N6-BenzoyladenineCAS# 4005-49-6 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 4005-49-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 97075 | Appearance | Powder |
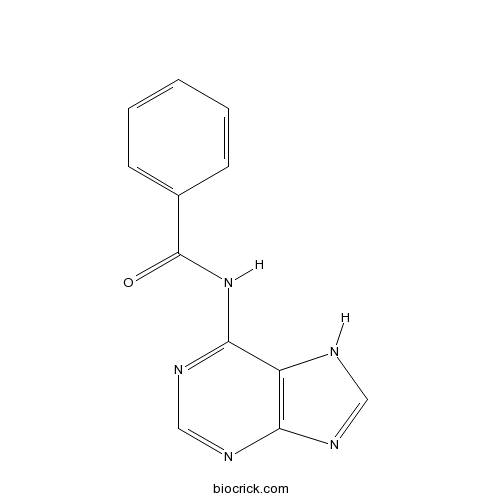
| Formula | C12H9N5O | M.Wt | 239 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | N-(7H-purin-6-yl)benzamide | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C=C1)C(=O)NC2=NC=NC3=C2NC=N3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QQJXZVKXNSFHRI-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C12H9N5O/c18-12(8-4-2-1-3-5-8)17-11-9-10(14-6-13-9)15-7-16-11/h1-7H,(H2,13,14,15,16,17,18) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

N6-Benzoyladenine Dilution Calculator

N6-Benzoyladenine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.1841 mL | 20.9205 mL | 41.841 mL | 83.682 mL | 104.6025 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8368 mL | 4.1841 mL | 8.3682 mL | 16.7364 mL | 20.9205 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4184 mL | 2.0921 mL | 4.1841 mL | 8.3682 mL | 10.4603 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0837 mL | 0.4184 mL | 0.8368 mL | 1.6736 mL | 2.0921 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0418 mL | 0.2092 mL | 0.4184 mL | 0.8368 mL | 1.046 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- SU 3327
Catalog No.:BCC7725
CAS No.:40045-50-9
- Syringetin-3-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN2610
CAS No.:40039-49-4
- 24, 25-Dihydroxy VD3
Catalog No.:BCC1303
CAS No.:40013-87-4
- H-Thr-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3104
CAS No.:39994-75-7
- Laricitrin 3-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN8149
CAS No.:39986-90-8
- p-Hydroxy-5,6-dehydrokawain
Catalog No.:BCN3597
CAS No.:39986-86-2
- Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabivarinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7967
CAS No.:39986-26-0
- HOAt
Catalog No.:BCC2815
CAS No.:39968-33-7
- Victoxinine
Catalog No.:BCN6745
CAS No.:39965-06-5
- LY 78335
Catalog No.:BCC6109
CAS No.:39959-66-5
- Norglaucine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN6568
CAS No.:39945-41-0
- 2'-Deoxycytidine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5434
CAS No.:3992-42-5
- 20-Hydroxyganoderic acid G
Catalog No.:BCN8231
CAS No.:400604-12-8
- Ceftaroline fosamil
Catalog No.:BCC5266
CAS No.:400827-46-5
- H-Arg-pNA.2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2858
CAS No.:40127-11-5
- Erucifoline
Catalog No.:BCN2081
CAS No.:40158-95-0
- Boc-N-Me-Phe.DCHA
Catalog No.:BCC3348
CAS No.:40163-88-0
- SKA 31
Catalog No.:BCC7743
CAS No.:40172-65-4
- Andarine
Catalog No.:BCC1168
CAS No.:401900-40-1
- Fmoc-β-homo-Arg(Pbf)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2649
CAS No.:401915-53-5
- Fmoc-β-Homo-Gln(Trt)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2647
CAS No.:401915-55-7
- H-Orn-OMe.2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3001
CAS No.:40216-82-8
- H-Hyp-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3248
CAS No.:40216-83-9
- 5-O-Feruloylquinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3788
CAS No.:40242-06-6
Discovery and structure-activity relationship studies of N6-benzoyladenine derivatives as novel BRD4 inhibitors.[Pubmed:25678016]
Bioorg Med Chem. 2015 Mar 1;23(5):953-9.
Bromodomain and extra-terminal domain (BET) proteins are epigenetic readers that bind to acetylated lysines in histones. Among them, BRD4 is a candidate target molecule of therapeutic agents for diverse diseases, including cancer and inflammatory disease. As a part of our continuing structural development studies of thalidomide to obtain a broad spectrum of biological modifiers based on the 'multi-template' approach, in this work we focused on BRD4-inhibitory activity, and discovered that N6-Benzoyladenine derivatives exhibit this activity. Structure-activity relationship studies led to N6-(2,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl)adenine (29), which exhibits potent BRD4 bromodomain1 inhibitory activity with an IC50 value of 0.427muM. N6-Benzoyladenine appears to be a new chemical scaffold for development of BRD4 inhibitors.
Synthesis and cytotoxicity of cyanoborane adducts of n6-benzoyladenine and 6-triphenylphosphonylpurine.[Pubmed:18475422]
Met Based Drugs. 2002;9(1-2):19-32.
N6-Benzoyladenine-cyanoborane (2), and 6-triphenylphosphonylpurine-cyanoborane (3) were selected for investigation of cytotoxicity in murine and human tumor cell lines, effects on human HL-60 leukemic metabolism and DNA strand scission to determine the feasibility of these compounds as clinical antineoplastic agents. Compounds 2 and 3 both showed effective cytotoxicity based on ED(50) values less than 4 mug/ml for L1210, P388, HL-60, Tmolt(3), HUT-78, HeLa-S(3) uterine, ileum HCT-8, and liver Hepe-2. Compound 2 had activity against ovary 1-A9, while compound 3 was only active against prostate PL and glioma UM. Neither compound was active against the growth of lung 549, breast MCF-7, osteosarcoma HSO, melanoma SK2, KB nasopharynx, and THP-1 acute monocytic leukemia. In mode of action studies in human leukemia HL-60 cells, both compounds demonstrated inhibition of DNA and protein syntheses after 60 min at 100 muM. These compounds inhibited RNA synthesis to a lesser extent. The utilization of the DNA template was suppressed by the compounds as determined by inhibition of the activities of DNA polymerase alpha, m-RNA polymerase, r-RNA polymerase and t-RNA polymerase, which would cause adequate inhibition of the synthesis of both DNA and RNA. Both compounds markedly inhibited dihydrofolate reductase activity, especially in compound 2. The compounds appeared to have caused cross-linking of the DNA strands after 24 hr at 100 muM in HL-60 cells, which was consistent with the observed increased in ct-DNA viscosity after 24 hr at 100 muM. The compounds had no inhibitory effects on DNA topoisomerase I and II activities or DNA-protein linked breaks. Neither compound interacted with the DNA molecule itself through alkylation of the nucleotide bases nor caused DNA interculation between base pairs. Overall, these antineoplastic agents caused reduction of DNA and protein replication, which would lead to killing of cancer cells.


