6-BenzoylheteratisineCAS# 99759-48-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
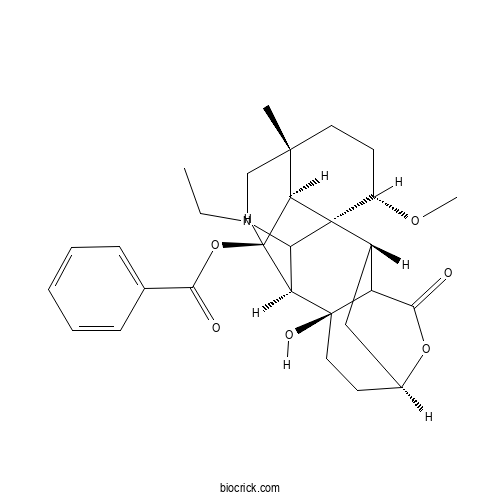
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 99759-48-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 165325156.0 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C29H37NO6 | M.Wt | 495.62 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | [(1S,2S,6S,9S,10R,14R,17S,18S,19S)-12-ethyl-9-hydroxy-17-methoxy-14-methyl-4-oxo-5-oxa-12-azahexacyclo[8.7.2.12,6.01,11.03,9.014,18]icosan-19-yl] benzoate | ||
| SMILES | CCN1CC2(CCC(C34C2C(C(C31)C5(CCC6CC4C5C(=O)O6)O)OC(=O)C7=CC=CC=C7)OC)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | XVVZJDDPRFFKTQ-PBCRGHHCSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C29H37NO6/c1-4-30-15-27(2)12-11-19(34-3)29-18-14-17-10-13-28(33,20(18)26(32)35-17)21(24(29)30)22(23(27)29)36-25(31)16-8-6-5-7-9-16/h5-9,17-24,33H,4,10-15H2,1-3H3/t17-,18-,19-,20?,21-,22+,23-,24?,27-,28+,29-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

6-Benzoylheteratisine Dilution Calculator

6-Benzoylheteratisine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0177 mL | 10.0884 mL | 20.1767 mL | 40.3535 mL | 50.4419 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4035 mL | 2.0177 mL | 4.0353 mL | 8.0707 mL | 10.0884 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2018 mL | 1.0088 mL | 2.0177 mL | 4.0353 mL | 5.0442 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0404 mL | 0.2018 mL | 0.4035 mL | 0.8071 mL | 1.0088 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0202 mL | 0.1009 mL | 0.2018 mL | 0.4035 mL | 0.5044 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Ilexoside O
Catalog No.:BCX1360
CAS No.:136552-23-3
- Neokurarinol
Catalog No.:BCX1359
CAS No.:52483-00-8
- Cantleyoside
Catalog No.:BCX1358
CAS No.:32455-46-2
- 6""-apiosyl sec-O-glucosylhamaudol
Catalog No.:BCX1357
CAS No.:2254096-95-0
- (3R)-dihydroarteannuin B
Catalog No.:BCX1356
CAS No.:87206-33-5
- Eugenitin
Catalog No.:BCX1355
CAS No.:480-12-6
- Ajugamacrin B
Catalog No.:BCX1354
CAS No.:123313-59-7
- Kaempferol 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-2)-α-L-rhamnopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCX1353
CAS No.:142451-65-8
- Umbelliprenine
Catalog No.:BCX1352
CAS No.:23838-17-7
- Yuanamide
Catalog No.:BCX1351
CAS No.:102421-42-1
- O-Methylbulbocapnine
Catalog No.:BCX1350
CAS No.:2490-83-7
- Calycanthidine
Catalog No.:BCX1349
CAS No.:5516-85-8
- Blestriarene B
Catalog No.:BCX1362
CAS No.:127211-03-4
- Gymnoside VII
Catalog No.:BCX1363
CAS No.:899430-07-0
- Crocetindial
Catalog No.:BCX1364
CAS No.:502-70-5
- Morroniaglycone
Catalog No.:BCX1365
CAS No.:1644061-02-8
- Ethyl (2E,4Z)-deca-2,4-dienoate
Catalog No.:BCX1366
CAS No.:3025-30-7
- Myristoleic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1367
CAS No.:544-64-9
- Elaidic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCX1368
CAS No.:1937-62-8
- Cis-11-Eicosenoic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1369
CAS No.:5561-99-9
- Octadec-11-enoic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1370
CAS No.:693-72-1
- Tridecanoic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1371
CAS No.:638-53-9
- Methyl tridecanoate
Catalog No.:BCX1372
CAS No.:1731-88-0
- Pentadecanoic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1373
CAS No.:1002-84-2
Neuropharmacological Potential of Diterpenoid Alkaloids.[Pubmed:37242531]
Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 May 14;16(5):747.
This study provides a narrative review of diterpenoid alkaloids (DAs), a family of extremely important natural products found predominantly in some species of Aconitum and Delphinium (Ranunculaceae). DAs have long been a focus of research attention due to their numerous intricate structures and diverse biological activities, especially in the central nervous system (CNS). These alkaloids originate through the amination reaction of tetra or pentacyclic diterpenoids, which are classified into three categories and 46 types based on the number of carbon atoms in the backbone structure and structural differences. The main chemical characteristics of DAs are their heterocyclic systems containing beta-aminoethanol, methylamine, or ethylamine functionality. Although the role of tertiary nitrogen in ring A and the polycyclic complex structure are of great importance in drug-receptor affinity, in silico studies have emphasized the role of certain sidechains in C13, C14, and C8. DAs showed antiepileptic effects in preclinical studies mostly through Na(+) channels. Aconitine (1) and 3-acetyl aconitine (2) can desensitize Na(+) channels after persistent activation. Lappaconitine (3), N-deacetyllapaconitine (4), 6-Benzoylheteratisine (5), and 1-benzoylnapelline (6) deactivate these channels. Methyllycaconitine (16), mainly found in Delphinium species, possesses an extreme affinity for the binding sites of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChR) and contributes to a wide range of neurologic functions and the release of neurotransmitters. Several DAs such as bulleyaconitine A (17), (3), and mesaconitine (8) from Aconitum species have a drastic analgesic effect. Among them, compound 17 has been used in China for decades. Their effect is explained by increasing the release of dynorphin A, activating the inhibitory noradrenergic neurons in the beta-adrenergic system, and preventing the transmission of pain messages by inactivating the Na(+) channels that have been stressed. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory, neuroprotective, antidepressant, and anxiolytic activities are other CNS effects that have been investigated for certain DAs. However, despite various CNS effects, recent advances in developing new drugs from DAs were insignificant due to their neurotoxicity.
Interaction of the structurally related aconitum alkaloids, aconitine and 6-benzyolheteratisine, in the rat hippocampus.[Pubmed:10618469]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1999 Dec 15;386(2-3):187-94.
Aconitine is a highly toxic diterpenoid alkaloid occurring in plants of the Aconitum genus. Aconitine is known to shift the voltage-dependence of the voltage-dependent Na(+) channel towards hyperpolarized direction, thereby leading to a permanent activation of the channel. 6-Benzoylheteratisine is a plant alkaloid which is structurally related with aconitine. The aim of the present study was to investigate the interaction of aconitine and 6-Benzoylheteratisine in the rat hippocampus. The experiments were carried out as extracellular recordings of stimulus evoked population spikes and field excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) in rat hippocampal slices. Aconitine (10-100 nM) exerted a concentration-dependent decrease in the amplitude of the orthodromic population spike. When aconitine was applied in presence of 6-Benzoylheteratisine (3 microM), the concentration-response curve was shifted to the right. Furthermore, the complete suppression of the population spike evoked by 100 nM aconitine was reversed by 10 microM 6-Benzoylheteratisine. The closely related alkaloid heteratisine (3 and 30 microM), however, was not capable to antagonize the aconitine action. 6-Benzoylheteratisine shifted the input-output relationship of the presynaptic fiber spike as function of the stimulation intensity and the input-output relationship of the field EPSP as function of the presynaptic fiber spike to the right. Thus, electrophysiologically this alkaloid seems to inhibit predominantly the excitability of the afferent fibres and, in consequence, neurotransmission between Schaffer collaterals and the CA1 neurons, thereby suppressing the firing of the latter. Spontaneously occurring epileptiform activity in area CA3 elicited by omission of Mg(2+) and elevation of K(+) was attenuated by 6-Benzoylheteratisine (1 and 10 microM). Patch clamp studies performed on cultured rat hippocampal pyramidal cells revealed an inhibitory action of 6-Benzoylheteratisine on whole cell Na(+) currents. It is concluded that the inhibitory and antiepileptiform effect of ajacine and lappaconitine is mediated by an inhibition of the voltage-dependent Na(+) channel which might be important for filtering high frequency bursts of action potentials characteristic for epileptiform activity in the hippocampus. Thus, 6-Benzoylheteratisine seems to be a naturally occurring antagonist of the Na(+) channel activator aconitine.
The alkaloid 6-benzoylheteratisine inhibits voltage-gated Na+ channels in rat brain synaptosomes.[Pubmed:9833644]
Neuropharmacology. 1998 Sep;37(9):1139-46.
The effects of the Aconitum alkaloid 6-Benzoylheteratisine on the aconitine-, veratridine-, oubain- and KCl-induced alterations in free synaptosomal Na + ([Na+]i) and Ca2+ ([Ca2+]i) and the release of endogenous glutamate from rat cerebrocortical synaptosomes were investigated. [Na+]i and [Ca2+]i were fluorometrically determined employing SBFI and Fura-2 as the Na+ and Ca2+ sensitive dyes, respectively. Glutamate was detected by a continuous enzyme-linked fluorometric assay. The study revealed a concentration-dependent inhibitory effect of 6-Benzoylheteratisine on aconitine-induced increases in [Na+]i, [Ca2+]i and the release of glutamate. The IC50 values were 4.1 microM (Na+), 4.8 microM (Ca2+) and 4.8 microM (glutamate release). Application of 100 microM 6-Benzoylheteratisine after stimulation with 5 microM veratridine also reduced the induced [Na+]i and [Ca2+]i with half-lives of 72.1 and 44.7 s, respectively. Furthermore, 100 microM 6-Benzoylheteratisine reduced the ouabain-induced Na+ influx to the same extent as the Na+ channel inhibitor tetrodotoxin, which points to an inhibition of non-activated Na+ channels by 6-Benzoylheteratisine. Additionally, 100 microM 6-Benzoylheteratisine failed to affect the release of glutamate and the increase in [Ca2+]i induced by 30 mM KCl, indicating that voltage-gated Ca2+ channels were not affected by 6-Benzoylheteratisine. The data suggest an inhibitory effect of 6-Benzoylheteratisine on voltage-gated Na+ channels as the only target, whereas mechanisms of Na+ and Ca2+ homoeostasis and pathways of glutamate release seem not to be affected by the drug.
Effects of the alkaloids 6-benzoylheteratisine and heteratisine on neuronal activity in rat hippocampal slices.[Pubmed:9294968]
Neuropharmacology. 1997 Aug;36(8):1039-46.
Alkaloids of different Aconitum species are employed as analgesics in traditional Chinese folk medicine. The present study was designed in order to investigate the effects of the structurally related alkaloids 6-Benzoylheteratisine and heteratisine on neuronal activity in rat hippocampus. Experiments were performed as extracellular recordings of stimulus evoked population spikes in rat hippocampal slices. 6-Benzoylheteratisine (0.01-10 microM) inhibited the ortho- and antidromic population spike as well as the field EPSP in a concentration- and frequency-dependent manner. Heteratisine (1-100 microM) was a less potent inhibitor. It exerted a depression of the orthodromic spike, but failed to affect the antidromic population spike. 6-Benzoylheteratisine (10 microM) diminished epileptiform activity induced by bicuculline. In hippocampal neurons, this compound reduced the peak amplitude of the sodium current. There was no effect of heteratisine on the sodium current in concentrations up to 100 microM. It is concluded that the frequency-dependent action of 6-Benzoylheteratisine suggests an inhibition of neuronal activity which underlies epileptiform burst discharges. The predominant effect is a suppression of neuronal activity due to a blockade of sodium channels.
6-Benzoylheteratisine - a class-I antiarrhythmic substance from Aconitum tanguticum (Maxim.) Stapf.[Pubmed:23195397]
Phytomedicine. 1997 Jun;4(2):109-15.
The antiarrhythmic action of 6-Benzoylheteratisine (6-bh), a C(19) diterpenoid alkaloid from Aconitum tanguticum (Maxim.) Stapf was investigated in left and right guinea pig isolated atria. Furthermore, possible effects on transmembrane action potential of isolated papillary muscles were studied using microelectrode techniques. At concentrations of more than 6 x 10(-8) mol/1, preincubation with 6-bh suppressed arrhythmias induced by aconitine, veratridine and ouabain. Bradycardia of the right atria as a sign of toxicity occurred at 1 x 10(-6) mol/1. The alkaloid significantly reduced the maximum rate of rise of the action potential as well as the action potential amplitude, indicating inhibition of voltage-dependent sodium channels as a functional principle. Additionally, a use-dependent mode of drug-action could be demonstrated. We conclude therefore, that 6-bh is a naturally occurring class-I antiarrhythmic substance. The compound is a main alkaloid of Aconitum tanguticum, a plant used to prepare a poison antidote in Chinese and Tibetan folk medicine. It may be speculated that the poison antidote effect is at least partially based on the antiarrhythmic properties of 6-bh.
Bicuculline-induced epileptiform activity in rat hippocampal slices: suppression by Aconitum alkaloids.[Pubmed:9225604]
Planta Med. 1997 Jun;63(3):228-32.
Alkaloids of Aconitum spec. (Ranunculaceae) are employed in traditional Chinese folk medicine as analgesics. The present study was designed in order to investigate the effects of the structurally related alkaloids aconitine, lappaconitine, and 6-Benzoylheteratisine on experimentally induced epileptiform activity. Experiments were performed as extracellular recordings of stimulus evoked population spikes in rat hippocampal slices. Epileptiform activity was induced by bicuculline. All three alkaloids exerted an inhibitory action on excitability of hippocampal pyramidal cells in a frequency-dependent manner. The onset of inhibition was accelerated by increasing the frequency of electrical stimulation. Aconitine (1 microM) evoked a complete suppression of both normal and epileptiform activity, whereas lappaconitine (10 microM) and 6-Benzoylheteratisine (10 microM) selectively diminished the epileptiform afterdischarges and the duration of the bursts, but spared the normal activity. The present findings suggest that the structurally related Aconitum alkaloids aconitine, lappaconitine, and 6-Benzoylheteratisine possess an anticonvulsive potential. The predominant effect of these alkaloids is to suppress the spread of seizure activity, and they may therefore tend to distort epileptic events. However, despite their similar structure, they exert qualitatively and quantitatively different inhibitory effects.
Electrophysiological actions of the plant alkaloid 6-benzoylheteratisine in rat hippocampal slices.[Pubmed:9109372]
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1997 Apr;355(4):538-44.
The effects of the Aconitum alkaloid 6-Benzoylheteratisine on neuronal activity was investigated in the in vitro slice preparation of rat hippocampus by extracellular recording of the stimulus-evoked population spike. 6-Benzoylheteratisine (0.01-10 microM) depressed the orthodromic and antidromic population spike in a concentration-dependent manner. The action of the drug was activity-dependent. The latency of onset of the inhibition was accelerated when the frequency of electrical stimulation had been increased. Furthermore, the effect of 6-Benzoylheteratisine was evaluated in two different models of epileptiform activity induced either by blockade of GABA receptors by bicuculline (10 microM) or by a nominal Mg2+-free bathing medium. Due to the activity-dependent mode of action, this drug effectively reduced the number and the size of the synaptically evoked population spikes in the presence of bicuculline or nominal Mg2+-free bathing medium, respectively.
Inhibition of neuronal activity in rat hippocampal slices by Aconitum alkaloids.[Pubmed:8949940]
Brain Res. 1996 Oct 28;738(1):154-7.
The structurally related Aconitum alkaloids aconitine, lappaconitine, and 6-Benzoylheteratisine inhibited the orthodromic and antidromic population spike in hippocampal CA1 area in a frequency-dependent manner. Aconitine (1 microM) completely suppressed epileptiform activity induced by omission of Mg2+ as well as normal neuronal activity, whereas lappaconitine (10 microM) and 6-Benzoylheteratisine (10 microM) diminished epileptiform activity by sparing normal neuronal activity.


