Nitidine chlorideCAS# 13063-04-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 13063-04-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 25659 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
| Formula | C21H18ClNO4 | M.Wt | 383.83 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in methan | ||
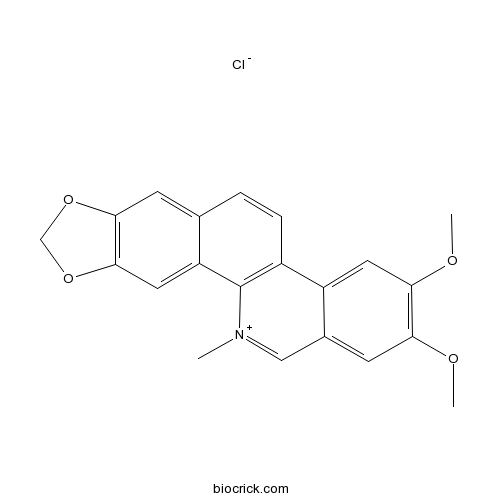
| Chemical Name | 2,3-dimethoxy-12-methyl-[1,3]benzodioxolo[5,6-c]phenanthridin-12-ium;chloride | ||
| SMILES | C[N+]1=CC2=CC(=C(C=C2C3=C1C4=CC5=C(C=C4C=C3)OCO5)OC)OC.[Cl-] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QLDAACVSUMUMOR-UHFFFAOYSA-M | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H18NO4.ClH/c1-22-10-13-7-17(23-2)18(24-3)8-15(13)14-5-4-12-6-19-20(26-11-25-19)9-16(12)21(14)22;/h4-10H,11H2,1-3H3;1H/q+1;/p-1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Nitidine chloride has protective effects on rats during myocardial ischemia/reperfusion, it also exerts an anti-inflammatory property by inhibiting TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 production in association with reduced NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways in RAW 264.7 cells. It has inhibitory effects on various tumors, such as renal cancer , breast cancer. |
| Targets | TNF-α | MAPK | IL Receptor | NF-kB | p65 | p53 | p21 | PARP | Bcl-2/Bax | PI3K | Akt | MMP(e.g.TIMP) |
| In vitro | Nitidine chloride inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory cytokines production via MAPK and NF-kappaB pathway in RAW 264.7 cells.[Pubmed: 22971898 ]J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Oct 31;144(1):145-50.Zanthoxylum nitidium (Roxb.) DC. has long been used as a traditional herbal medicine for inflammatory diseases such as rheumatic arthritis and peridentitis. However, the anti-inflammatory mechanism of Nitidine chloride has not been fully elucidated.
To determine the anti-inflammatory effects and mechanism of Nitidine chloride (NTD), a pentacyclic alkaloid is isolated from the root of Z. nitidium, in murine macrophages.
Nitidine chloride inhibits renal cancer cell metastasis via suppressing AKT signaling pathway.[Pubmed: 23911800]Food Chem Toxicol. 2013 Oct;60:246-51.Nitidine chloride (NC) has been shown to have anti-cancer effects on various tumors. However, whether NC could exert anti-metastasis activity in renal cancer cells and the underlying mechanisms have not been elucidated.
|
| Cell Research | Nitidine chloride induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through a pathway involving p53, p21, Bax and Bcl-2.[Pubmed: 25530218]Nitidine chloride induces apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, and synergistic cytotoxicity with doxorubicin in breast cancer cells.[Pubmed: 25027404]Tumour Biol. 2014 Oct;35(10):10201-12.Medicinal plant extracts have been widely used for cancer treatment. Nitidine chloride (NC) is a natural bioactive alkaloid that has recently been reported to have diverse anticancer properties.
We aimed to investigate the cytotoxic effects of NC and the effectiveness of combinatorial treatment including NC and doxorubicin in breast cancer cells.
Oncol Rep. 2015 Mar;33(3):1264-74.Nitidine chloride (NC), a novel benzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloid, induces the growth inhibition of cancer cells. Previously it was demonstrated that SMMC-7721 human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells are highly susceptible to the antiproliferative effects of NC. However, the specific mechanisms remained unclear.
In the present study the pathways of growth inhibition induced by NC in SMMC-7721 cells were investigated.
|
| Animal Research | Protective effects of nitidine chloride on rats during myocardial ischemia/reperfusion.[Reference: WebLink]Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation, 2006, 10(27):171-4.①1 and 2 mg/kg Nitidine chloride can reduce the incidence rate of cardiac arrhythmia in rats with myocardial ischemia and reperfusion, postpone the emergence time of cardiac arrhythmia and shorten its duration, decrease the degree of ST segment elevation after reperfusion for 15 minutes and 60 minutes, which have similar effect with verapamil. ②1 and 2 mg/kg Nitidine chloride can reduce the release of myocardial enzyme, relieve the severity of oxygen-derived free radicals injury, and has the effect of protecting myocardial injury during ischemia-reperfusion, in which represents a dose-dependent effect. |

Nitidine chloride Dilution Calculator

Nitidine chloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6053 mL | 13.0266 mL | 26.0532 mL | 52.1064 mL | 65.133 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5211 mL | 2.6053 mL | 5.2106 mL | 10.4213 mL | 13.0266 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2605 mL | 1.3027 mL | 2.6053 mL | 5.2106 mL | 6.5133 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0521 mL | 0.2605 mL | 0.5211 mL | 1.0421 mL | 1.3027 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0261 mL | 0.1303 mL | 0.2605 mL | 0.5211 mL | 0.6513 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Yangambin
Catalog No.:BCN6706
CAS No.:13060-14-5
- alpha-Terthienylmethanol
Catalog No.:BCN6161
CAS No.:13059-93-3
- Mogroside III
Catalog No.:BCN3167
CAS No.:130567-83-8
- Liriope muscari baily Saponins
Catalog No.:BCN2817
CAS No.:130551-41-6
- Cannabisin A
Catalog No.:BCC8138
CAS No.:130508-46-2
- SKF 96365 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6953
CAS No.:130495-35-1
- TC-F 2
Catalog No.:BCC6147
CAS No.:1304778-15-1
- L-655,708
Catalog No.:BCC7023
CAS No.:130477-52-0
- ent-11alpha-Hydroxyabieta-8(14),13(15)-dien-16,12alpha-olide
Catalog No.:BCN7330
CAS No.:130466-20-5
- A 68930 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7104
CAS No.:130465-39-3
- Batimastat sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC2075
CAS No.:130464-84-5
- Peucedanocoumarin III
Catalog No.:BCN3471
CAS No.:130464-57-2
- (R)-(+)-Corypalmine
Catalog No.:BCN2289
CAS No.:13063-54-2
- N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)propylamine
Catalog No.:BCC9053
CAS No.:130634-09-2
- Bindarit
Catalog No.:BCC4965
CAS No.:130641-38-2
- PD123319
Catalog No.:BCC5010
CAS No.:130663-39-7
- Ozanimod (RPC1063)
Catalog No.:BCC6533
CAS No.:1306760-87-1
- RP 001 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7905
CAS No.:1306761-53-4
- Dorzolamide HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2311
CAS No.:130693-82-2
- (R)-(+)-Propranolol hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6810
CAS No.:13071-11-9
- SDZ WAG 994
Catalog No.:BCC7374
CAS No.:130714-47-5
- FR 122047 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7092
CAS No.:130717-51-0
- Decloxizine dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5549
CAS No.:13073-96-6
- m-CPP hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5680
CAS No.:13078-15-4
Nitidine chloride inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory cytokines production via MAPK and NF-kappaB pathway in RAW 264.7 cells.[Pubmed:22971898]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Oct 31;144(1):145-50.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Zanthoxylum nitidium (Roxb.) DC. has long been used as a traditional herbal medicine for inflammatory diseases such as rheumatic arthritis and peridentitis. However, the anti-inflammatory mechanism of Nitidine chloride has not been fully elucidated. AIM OF THE STUDY: To determine the anti-inflammatory effects and mechanism of Nitidine chloride (NTD), a pentacyclic alkaloid is isolated from the root of Z. nitidium, in murine macrophages. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Anti-inflammatory properties of NTD were investigated using lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated Raw 264.7 macrophages as in vitro model. The pro-inflammatory cytokines were evaluated by real-time RT-PCR and ELISA. Furthermore, intracellular signaling pathways were analyzed by Western blot and Immunofluorescence staining using specific antibodies. RESULTS: NTD significantly reduced the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta), and IL-6 in both RNA and protein level. Moreover, transcriptional activity of NF-small ka, CyrillicB as well as the phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) in LPS-treated RAW 264.7 was significantly inhibited by NTD in a dose dependent manner. These results suggested that NTD exerts an anti-inflammatory property by inhibiting TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, and IL-6 production in association with reduced NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling pathways in RAW 264.7 cells. CONCLUSION: These results suggested that NTD exerts an anti-inflammatory property by inhibiting TNF-alpha, IL-1beta, and IL-6 production in association with reduced NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling pathways in RAW 264.7 cells. Nitidine chloride inhibits LPS-induced TNF alpha, IL-1beta and IL-6 production via the suppression of phosphorylation of MAPK and the translocation of p65. In addition, these results revealed a novel role of NTD in regulation of inflammatory diseases.
Nitidine chloride inhibits renal cancer cell metastasis via suppressing AKT signaling pathway.[Pubmed:23911800]
Food Chem Toxicol. 2013 Oct;60:246-51.
Nitidine chloride (NC) has been shown to have anti-cancer effects on various tumors. However, whether NC could exert anti-metastasis activity in renal cancer cells and the underlying mechanisms have not been elucidated. In this work, our data demonstrated the anti-metastasis effects of NC on renal cancer cells in vitro. With scratch assay and transwell assays, we found that NC potently suppressed the migration and invasion of 786-O and A498 cells. Mechanistically, we presented that NC significantly decreased phosphorylation of AKT, accompanied by down-regulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9. Furthermore, a specific AKT inhibitor, LY294002, could enhance the anti-metastasis effects of NC, which indicated that NC suppressed metastasis of renal cancer cells partly via inhibition of AKT activity. Taken together, our results imply that NC can be developed as a potential anti-metastasis agent to renal cancer.
Nitidine chloride induces apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, and synergistic cytotoxicity with doxorubicin in breast cancer cells.[Pubmed:25027404]
Tumour Biol. 2014 Oct;35(10):10201-12.
Medicinal plant extracts have been widely used for cancer treatment. Nitidine chloride (NC) is a natural bioactive alkaloid that has recently been reported to have diverse anticancer properties. We aimed to investigate the cytotoxic effects of NC and the effectiveness of combinatorial treatment including NC and doxorubicin in breast cancer cells. Using MTT and flowcytometry assays, we found that NC induced cell growth inhibition and G2/M cell cycle arrest in a time- and dose-dependent manner both in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell lines. Cancer cell growth inhibition was associated with increased levels of the p53 and p21 proteins. Apoptosis induction by NC treatment was confirmed by JC-1 mitochondrial membrane potential, annexin V-positive cell, and TUNEL staining. Using western blot analysis, we found that NC upregulated the pro-apoptotic proteins Bax, cleaved caspase-9 and -3 and cleaved PARP and that it downregulated the anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and PARP. By using the PI3K/Akt inhibitor LY294002, we further demonstrated that NC-induced apoptosis might be Akt-specific or dependent. In addition, NC exhibited a synergistic effect with doxorubicin on the growth inhibition of the human breast cancer cell lines MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231. Our study demonstrated the anticancer effect of NC on breast cancer and highlighted the potential clinical application of NC.
Nitidine chloride induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through a pathway involving p53, p21, Bax and Bcl-2.[Pubmed:25530218]
Oncol Rep. 2015 Mar;33(3):1264-74.
Nitidine chloride (NC), a novel benzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloid, induces the growth inhibition of cancer cells. Previously it was demonstrated that SMMC-7721 human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells are highly susceptible to the antiproliferative effects of NC. However, the specific mechanisms remained unclear. In the present study the pathways of growth inhibition induced by NC in SMMC-7721 cells were investigated. The effects of NC on SMMC-7721 cell proliferation were characterized by MTT and colony formation assays. Additionally, BALB/c nude mice were transplanted with SMMC-7721 cells to verify the inhibition of HCC by NC in vivo. The results showed that NC inhibited the proliferation of SMMC-7721 cells in vitro in a time- and dose-dependent manner and identified efficacy in vivo in a mouse model of HCC. Acridine orange (AO) staining, transmission electron microscopy, Annexin V/PI staining, TUNEL assay and caspase-3 activation assays were used to investigate apoptosis and the cell cycle distribution. Inhibition was mediated in part by cell cycle arrest in G2/M, leading to chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation and the formation of apoptotic bodies. Apoptosis was also verified by Annexin V/PI staining, TUNEL assay and caspase-3 activation. To assess the levels of the cell cycle and apoptotic regulators, immunohistochemical staining, ELISA, real-time PCR and RNA interference (RNAi) were employed. The apoptotic process triggered by NC involved the upregulation of p53, p21 and Bax, and the downregulation of Bcl-2. These data elucidate a pathway of apoptosis in SMMC7721 cells that involves G2/M arrest, upregulation of p53, Bax, caspase-3 and p21, and downregulation of Bcl-2.


