double helical glucan (SDG). Profiling revealed the exceptional LNT content in DMRO-623 (TG: 46.74%, SDG: 9.34%, THG: 37.39%) which emerged as the highest documented to date. Beyond the culinary delight, this research and the novel approach to LNT quantification will create a pivotal platform for advanced mushroom research, offering prospects for novel discoveries, innovative applications, and therapeutic potential.
Dextrans, Pullulan and Lentinan, New Scaffold Materials for Use as Hydrogels in Tissue Engineering.[Pubmed:38217885]
Chemistry. 2024 Apr 16;30(22):e202303843.
The development of hydrogels based on dextrans, pullulan and Lentinan to be used in biomedical applications including tissue engineering is reported. Despite the fact that selected polysaccharides such as hyaluronic acid are well established, little is known, how these polysaccharides can be chemically modified to create hydrogels under controlled conditions. In this study we present a small library of chemically modified polysaccharides which are used for a divergent approach to achieve biomedical relevant hydrogels. In this case the crosslinking is based on thio ether formation between thiol modified donor and vinylsulfone or maleimide modified acceptor components. Successful synthesis of the linker systems and coupling at the polysaccharides, hydrogel formation takes place under physiological conditions. We extended the study by coupling small molecules like adhesion factors for increasing cell compatibility as well as a dye for further studies. The different hydrogels were studied to their rheological properties, water uptake, their permeability, biodegrability and their cytotoxicity.
Lentinan progress in inflammatory diseases and tumor diseases.[Pubmed:38172925]
Eur J Med Res. 2024 Jan 3;29(1):8.
Shiitake mushrooms are a fungal food that has been recorded in Chinese medicine to nourish the blood and qi. Lentinan (lLNT) is an active substance extracted from shiitake mushrooms with powerful antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor functions. Inflammatory diseases and cancers are the leading causes of death worldwide, posing a serious threat to human life and health and posing enormous challenges to global health systems. There is still a lack of effective treatments for inflammatory diseases and cancer. LNT has been approved as an adjunct to chemotherapy in China and Japan. Studies have shown that LNT plays an important role in the treatment of inflammatory diseases as well as oncological diseases. Moreover, clinical experiments have confirmed that LNT combined with chemotherapy drugs has a significant effect in improving the prognosis of patients, enhancing their immune function and reducing the side effects of chemotherapy in lung cancer, colorectal cancer and gastric cancer. However, the relevant mechanism of action of the LNT signaling pathway in inflammatory diseases and cancer. Therefore, this article reviews the mechanism and clinical research of LNT in inflammatory diseases and tumor diseases in recent years.
Safety and efficacy of lentinan nasal drops in patients infected with the variant of COVID-19: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial.[Pubmed:38108068]
Front Pharmacol. 2023 Dec 1;14:1292479.
Objective: Lentinan has antiviral, anti-tumor, immunomodulatory, stimulating interferon production, and other pharmacological effects. Previous animal experiments have shown that Lentinan nasal drops can assist [Corona Virus Disease 2019) COVID-19] vaccine to induce high levels of neutralizing antibodies and can effectively resist the invasion of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). This study aimed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of Lentinan nasal drops in patients infected with Omicron (SARS-CoV-2 variant) through a dose-escalation study and a placebo-controlled trial. Methods: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. The study was divided into two phases: Phase I: a dose escalation trial in which 24 COVID-19 patients were enrolled, that is, 12 in the escalation dose group (50, 75, and 100 microg/day) and 12 in the standard treatment group. The aim was to evaluate the safety and tolerance of Lentinan nasal drops. The second stage was a placebo-controlled study. The optimal dose group of the first stage was used as the therapeutic dose, and the sample size was expanded to verify the anti-COVID-19 efficacy of Lentinan nasal drops. Results: In the dose-increasing study, Lentinan nasal drops showed good safety, and no serious adverse reactions occurred. The virus shedding time of the 100 microg dose group was significantly shorter than that in the control group (7.75 +/- 1.71 VS 13.41 +/- 3.8 days) (p = 0.01), and the 100 microg/day Lentinan nasal drops were tolerated well. The results of the placebo-controlled study showed that compared with that in the placebo group, the time for COVID-19 antigen to turn negative was significantly shorter in the 100 microg Lentinan nasal drop group (p = 0.0298), but no significant difference was observed in symptom improvement between the two groups. In the placebo-controlled study, two patients experienced mild nasal discomfort with nasal drops, but the symptoms relieved themselves. Conclusion: Lentinan nasal drops are tolerated well and can shorten the time of virus clearance.
Systematic review and meta-analysis on the efficacy and safety of Injectable Lentinan combined with chemotherapy in the treatment of gastric cancer.[Pubmed:38100922]
Phytomedicine. 2024 Jan;123:155242.
BACKGROUND: This study employed a meta-analysis to evaluate the efficacy and safety of adjunctive treatment with injectable Lentinan (LNT) in combination with chemotherapy for gastric cancer (GC). METHODS: Computer-based searches of 6 databases were performed to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) relevant to the treatment of GC with LNT through mid-March 2023. Two independent researchers performed risk of bias assessment and trial sequential analysis(TSA), extracted the data and used Revman 5.3 software for data analysis. The certainty of evidence was graded based on the GRADE (Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation) approach. RESULTS: A total of 31 RCTs with 2729 patients were included in the analysis. The results revealed that adjunctive therapy with LNT was associated with improved treatment efficacy (RR = 1.48, 95%CI: 1.36 approximately 1.61, p < 0.00001), improvement in clusters of differentiation (CD3(+), CD4(+), and CD4(+)/CD8(+)), natural killer (NK) cells, and quality of life assessment (RR = 1.32, 95%CI: 1.20 approximately 1.45, p < 0.00001) compared to using chemotherapy alone. In addition, there was a reduction in CD8(+) levels, incidence of white blood cell decline, gastrointestinal reactions, and platelet decline. TSA results indicated that there was sufficient evidence to draw firm conclusions about these outcomes, and the GRADE scores showed 'high' or 'moderate' quality of evidence for these outcomes. CONCLUSION: The efficacy of treatment of GC with LNT in combination with chemotherapy was found to be better than chemotherapy alone. And no serious adverse effects were observed. However, further RCTs are needed to further validate the results of this study.
Lentinan has a beneficial effect on cognitive deficits induced by chronic Toxoplasma gondii infection in mice.[Pubmed:38093309]
Parasit Vectors. 2023 Dec 13;16(1):454.
BACKGROUND: Toxoplasma gondii (T. gondii) is increasingly considered a risk factor for neurodegenerative diseases. However, there is only limited information on the development of drugs for T. gondii infection. Lentinan from Lentinula edodes is a bioactive ingredient with the potential to enhance anti-infective immunity. The present study aimed to investigate the neuroprotective effect of Lentinan on T. gondii-associated cognitive deficits in mice. METHODS: A chronic T. gondii infection mouse model was established by administering 10 cysts of T. gondii by gavage. Lentinan was intraperitoneally administered 2 weeks before infection. Behavioral tests, RNA sequencing, immunofluorescence, transmission electron microscopy and Golgi-Cox staining were performed to assess the effect of Lentinan on cognitive deficits and neuropathology in vivo. In vitro, the direct and indirect effects of Lentinan on the proliferation of T. gondii tachyzoites were evaluated in the absence and presence of BV-2 cells, respectively. RESULTS: Lentinan prevented T. gondii-induced cognitive deficits and altered the transcriptome profile of genes related to neuroinflammation, microglial activation, synaptic function, neural development and cognitive behavior in the hippocampus of infected mice. Moreover, Lentinan reduced the infection-induced accumulation of microglia and downregulated the mRNA expression of proinflammatory cytokines. In addition, the neurite and synaptic ultrastructural damage in the hippocampal CA1 region due to infection was ameliorated by Lentinan administration. Lentinan decreased the cyst burden in the brains of infected mice, which was correlated with behavioral performance. In line with this finding, Lentinan could significantly inhibit the proliferation of T. gondii tachyzoites in the microglial cell line BV2, although Lentinan had no direct inhibitory effect on parasite growth. CONCLUSIONS: Lentinan prevents cognitive deficits via the improvement of neurite impairment and synaptic loss induced by T. gondii infection, which may be associated with decreased cyst burden in the brain. Overall, our findings indicate that Lentinan can ameliorate T. gondii-related neurodegenerative diseases.
Induction of Autophagy and Its Role in Peripheral Nerve Regeneration after Peripheral Nerve Injury.[Pubmed:38003409]
Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 11;24(22):16219.
No matter what treatment is used after nerve transection, a complete cure is impossible, so basic and clinical research is underway to find a cure. As part of this research, autophagy is being investigated for its role in nerve regeneration. Here, we review the existing literature regarding the involvement and significance of autophagy in peripheral nerve injury and regeneration. A comprehensive literature review was conducted to assess the induction and role of autophagy in peripheral nerve injury and subsequent regeneration. Studies were included if they were prospective or retrospective investigations of autophagy and facial or peripheral nerves. Articles not mentioning autophagy or the facial or peripheral nerves, review articles, off-topic articles, and those not written in English were excluded. A total of 14 peripheral nerve studies that met these criteria, including 11 involving sciatic nerves, 2 involving facial nerves, and 1 involving the inferior alveolar nerve, were included in this review. Studies conducted on rats and mice have demonstrated activation of autophagy and expression of related factors in peripheral nerves with or without stimulation of autophagy-inducing factors such as rapamycin, curcumin, three-dimensional melatonin nerve scaffolds, CXCL12, resveratrol, nerve growth factor, Lentinan, adipose-derived stem cells and melatonin, basic fibroblast growth factor, and epothilone B. Among the most studied of these factors in relation to degeneration and regeneration of facial and sciatic nerves are LC3II/I, PI3K, mTOR, Beclin-1, ATG3, ATG5, ATG7, ATG9, and ATG12. This analysis indicates that autophagy is involved in the process of nerve regeneration following facial and sciatic nerve damage. Inadequate autophagy induction or failure of autophagy responses can result in regeneration issues after peripheral nerve damage. Animal studies suggest that autophagy plays an important role in peripheral nerve degeneration and regeneration.
Single-injection subunit vaccine for rabies prevention using lentinan as adjuvant.[Pubmed:37977452]
Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Jan;254(Pt 3):128118.
Current rabies vaccines require 5 doses to provide full protection from the deadly virus, which significantly reduce the compliance of recipients. To minimize the number of immunizations herein single injection vaccines were developed. First a single injection vaccine was designed using rabies virus glycoprotein (G protein) as antigen. A time-controlled release system which uses dynamic layer-by-layer films as erodible coating was employed to accomplish multiply pulsatile releases of G protein. The single-injection vaccine elicits potent humoral and cellular immune responses comparable to the corresponding multi-dose ordinary vaccines because of their similar release pattern of G protein. To further improve its performance, a second single injection vaccine, in which Lentinan was added as adjuvant, was designed. This single-injection vaccine again elicits humoral and cellular immune responses comparable to the corresponding multi-dose ordinary vaccines because of their similar release pattern of antigen and adjuvant. In addition, the second single-injection vaccine elicits higher level immune response and provides higher efficiency on virus inhibition than the first one because Lentinan can booster immune response.


