Nagilactone CCAS# 24338-53-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 24338-53-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 72505 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C19H22O7 | M.Wt | 362.4 |
| Type of Compound | Diterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
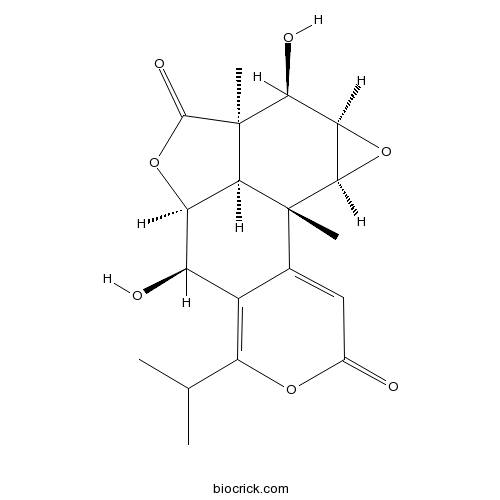
| SMILES | CC(C)C1=C2C(C3C4C(C(C5C(C4(C2=CC(=O)O1)C)O5)O)(C(=O)O3)C)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DGNOPGIIPQKNHD-RSKPZANQSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H22O7/c1-6(2)11-9-7(5-8(20)24-11)18(3)14-12(10(9)21)26-17(23)19(14,4)15(22)13-16(18)25-13/h5-6,10,12-16,21-22H,1-4H3/t10-,12-,13-,14-,15+,16-,18-,19-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Nagilactone C possesses potent antiproliferative activity against human fibrosarcoma and murine colon carcinoma tumor cell lines exhibiting ED50 values of 2.3 and 1.2 microg/ml, respectively. 2. Nagilactone C and phyllanthoside are novel protein synthesis inhibitors, they are specific for the eukaryotic translation apparatus, function in vivo and in vitro, and interfere with translation elongation. 3. Nagilactone C shows high insecticidal activity against second-instar nymphs of Eocanthecona furcellata. |
| Targets | Antifection |

Nagilactone C Dilution Calculator

Nagilactone C Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7594 mL | 13.7969 mL | 27.5938 mL | 55.1876 mL | 68.9845 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5519 mL | 2.7594 mL | 5.5188 mL | 11.0375 mL | 13.7969 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2759 mL | 1.3797 mL | 2.7594 mL | 5.5188 mL | 6.8985 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0552 mL | 0.2759 mL | 0.5519 mL | 1.1038 mL | 1.3797 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0276 mL | 0.138 mL | 0.2759 mL | 0.5519 mL | 0.6898 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Tricosanoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5394
CAS No.:2433-96-7
- 9-Fluorenylmethanol
Catalog No.:BCC2801
CAS No.:24324-17-2
- Cephalotaxine
Catalog No.:BCN2957
CAS No.:24316-19-6
- Scandine
Catalog No.:BCN5099
CAS No.:24314-59-8
- Hesperidin methylchalcone
Catalog No.:BCN8125
CAS No.:24292-52-2
- Mycophenolic acid
Catalog No.:BCC4803
CAS No.:24280-93-1
- Boc-Glu-OtBu
Catalog No.:BCC3388
CAS No.:24277-39-2
- Sodium ferulic
Catalog No.:BCN8542
CAS No.:24276-84-4
- Acetylcephalotaxine
Catalog No.:BCN5098
CAS No.:24274-60-0
- Cannabidivarin
Catalog No.:BCN7536
CAS No.:24274-48-4
- Furanodienone
Catalog No.:BCN3010
CAS No.:24268-41-5
- Shikokianin
Catalog No.:BCN3278
CAS No.:24267-69-4
- 6-Amino-1-methyluracil
Catalog No.:BCC8757
CAS No.:2434-53-9
- Apamin
Catalog No.:BCC7141
CAS No.:24345-16-2
- S-(5'-Adenosyl)-L-methionine chloride
Catalog No.:BCN2229
CAS No.:24346-00-7
- 3,5-Cycloergosta-6,8(14),22-triene
Catalog No.:BCN5100
CAS No.:24352-51-0
- (-)-alpha-Pinene
Catalog No.:BCC8295
CAS No.:2437-95-8
- Bufexamac
Catalog No.:BCC4427
CAS No.:2438-72-4
- L-(-)-Fucose
Catalog No.:BCN8326
CAS No.:2438-80-4
- pep2m
Catalog No.:BCC5782
CAS No.:243843-42-7
- pep4c
Catalog No.:BCC5783
CAS No.:243843-43-8
- Glycoside L-F2
Catalog No.:BCN2158
CAS No.:243857-99-0
- 5-Iodotubercidin
Catalog No.:BCC1312
CAS No.:24386-93-4
- Kynurenic acid sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7754
CAS No.:2439-02-3
Sequestration of host plant-derived compounds by geometrid moth, Milionia basalis, toxic to a predatory stink bug, Eocanthecona furcellata.[Pubmed:11504032]
J Chem Ecol. 2001 Jul;27(7):1345-53.
A predatory stink bug, Eocanthecona furcellata, died after feeding on Milionia basalis larvae. The compounds toxic to E. furcellata were isolated from the hemolymph of M. basalis larvae and identified as inumakilactone A, Nagilactone C, and Nagilactone C glucoside. The concentrations of inumakilactone A, Nagilactone C, and Nagilactone C glucoside in the hemolymph of the final instar larvae were 130, 50, and 770 microg/ml, respectively. Nagilactone C showed the highest insecticidal activity against second-instar nymphs of E. furcellata, while Nagilactone C glucoside showed the lowest, one twentieth of that of Nagilactone C. When mixed compounds were given at the same concentrations as those in hemolymph of M. basalis, all nymphs of E. furcellata died with in three days. Inumakilactone A and Nagilactone C were found to be in the leaves of podocarp, Podocarpus macrophyllus, the only host plant of M. basalis, at concentrations of 13 and 175 microg/g fresh weight, respectively. However, no Nagilactone C glucoside was detected in the leaves of this species. These results suggested that M. basalis may transform Nagilactone C to its glucoside.
Cytotoxic constituents from Podocarpus fasciculus.[Pubmed:18379113]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2008 Apr;56(4):585-8.
A new diterpene, 16-hydroxy communic acid (1), along with thirty one known compounds including five norditerpenes (2-6), twenty two flavonoids containing four biflavonoids (7-10), nine monoflavonoids (11-19) and nine flavanoid glycosides (20-28), as well as four phenolic constituents (29-32) were isolated from the 95% ethanolic extract of Podocarpus fasciculus. The structure of 1 was elucidated using spectral methods. Of these isolates, Nagilactone C (2) showed the most significant inhibitory effects against DLD cells (human colon carcinoma) (ED(50)=2.57 microg/ml) and compounds 7, 8, 10, 11, and 12 had moderate cytotoxic activity against human KB (human oral epithelium carcinoma), Hela (human cervical carcinoma), Hepa (human hepatoma), DLD (colon carcinoma), and A-549 (human lung carcinoma) tumor cell lines. Preliminary structure-activity relationship studies of the isolated diterpenoids and biflavonoids are discussed.
Eukaryotic protein synthesis inhibitors identified by comparison of cytotoxicity profiles.[Pubmed:14970397]
RNA. 2004 Mar;10(3):528-43.
The National Cancer Institute (NCI) Human Tumor Cell Line Anti-Cancer Drug Screen has evaluated the cytotoxicity profiles of a large number of synthetic compounds, natural products, and plant extracts on 60 different cell lines. The data for each compound/extract can be assessed for similarity of cytotoxicity pattern, relative to a given test compound, using an algorithm called COMPARE. In applying a chemical biology approach to better understand the mechanism of eukaryotic protein synthesis, we used these resources to search for novel inhibitors of translation. The cytotoxicity profiles of 31 known protein synthesis inhibitors were used to identify compounds from the NCI database with similar activity profiles. Using this approach, two natural products, phyllanthoside and Nagilactone C, were identified and characterized as novel protein synthesis inhibitors. Both compounds are specific for the eukaryotic translation apparatus, function in vivo and in vitro, and interfere with translation elongation. Our results demonstrate the feasibility of utilizing cytotoxicity profiles to identify new inhibitors of translation.
An antiproliferative norditerpene dilactone, Nagilactone C, from Podocarpus neriifolius.[Pubmed:11824527]
Phytomedicine. 2001 Nov;8(6):489-91.
An ethanolic extract of Podocarpus neriifolius D. Don (Podocarpaceae) showed antiproliferative activity against two major tumor cell lines, viz. human HT-1080 fibrosarcoma and murine color 26-L5 carcinoma. Bioassay guided fractionation showed the highest antiproliferative activity in chloroform-soluble fraction. Nagilactone C, the major constituent of this fraction was isolated and characterized by using NMR, IR and FAB-MS spectroscopic methods. Nagilactone C possessed potent antiproliferative activity against human fibrosarcoma and murine colon carcinoma tumor cell lines exhibiting ED50 values of 2.3 and 1.2 microg/ml, respectively. Hence, Nagilactone C could be the active constituent present in this plant.


