L-655,708CAS# 130477-52-0 |
- GW1929
Catalog No.:BCC1611
CAS No.:196808-24-9
- Balaglitazone
Catalog No.:BCC1395
CAS No.:199113-98-9
- Inolitazone
Catalog No.:BCC1652
CAS No.:223132-37-4
- Inolitazone dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1653
CAS No.:223132-38-5
- Aleglitazar
Catalog No.:BCC1337
CAS No.:475479-34-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 130477-52-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5311203 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H19N3O4 | M.Wt | 341.37 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 20 mg/mL (58.59 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
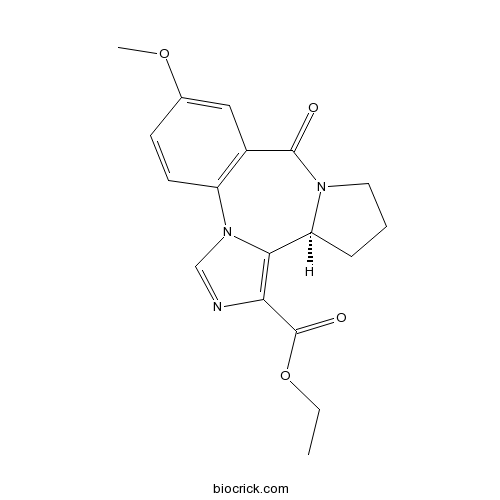
| SMILES | CCOC(=O)C1=C2C3CCCN3C(=O)C4=C(N2C=N1)C=CC(=C4)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YKYOQIXTECBVBB-AWEZNQCLSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H19N3O4/c1-3-25-18(23)15-16-14-5-4-8-20(14)17(22)12-9-11(24-2)6-7-13(12)21(16)10-19-15/h6-7,9-10,14H,3-5,8H2,1-2H3/t14-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent, selective inverse agonist for the benzodiazepine site of GABAA receptors containing the α5 subunit (Ki = 0.45 nM). Displays 50-100-fold selectivity over GABAA receptors containing α1, α2, α3 or α6 subunits in combination with β3 and γ2. Enhances LTP in a mouse hippocampal slice model and increases spatial learning, without displaying proconvulsant activity. |

L-655,708 Dilution Calculator

L-655,708 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9294 mL | 14.6469 mL | 29.2937 mL | 58.5875 mL | 73.2343 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5859 mL | 2.9294 mL | 5.8587 mL | 11.7175 mL | 14.6469 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2929 mL | 1.4647 mL | 2.9294 mL | 5.8587 mL | 7.3234 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0586 mL | 0.2929 mL | 0.5859 mL | 1.1717 mL | 1.4647 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0293 mL | 0.1465 mL | 0.2929 mL | 0.5859 mL | 0.7323 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- ent-11alpha-Hydroxyabieta-8(14),13(15)-dien-16,12alpha-olide
Catalog No.:BCN7330
CAS No.:130466-20-5
- A 68930 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7104
CAS No.:130465-39-3
- Batimastat sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC2075
CAS No.:130464-84-5
- Peucedanocoumarin III
Catalog No.:BCN3471
CAS No.:130464-57-2
- Peucedanocoumarin II
Catalog No.:BCN3435
CAS No.:130464-56-1
- Peucedanocoumarin I
Catalog No.:BCN3434
CAS No.:130464-55-0
- A-71623
Catalog No.:BCC7354
CAS No.:130408-77-4
- (-)-Catechin gallate(CG)
Catalog No.:BCN5330
CAS No.:130405-40-2
- Paulownin
Catalog No.:BCN6160
CAS No.:13040-46-5
- (RS)-MCPG disodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7756
CAS No.:1303994-09-3
- CHPG Sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7755
CAS No.:1303993-73-8
- DL-AP5 Sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7753
CAS No.:1303993-72-7
- TC-F 2
Catalog No.:BCC6147
CAS No.:1304778-15-1
- SKF 96365 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6953
CAS No.:130495-35-1
- Cannabisin A
Catalog No.:BCC8138
CAS No.:130508-46-2
- Liriope muscari baily Saponins
Catalog No.:BCN2817
CAS No.:130551-41-6
- Mogroside III
Catalog No.:BCN3167
CAS No.:130567-83-8
- alpha-Terthienylmethanol
Catalog No.:BCN6161
CAS No.:13059-93-3
- Yangambin
Catalog No.:BCN6706
CAS No.:13060-14-5
- Nitidine chloride
Catalog No.:BCN4957
CAS No.:13063-04-2
- (R)-(+)-Corypalmine
Catalog No.:BCN2289
CAS No.:13063-54-2
- N-(2-Hydroxyethyl)-3-(4-nitrophenyl)propylamine
Catalog No.:BCC9053
CAS No.:130634-09-2
- Bindarit
Catalog No.:BCC4965
CAS No.:130641-38-2
- PD123319
Catalog No.:BCC5010
CAS No.:130663-39-7
Short-term memory impairment after isoflurane in mice is prevented by the alpha5 gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor inverse agonist L-655,708.[Pubmed:20966663]
Anesthesiology. 2010 Nov;113(5):1061-71.
BACKGROUND: Memory blockade is an essential component of the anesthetic state. However, postanesthesia memory deficits represent an undesirable and poorly understood adverse effect. Inhibitory alpha5 subunit-containing gamma-aminobutyric acid subtype A receptors (alpha5GABAA) are known to play a critical role in memory processes and are highly sensitive to positive modulation by anesthetics. We postulated that inhibiting the activity of alpha5GABAA receptors during isoflurane anesthesia would prevent memory deficits in the early postanesthesia period. METHODS: Mice were pretreated with L-655,708, an alpha5GABAA receptor-selective inverse agonist, or vehicle. They were then exposed to isoflurane for 1 h (1.3%, or 1 minimum alveolar concentration, or air-oxygen control). Then, either 1 or 24 h later, mice were conditioned in fear-associated contextual and cued learning paradigms. In addition, the effect of L-655,708 on the immobilizing dose of isoflurane was studied. Motor coordination, sedation, anxiety, and the concentration of isoflurane in the brain at 5 min, 1 h, and 24 h after isoflurane were also examined. RESULTS: Motor and sensory function recovered within minutes after termination of isoflurane administration. In contrast, a robust deficit in contextual fear memory persisted for at least 24 h. The alpha5GABAA receptor inverse agonist, L-655,708, completely prevented memory deficits without changing the immobilizing dose of isoflurane. Trace concentrations of isoflurane were measured in the brain 24 h after treatment. CONCLUSIONS: Memory deficits occurred long after the sedative, analgesic, and anxiolytic effects of isoflurane subsided. L-655,708 prevented memory deficit, suggesting that an isoflurane interaction at alpha5GABAA receptors contributes to memory impairment during the early postanesthesia period.
L-655,708 enhances cognition in rats but is not proconvulsant at a dose selective for alpha5-containing GABAA receptors.[Pubmed:17046030]
Neuropharmacology. 2006 Nov;51(6):1023-9.
The in vitro and in vivo properties of L-655,708, a compound with higher affinity for GABA(A) receptors containing an alpha5 compared to an alpha1, alpha2 or alpha3 subunit have been examined further. This compound has weak partial inverse agonist efficacy at each of the four subtypes but, and consistent with the binding data, has higher functional affinity for the alpha5 subtype. In a mouse hippocampal slice model, L-655,708 was able to enhance the long-term potentiation produced by a theta burst stimulation, consistent with a potential role for the alpha5 subtype in processes involving synaptic plasticity, such as learning and memory. When administered in a formulation specifically designed to achieve relatively constant plasma drug concentrations, and therefore maintain selective occupancy of alpha5- compared to alpha1-, alpha2- and alpha3-containing receptors (75+/-4% versus 22+/-10%, respectively), L-655,708 did not alter the dose of pentylenetetrazole required to induce seizures, indicating that the inverse agonist effects of L-655,708 at the alpha5 subtype are not associated with a proconvulsant liability. In the Morris water maze, L-655,708 enhanced performance not only during acquisition but also in a probe trial, demonstrating that this compound has cognition enhancing effects. These data further support the potential of alpha5-containing GABA(A) receptors as a target for novel cognition enhancing drugs.
In vivo labelling of alpha5 subunit-containing GABA(A) receptors using the selective radioligand [(3)H]L-655,708.[Pubmed:15996568]
Neuropharmacology. 2005 Aug;49(2):220-9.
L-655,708 is an imidazobenzodiazepine possessing 30-70-fold selectivity for the benzodiazepine binding site of GABA(A) receptors containing an alpha5 rather than alpha1, alpha2 or alpha3 subunit. In the present study, [(3)H]L-655,708 was used to label mouse brain benzodiazepine binding sites in vivo. When compared to inhibition of in vivo binding of the non-selective ligand [(3)H]Ro 15-1788, the pharmacology of mouse in vivo [(3)H]L-655,708 binding was consistent with selective in vivo labelling of alpha5 subunit-containing GABA(A) receptors. Thus, diazepam was equipotent at inhibiting in vivo [(3)H]L-655,708 and [(3)H]Ro 15-1788 binding; zolpidem, which has very low affinity for alpha5-containing GABA(A) receptors, gave no inhibition of in vivo [(3)H]L-655,708 binding despite inhibiting in vivo [(3)H]Ro 15-1788 binding; and L-655,708 was more potent at inhibiting the in vivo binding of [(3)H]L-655,708 compared to [(3)H]Ro 15-1788. This pharmacological specificity of in vivo [(3)H]L-655,708 binding was confirmed autoradiographically. Hence, the anatomical distribution of in vivo [(3)H]L-655,708 binding was comparable to the distribution of alpha5-containing GABA(A) receptors identified in vitro. Moreover, this distribution was distinct from that identified using [(3)H]Ro 15-1788. These data therefore suggest that [(3)H]L-655,708 can be used to identify alpha5-containing GABA(A) receptors in vivo and that this ligand can be used to measure receptor occupancy of alpha5-selective ligands.
Rat pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a sustained release formulation of the GABAA alpha5-selective compound L-655,708.[Pubmed:16455808]
Drug Metab Dispos. 2006 May;34(5):887-93.
The pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic (i.e., receptor occupancy) properties of L-655,708, a compound with selectivity for alpha5-over alpha1-, alpha2-, and alpha3-containing GABA(A) receptors, were examined in rats with the aim of developing a formulation that would give sustained (up to 6 h) and selective occupancy of alpha5-containing GABA(A) receptors suitable for behavioral studies. Standard rat pharmacokinetic analyses showed that L-655,708 has a relatively short half-life with kinetics in the brain mirroring those in the plasma. In vivo binding experiments showed that plasma concentrations of around 100 ng/ml gave relatively selective in vivo occupancy of rat brain alpha5-versus alpha1-, alpha2-, and alpha3-containing GABA(A) receptors. Therefore, this plasma concentration was chosen as a target to achieve relatively selective occupancy of alpha5-containing receptors using s.c. implantations of L-655,708 (0.4, 1.5, or 2.0 mg) formulated into tablets of various size (20 or 60 mg) containing different amounts of L-655,708 and combinations of low and high viscosity hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (LV- and HV-HPMC). The optimum formulation, 1.5 mg of L-655,708 compressed into a 60-mg tablet with 100% HV-HPMC, resulted in relatively constant plasma concentrations being maintained for at least 6 h with very little difference between C(max) concentrations (125-150 ng/ml) and plateau concentrations (100-125 ng/ml). In vivo binding experiments confirmed the selective occupancy of rat brain alpha5-over alpha1-, alpha2-, and alpha3-containing GABA(A) receptors.


