O-MethylbulbocapnineCAS# 2490-83-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 2490-83-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 273033.0 | Appearance | Powder |
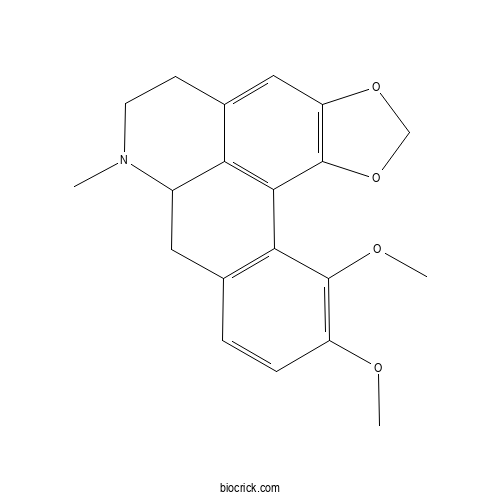
| Formula | C20H21NO4 | M.Wt | 339.39 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 17,18-dimethoxy-11-methyl-3,5-dioxa-11-azapentacyclo[10.7.1.02,6.08,20.014,19]icosa-1(20),2(6),7,14(19),15,17-hexaene | ||
| SMILES | CN1CCC2=CC3=C(C4=C2C1CC5=C4C(=C(C=C5)OC)OC)OCO3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GDVPELGSXTWKDA-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H21NO4/c1-21-7-6-12-9-15-20(25-10-24-15)18-16(12)13(21)8-11-4-5-14(22-2)19(23-3)17(11)18/h4-5,9,13H,6-8,10H2,1-3H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

O-Methylbulbocapnine Dilution Calculator

O-Methylbulbocapnine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9465 mL | 14.7323 mL | 29.4646 mL | 58.9293 mL | 73.6616 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5893 mL | 2.9465 mL | 5.8929 mL | 11.7859 mL | 14.7323 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2946 mL | 1.4732 mL | 2.9465 mL | 5.8929 mL | 7.3662 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0589 mL | 0.2946 mL | 0.5893 mL | 1.1786 mL | 1.4732 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0295 mL | 0.1473 mL | 0.2946 mL | 0.5893 mL | 0.7366 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Calycanthidine
Catalog No.:BCX1349
CAS No.:5516-85-8
- Volvalerenal E
Catalog No.:BCX1348
CAS No.:1247014-33-0
- 8-Formylophiopogonone B
Catalog No.:BCX1347
CAS No.:1316224-74-4
- 5, 9-epi-Phlomiol
Catalog No.:BCX1346
CAS No.:1621908-70-0
- 9-epi-Phlomiol
Catalog No.:BCX1345
CAS No.:1621720-47-5
- 6β-Hydroxy-7-epiloganin
Catalog No.:BCX1344
CAS No.:125410-28-8
- 8-Geranyl daidzein
Catalog No.:BCX1343
CAS No.:1072940-16-9
- 3'-Methoxycoumestrol
Catalog No.:BCX1342
CAS No.:13360-66-2
- Paratocarpin K
Catalog No.:BCX1341
CAS No.:170900-13-7
- Linderanine C
Catalog No.:BCX1340
CAS No.:139681-96-2
- Dracaenoside F
Catalog No.:BCX1339
CAS No.:109460-83-5
- Phloyoside I
Catalog No.:BCX1338
CAS No.:139757-58-7
- Yuanamide
Catalog No.:BCX1351
CAS No.:102421-42-1
- Umbelliprenine
Catalog No.:BCX1352
CAS No.:23838-17-7
- Kaempferol 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-2)-α-L-rhamnopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCX1353
CAS No.:142451-65-8
- Ajugamacrin B
Catalog No.:BCX1354
CAS No.:123313-59-7
- Eugenitin
Catalog No.:BCX1355
CAS No.:480-12-6
- (3R)-dihydroarteannuin B
Catalog No.:BCX1356
CAS No.:87206-33-5
- 6""-apiosyl sec-O-glucosylhamaudol
Catalog No.:BCX1357
CAS No.:2254096-95-0
- Cantleyoside
Catalog No.:BCX1358
CAS No.:32455-46-2
- Neokurarinol
Catalog No.:BCX1359
CAS No.:52483-00-8
- Ilexoside O
Catalog No.:BCX1360
CAS No.:136552-23-3
- 6-Benzoylheteratisine
Catalog No.:BCX1361
CAS No.:99759-48-5
- Blestriarene B
Catalog No.:BCX1362
CAS No.:127211-03-4
O-Methylbulbocapnine and Dicentrine Suppress LPS-Induced Inflammatory Response by Blocking NF-kappaB and AP-1 Activation through Inhibiting MAPKs and Akt Signaling in RAW264.7 Macrophages.[Pubmed:30068871]
Biol Pharm Bull. 2018;41(8):1219-1227.
The natural aporphine alkaloids including crebanine (CN), O-Methylbulbocapnine (OMP), and dicentrine (DC), and protoberberine alkaloids, tetrahydropalmatine (THP) and N-methyl tetrahydropalmatine (NTHP), have been found in Stephania venosa. Previous reports demonstrated CN and THP exhibited anti-inflammatory properties. In this study, we investigated anti-inflammatory effect of CN analogs including OMP, DC, THP, and NTHP in RAW264.7 macrophages. The pre-treatment of macrophages with CN, OMP and DC suppressed lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced pro-inflammatory cytokines and mediators including interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor alpha, prostaglandin E2 and nitric oxide, in which the rank-order of inhibitory potency was DC>CN>/=OMP. Whereas, high dose THP (30-40 microg/mL) reduced LPS-induced IL-6 production in RAW264.7 cells but NTHP did not effect. Moreover, CN, OMP and DC inhibited the LPS-induced expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2. OMP and DC inhibited LPS-induced nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) activation by suppressing the phosphorylation of NF-kappaB at Ser536, but not the nucleus translocation and inhibitor of kappaB (IkappaB)-alpha degradation. In addition, OMP and DC also reduced the phosphorylation and nucleus translocation of activator protein-1 (AP-1). Furthermore, OMP and DC suppressed the LPS-activated myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88), Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) signaling pathway, which were the upstream signaling regulators of AP-1 and NF-kappaB. Collectively, OMP and DC have an anti-inflammatory effect on RAW264.7 macrophages by the suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and mediators. The inhibitory property of OMP and DC is mediated by blockage the activation of MyD88, MAPKs, Akt, NF-kappaB and AP-1 signaling molecules.
Alkaloids from Stephania venosa as Chemo-Sensitizers in SKOV3 Ovarian Cancer Cells via Akt/NF-kappaB Signaling.[Pubmed:29386467]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2018;66(2):162-169.
Crebanine (CN), tetrahydropalmatine (THP), O-Methylbulbocapnine (OMBC) and N-methyl tetrahydropalmatine (NMTHP) are isoquinoline derived natural alkaloids isolated from tubers of Stephania venosa. We investigated chemo-sensitizing effects of these alkaloids in ovarian cancer cells and evaluated underlying molecular mechanisms involved in chemo-sensitivity. Detection of cell apoptosis was evaluated by using flow cytometry. Cell viability was analyzed using 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. Chou-Talalay median effect principle was used to evaluate potential drug interactions. Protein analyses were performed on ovarian carcinoma cells using Western blotting upon treatment with anticancer drug and alkaloids. Aporphine alkaloids, such as CN and OMBC, enhanced cisplatin sensitivity in intrinsic cisplatin resistant SKOV3 cells, but not in cisplatin sensitive A2780 cells. Protoberberine alkaloids, such as THP and NMTHP, had no synergistic effect on cisplatin sensitivity in either cell line. Chemo-sensitizing effects of CN and OMBC in SKOV3 cells were mediated via activating apoptosis-induced cell death through caspase-3, -8 and cleaved poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) and via inhibiting anti-apopotic and survival protein expression, such as Bcl-xL, Baculoviral IAP repeat-containing protein 3 (cIAP-2), survivin and interleukin (IL) -6. Cisplatin stimulated protein kinase B (Akt) and nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) signaling pathways, but not mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), activator protein 1 (AP-1) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) in SKOV3 cells. Akt/NF-kappaB signaling was blocked by CN and OMBC leading to increased sensitization to cisplatin. These findings demonstrate that CN and OMBC sensitizes SKOV3 cells to cisplatin via inhibition of Akt/NF-kappaB signaling and the down regulation of NF-kappaB mediated gene products. Our results suggest that alkaloids obtained from S. venosa could be used as chemo-sensitizers in ovarian cancer to sensitize and minimize the dose related toxicity of platinum-based chemotherapeutic drugs.
Stephanine from Stephania venosa (Blume) Spreng Showed Effective Antiplasmodial and Anticancer Activities, the Latter by Inducing Apoptosis through the Reverse of Mitotic Exit.[Pubmed:28703314]
Phytother Res. 2017 Sep;31(9):1357-1368.
Extracts from the tubers of Stephania venosa (Blum) Spreng growing in Vietnam significantly inhibited cell proliferation against a number of cancer cells including HeLa, MDA-MB231 and MCF-7 cells. A bioassay-guided fractionation led to the isolation of four aporphine and one tetrahydroprotoberberine alkaloids: dehydrocrebanine 1, tetrahydropalmatine 2, stephanine 3, crebanine 4 and O-Methylbulbocapnine 5. The characterization of these compounds was based on MS, NMR and published data. A study by structure-bioactivity relationship on these isolates showed that stephanine is the most active compound. Cell biological studies showed that stephanine induces the reverse of mitotic exit, eventually leading to cell death by apoptosis. This data suggests that stephanine has a unique mode of cell-killing activity against cancer cells, which is seldom observed with known synthetic compounds. In addition to its anticancer property, our data from an in vitro study showed that S. venosa also possesses effective antiplasmodial activity and stephanine was also the most interesting compound but is the most cytotoxic with the lowest selectivity index. Copyright (c) 2017 Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada Phytotherapy Research StartCopTextCopyright (c) 2017 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
A new alkaloid from the fruit of Nandina domestica Thunb.[Pubmed:24897106]
Nat Prod Res. 2014;28(15):1159-64.
A new steroidal alkaloid, (20S,22R,24R)-24-ethyl-3-oxocholest-4-en-22-amino, named as nandsterine (1), together with 10 known alkaloids, palmatine (2), O-Methylbulbocapnine (3), nantenine (4), dehydronantenine (5), glaucine (6), didehydroglaucine (7), dehydrocorydaline (8), jatrorrhizine (9), magnoflorine (10) and berberine (11), was isolated from the fruit of Nandina domestica Thunb. Their structures were elucidated by using spectroscopic methods as well as by comparing with the published data. Compound 1 was a new class of steroidal alkaloid isolated from the family Berberidaceae, meanwhile compounds 2, 3, 6-8 and 10 were obtained from N. domestica for the first time. Compound 1 exhibited cytotoxicity against HL-60 cells (human leukaemia) with IC50 values of 52.1 muM.
Anti-invasion effect of crebanine and O-methylbulbocapnine from Stephania venosa via down-regulated matrix metalloproteinases and urokinase plasminogen activator.[Pubmed:23985774]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2013;61(11):1156-65.
The alkaloids isolated from Stephania venosa (S. venosa) have been shown to inhibit the proliferation and to induce the apoptosis of cancer cells. However, the anti-metastatic effect of the alkaloids on cancer cell invasion is unknown. In this study, we investigated the anti-invasive properties of four alkaloids from S. venosa, crebanine (CN), O-Methylbulbocapnine (OMBC), tetrahydropalmatine (THP), and N-methyltetrahydropalmatine (NMTHP), in HT1080 human fibrosacroma cells. Treatment of the cells with 15 microg/mL of CN and OMBC reduced the chemo-invasion of HT1080 cells to 45 and 50%, respectively, whereas THP and NMTHP had a negative effect. On the other hand, CN and OMBC had no effect on cell migration. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) are the extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation enzymes that play an important role in cancer cell metastasis. Results from zymography and western blot analysis showed that CN and OMBC comparatively reduced MMP-2, MMP-9, MT1-MMP and uPA expression in a dose-dependent manner. However, CN and OMBC had no effect on the activity of collagenase, MMP-2 and MMP-9. We also found that CN and OMBC reduced the nuclear translocation and DNA binding activity of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB), which is the expressed mediator of ECM degradation enzymes. These findings demonstrated that CN and OMBC mediated HT1080 cell invasion by the reduction of MMP-2, MMP-9, uPA and MT1-MMP expression, possibly by targeting of NF-kappaB signaling pathway in the HT1080 cells.
[Chemical constituents from Corydalis yanhusuo].[Pubmed:19894534]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2009 Aug;34(15):1917-20.
OBJECTIVE: To study the chemical constituents from the 60% ethanol extract of Corydalis yanhusuo. METHOD: The chemical constituents were separated and purified by various chromatographic techniques, and their structures were elucidated by chemical evidence and spectroscopic analysis. RESULT: Nine alkaloids were obtained and determined as 7-formyldidehydroglaucine (1), nantenine (2), (+)-O-Methylbulbocapnine (3), d-corydaline (4), tetrahydrocoptisine (5), 8-oxocoptisine (6), palmatine (7), tetrahydropalmatine (8), and dehydrocorydaline (9), respectively. CONCLUSION: Compound 1 was obtained from natural products for the first time, and its NMR data were firstly reported. Compound 3 was reported from Papaveraceae for the first time, and compound 6 was firstly reported from Corydalis yanhusuo.
Vasorelaxing and antioxidant constituents from Hernandia nymphaeifolia.[Pubmed:11582533]
Planta Med. 2001 Oct;67(7):593-8.
Three new alkaloids, (+)-nymphaedaline (1), oxo-O-Methylbulbocapnine (2), and (+)-laetine (3), have been isolated from the trunk bark of Hernandia nymphaeifolia. The structures of these new compounds were elucidated by spectroscopic analysis. Among the isolates of this plant obtained till now, sixteen compounds show effective inhibitory activities on the contraction of vascular smooth muscles induced by high K+ (80 mM) or norepinephrine (3 microM). In addition, eight compounds showed effective antioxidant activities in scavenging the stable free radical, diphenyl-picryl-hydrazyl (DPPH).
Bioactive alkaloids from Illigera luzonensis.[Pubmed:9214740]
J Nat Prod. 1997 Jun;60(6):645-7.
Using antiplatelet aggregation as a guide to fractionation, seven aporphines, actinodaphnine (1), N-methylactinodaphnine (2), launobine (3), dicentrine (4), O-Methylbulbocapnine (5), hernovine (7), and bulbocapnine (9), and two oxoaporphines, dicentrinone (6) and liriodenine (8), were isolated from the stems of Illigera luzonensis. Among them, compounds 2, 4, 5, 8, and 9 were isolated for the first time from this species. Moreover, compounds 1-5, and 8 showed significant antiplatelet aggregation and compounds 1 and 6 exhibited significant vasorelaxant activities, respectively.
Antiplatelet and vasorelaxing actions of some aporphinoids.[Pubmed:8657745]
Planta Med. 1996 Apr;62(2):133-6.
A series of aporphines and oxoaporphines was tested for antiplatelet and vasorelaxing actions. (+)-N-Methylactinodaphnine, (-)-norannuradhapurine x HBr, xylopine, actinodaphnine, and N-methylnandigerine showed strong inhibition of adenosine 5'-diphosphate (ADP)-induced platelet aggregation. Boldine, (+)-N-methylactinodaphnine, (-)-norannuradhapurine x HBr, xylopine, N-acetyllaurolitsine, N-methyllaurotetanine, actinodaphnine, N-methylnandigerine, O-Methylbulbocapnine, and liriodenine showed strong inhibition of arachidonic acid (AA)-induced platelet aggregation. (+)-N-Methylactinodaphnine, fissoldine x HCIO4, (-)-norannuradhapurine x HBr, xlylopine, N-methyllaurotetanine, actinodaphnine, N-methylnandigerine, O-Methylbulbocapnine, and liriodenine showed strong inhibiton of collagen-induced platelet aggregation. (-)-Norannuradhapurine x HBr, xylopine, N-methyllaurotetanine, and actinodaphnine showed strong inhibition of platelet-activating factor (PAF; 1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine)-induced platelet aggregation. (+)-N-Methylactinodaphnine, laurotetanine, N-methylactinodaphnine N-oxide, oxoglaucine, boldine, and actinodaphnine showed vasorelaxing action in rat thoracic aorta. The results are discussed on the basis of structure-activity relationships.


