Tridecanoic acidCAS# 638-53-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 638-53-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 12530.0 | Appearance | Powder |
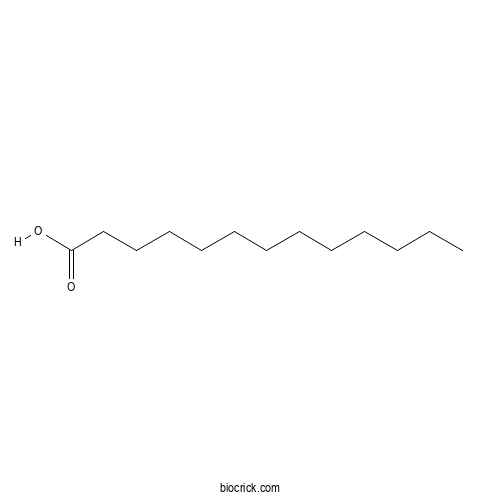
| Formula | C13H26O2 | M.Wt | 214.35 |
| Type of Compound | Aliphatics | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | tridecanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | SZHOJFHSIKHZHA-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C13H26O2/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13(14)15/h2-12H2,1H3,(H,14,15) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Tridecanoic acid Dilution Calculator

Tridecanoic acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.6653 mL | 23.3263 mL | 46.6527 mL | 93.3053 mL | 116.6317 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.9331 mL | 4.6653 mL | 9.3305 mL | 18.6611 mL | 23.3263 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4665 mL | 2.3326 mL | 4.6653 mL | 9.3305 mL | 11.6632 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0933 mL | 0.4665 mL | 0.9331 mL | 1.8661 mL | 2.3326 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0467 mL | 0.2333 mL | 0.4665 mL | 0.9331 mL | 1.1663 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Octadec-11-enoic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1370
CAS No.:693-72-1
- Cis-11-Eicosenoic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1369
CAS No.:5561-99-9
- Elaidic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCX1368
CAS No.:1937-62-8
- Myristoleic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1367
CAS No.:544-64-9
- Ethyl (2E,4Z)-deca-2,4-dienoate
Catalog No.:BCX1366
CAS No.:3025-30-7
- Morroniaglycone
Catalog No.:BCX1365
CAS No.:1644061-02-8
- Crocetindial
Catalog No.:BCX1364
CAS No.:502-70-5
- Gymnoside VII
Catalog No.:BCX1363
CAS No.:899430-07-0
- Blestriarene B
Catalog No.:BCX1362
CAS No.:127211-03-4
- 6-Benzoylheteratisine
Catalog No.:BCX1361
CAS No.:99759-48-5
- Ilexoside O
Catalog No.:BCX1360
CAS No.:136552-23-3
- Neokurarinol
Catalog No.:BCX1359
CAS No.:52483-00-8
- Methyl tridecanoate
Catalog No.:BCX1372
CAS No.:1731-88-0
- Pentadecanoic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1373
CAS No.:1002-84-2
- Heptadecanoic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1374
CAS No.:506-12-7
- Methyl heptadecanoate
Catalog No.:BCX1375
CAS No.:1731-92-6
- Nonadecanoic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1376
CAS No.:646-30-0
- Ethyl palmitoleate
Catalog No.:BCX1377
CAS No.:56219-10-4
- Palmitoleic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1378
CAS No.:373-49-9
- Arachidic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1379
CAS No.:506-30-9
- Ethyl Arachidonate
Catalog No.:BCX1380
CAS No.:1808-26-0
- Methyl arachidonate
Catalog No.:BCX1381
CAS No.:2566-89-4
- Ethyl oleate
Catalog No.:BCX1382
CAS No.:111-62-6
- Docosahexaenoic acid ethyl ester
Catalog No.:BCX1383
CAS No.:84494-72-4
Evaluation of Antifungal Activity of Endophytic Bacillus spp. and Identification of Secondary Metabolites Produced Against the Phytopathogenic Fungi.[Pubmed:38580768]
Curr Microbiol. 2024 Apr 5;81(5):128.
Endophytic bacteria serve as a rich source of diverse antimicrobial compounds. Recently, there has been a growing interest in utilizing endophytic Bacillus spp. as biological agents against phytogenic fungi, owing to their potential to produce a wide range of antimicrobial substances. The objective of this research was to investigate the protective abilities of 15 endophytic Bacillus spp. isolated from previous study from wheat plant, against the phytopathogenic fungi, Fusarium graminearum and Macrophomina phaseolina. A dual culture plate assay was conducted as a preliminary analysis, revealing that 7 out of 15 endophytic Bacillus spp. demonstrated inhibition against one or both of the phytopathogenic fungi used in this study. All seven endophytes were further assessed for the presence of diffusible antifungal metabolites. The cultures were grown in potato dextrose broth for 120 h, and the cell-free supernatant was extracted and analyzed using the cup plate method. The methanolic extract yielded similar results to the dual culture plate analysis, except for WL2-15. Additionally, deformities in the mycelial structure were examined under the light microscope upon exposure to methanolic extract. Furthermore, the analysis and identification of metabolites were carried out via gas chromatography-mass spectrometry of methanolic extract from selected seven endophytic Bacillus spp. The chromatogram revealed the presence of some major peaks such as Tridecanoic acid, methyl ester, hydroperoxide, 1-methylbutyl, 9-octadecenamide, (z)-, hexane-1,3,4-triol, 3,5-dimethyl- tetradecanoic acid. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of these biocontrol agents in endophytic Bacillus spp. Interestingly, volatile organic compound production was also seen in all the isolates against the phytopathogenic fungi.
Occurrence and pattern of legacy and emerging per- and Poly-FluoroAlkyl substances (PFAS) in eggs of loggerhead turtle Caretta caretta from western Mediterranean.[Pubmed:38159636]
Environ Pollut. 2024 Feb 15;343:123257.
Per-and Poly-FluoroAlkyl Substances (PFAS) are a class of persistent, toxic, and mobile and chemicals both from industrial sources and from the use and disposal of Consumers products containing PFAS, whose concentration in marine food webs could pose a toxicological risk for biota and humans. In 2021, unhatched eggs were sampled from 41 loggerhead turtle Caretta caretta nests from the Italian shores of the Campania Region (Southern Italy). Whole eggs were analysed for the presence of 66 legacy and emerging PFAS with Liquid Chromatography coupled to Hybrid High Resolution Mass Spectrometry. A median Sigma(66) Per- and Poly-FluoroAlkyl Substances value of 3.34 ng/g egg fresh weight was found; perfluoroctane sulfonate (PFOS) represented the most contributing congener (47%), followed by perfluoro-n-undecanoic acid, perfluoro-n-Tridecanoic acid, perfluoro-n-decanoic acid, perfluoro-n-decanoic acid, and perfluoro-n-tetradecanoic acid, respectively. Such compounds showed a log-norm distribution, suggesting found concentrations could represent the baseline levels in the considered sampling area. Emerging ChloroPolyFluoroPolyEthers Carboxylic Acids (ClPFECAs) were found in 20 out of 41 samples in the range 0.01-1.59 ng/g. Four samples had 20-100 fold higher concentration compared to that of other samples, suggesting the presence of hot spot areas possibly related to presence of fluoropolymer-based marine litter turtles may ingest. The analysis of two paired eggs/liver samples recovered from stranded animals revealed PFAS concentration in the same order of magnitude, supporting the role of vitellogenin in their selective transfer to yolk. Significant (P = 0.0155) Kendall negative correlation coefficient of -0.2705 among PFOS content in eggs and the recorded hatching success prompts for further investigation on associated exposure assessment and related eco-toxicity risk. This work reports for the first time PFAS presence in georeferenced loggerhead turtle eggs of the Mediterranean Sea and results represent a starting point to study PFAS time-trends in this vulnerable species.
Network pharmacology‒based analysis of marine cyanobacteria derived bioactive compounds for application to Alzheimer's disease.[Pubmed:37927608]
Front Pharmacol. 2023 Oct 19;14:1249632.
In recent years, the Alzheimer's disease (AD) epidemic has become one of the largest global healthcare crises. Besides, the available systemic therapies for AD are still inadequate. Due to the insufficient therapeutic options, new treatment strategies are urgently needed to achieve a satisfactory therapeutic effect. Marine bio-resources have been accepted as one of the most economically viable and sustainable sources with potential applications for drug discovery and development. In this study, a marine cyanobacteria-Synechococcus sp. XM-24 was selected as the object of research, to systematically investigate its therapeutic potential mechanisms for AD. The major active compounds derived from the Synechococcus sp. biomass were identified via pyrolysis-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS), and 22 compounds were identified in this strain. The most abundant chemical compounds was (E)-octadec-11-enoic acid, with the peak area of 30.6%. Follow by Tridecanoic acid, 12-methyl- and hexadecanoic acid, with a peak area of 23.26% and 18.23%, respectively. GC-MS analysis also identified indolizine, isoquinoline, 3,4-dihydro- and Phthalazine, 1-methyl-, as well as alkene and alkane from the strain. After the chemical toxicity test, 10 compounds were finally collected to do the further analysis. Then, network pharmacology and molecular docking were adopted to systematically study the potential anti-AD mechanism of these compounds. Based on the analysis, the 10 Synechococcus-derived active compounds could interact with 128 related anti-AD targets. Among them, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) and mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 (MAPK3) were the major targets. Furthermore, the compounds N-capric acid isopropyl ester, (E)-octadec-11-enoic acid, and 2H-Pyran-2,4(3H)-dione, dihydro-6-methyl- obtained higher degrees in the compounds-intersection targets network analysis, indicating these compounds may play more important role in the process of anti-AD. In addition, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analysis showed that these active compounds exert the anti-AD effects mainly through PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction and ras signaling pathway. Our study identified Synechococcus-derived bioactive compounds have the potential for application to AD by targeting multiple targets and related pathways, which will provide a foundation for future research on applications of marine cyanobacteria in the functional drug industry.
Epicuticular wax chemicals of Lablab purpureus subsp. bengalensis influence short-range attraction and oviposition responses in Aphis craccivora and Aphis gossypii.[Pubmed:37855212]
Bull Entomol Res. 2023 Dec;113(6):794-807.
Lablab purpureus subsp. bengalensis (Jacq.) Verdc. is an important legume of India and Africa. Both aphids, Aphis craccivora Koch and A. gossypii Glover (Hemiptera: Aphididae), are important herbivorous pests of this legume crop. These viviparous females lay nymphs on the leaf surface of this legume plant. Therefore, it is of considerable interest to study whether leaf surface wax chemicals (long-chain alkanes and free fatty acids) of this legume plant served as short-range attractants and oviposition stimulants in both females to lay nymphs. Twenty-one n-alkanes from n-C(12) to n-C(35) and 11 free fatty acids from C12:0 to C22:0 were identified in leaf surface waxes. Nonacosane and nonadecanoic acid were the most abundant among n-alkanes and free fatty acids, respectively. Both females were attracted towards one leaf equivalent surface wax against the control solvent (petroleum ether) in short Y-tube olfactometer bioassays. A synthetic blend of tetradecane, pentadecane, tetracosane, Tridecanoic acid, tetradecanoic acid, and heneicosanoic acid comparable to one leaf equivalent surface wax served as short-range attractants and oviposition stimulants in A. craccivora; whereas a synthetic blend of tetradecane, hexadecane, docosane, nonadecanoic acid, and arachidic acid comparable to one leaf equivalent surface wax acted as short-range attractants and oviposition stimulants in A. gossypii. These results can provide the basis for efficient pest management strategies of A. craccivora and A. gossypii against L. purpureus subsp. bengalensis using host plant leaf surface wax compounds. Further, SEM studies of antennae and forelegs of both aphids were conducted to observe sensilla structures, which help in chemoreception.
Untargeted metabolomics analysis of plasma metabolic characteristics in patients with acne and insulin resistance.[Pubmed:37726574]
Amino Acids. 2023 Oct;55(10):1417-1428.
Acne vulgaris is a chronic inflammatory disease with high incidence, diverse clinical manifestations, poor clinical efficacy, and easy recurrence. Recent studies have found that the occurrence of acne is related to metabolic factors such as insulin resistance; however, the specific mechanism of action remains unclear. This study aimed to identify significantly different metabolites and related metabolic pathways in the serum of acne vulgaris patients with or without insulin resistance. LC-MS/MS was used to analyze serum samples from patients about acne with insulin resistance (n = 51) and acne without insulin resistance (n = 69) to identify significant metabolites and metabolic pathways. In this study, 18 significant differential metabolites were screened for the first time. In the positive-ion mode, the upregulated substances were creatine, sarcosine, D-proline, uracil, Phe-Phe, L-pipecolic acid, and DL-phenylalanine; the downregulated substances were Tridecanoic acid (tridecylic acid), L-lysine, cyclohexylamine, sphingomyelin (d18:1/18:0), gamma-L-Glu-epsilon-L-Lys, and 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidylcholine. In the negative-ion mode, the upregulated substance was cholesterol sulfate, and the downregulated substances were D(-)-beta-hydroxybutyric acid, myristic acid, D-galacturonic acid, and dihydrothymine. Cholesterol sulfate showed the most significant expression among all differential metabolites (VIP = 7.3411). Based on the KEGG database, necroptosis and ABC transporters were the most significantly enriched metabolic pathways in this experiment. The differential metabolites and pathways identified in this study may provide new possibilities for the clinical diagnosis and development of targeted drugs for acne patients with insulin resistance.
Dietary Supplementation with Putrescine Improves Growth Performance and Meat Quality of Wenchang Chickens.[Pubmed:37174601]
Animals (Basel). 2023 May 7;13(9):1564.
This study was to investigate the effects of dietary supplementation with putrescine on the growth performance and meat quality of chickens. A total of 480 eighty-day-old female Wenchang chickens were randomly assigned into four groups, with 8 replications per group and 15 animals per replicate. The chickens in the control group (Con) were fed a basal diet; the 3 experimental groups were fed a basal diet with 0.01%, 0.03%, and 0.05% putrescine, respectively. The experiment lasted for 40 days. The results showed that dietary supplementation with 0.05% putrescine increased (p < 0.05) the final body weight and average daily weight gain, and decreased the ratio of feed intake to the body weight gain of Wenchang chickens. Dietary supplementation with putrescine decreased the concentrations of putrescine, spermidine, and spermine in serum (p < 0.05). The contents of methionine, phenylalanine, lysine, aspartic acid, tyrosine, total essential amino acids, and total amino acids in breast muscle were higher (p < 0.05) in 0.03% and 0.05% groups than those in Con group. However, the contents of undecanoic acid, lauric acid, Tridecanoic acid, myristic acid, pentadecanoic acid, arachidic acid, docosanoic acid, tricosanic acid, lignoceric acid, erucic acid, cis-11,14,17-eicosatrienoate, linoleic acid, and total n-6 monounsaturated fatty acids in breast muscle were lower (p < 0.05) in 0.03% and 0.05% groups than those in Con group. In addition, putrescine supplementation decreased (p < 0.05) the ratio of n-6/n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in breast meat. Overall, dietary supplementation with 0.05% putrescine enhanced the growth performance and meat quality of Wenchang chickens.
Antibacterial and Anti-HIV Metabolites from Marine Streptomyces albus MAB56 Isolated from Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India.[Pubmed:37086378]
Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2023 Dec;195(12):7738-7754.
Marine-derived actinobacteria have tremendous potential to produce novel metabolites with diverse biological activities. The Andaman coast of India has a lot of microbial diversity, but it is still a relatively unknown ecology for isolating novel actinobacteria with beneficial bioactive compounds. We have isolated 568 actinobacterial strains from mangrove rhizosphere sediments and sponge samples. Crude extracts from 75 distinct strains were produced by agar surface fermentation and extracted using ethyl acetate. In the disc diffusion method, 25 actinobacterial strains showed antimicrobial activity; notably, the strain MAB56 demonstrated promising broad-spectrum activity. Strain MAB56 was identified as Streptomyces albus by cultural, microscopic, and molecular methods. Conditions for bioactive metabolites from MAB56 were optimized and produced in a lab-scale fermenter. Three active metabolites (C1, C2, and C3) that showed promising broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity were isolated through HPLC-based purification. Based on the UV, FT-IR, NMR, and LC-MS analysis, the chemical nature of the active compounds was confirmed as 12-methyltetradecanoic acid (C1), palmitic acid (C2), and Tridecanoic acid (C3) with molecular formulae C(14)H(28)O(2), C(16)H(32)O(2), and C(13)H(26)O(2), respectively. Interestingly, palmitic acid (C2) also exhibited anti-HIV activity with an IC50 value of < 1 microg/ml. Our findings reveal that the actinobacteria from the Andaman marine ecosystems are promising for isolating anti-infective metabolites.
Gum arabic/guar gum stabilized Hydnocarpus wightiana oil nanohydrogel: Characterization, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and anti-biofilm activities.[Pubmed:37030463]
Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Jun 1;239:124341.
Hydnocarpus wightiana oil has proven to inhibit the growth of pathogenic microorganisms; however, the raw form is highly susceptible to oxidation, and thus it becomes toxic when uptake is in high amounts. Therefore, to minimize the deterioration, we formulated Hydnocarpus wightiana oil-based nanohydrogel and studied its characteristics as well biological activity. The low energy-assisted hydrogel was formulated by including gelling agent, connective linker, and cross-linker and it resulted in internal micellar polymerization of the milky white emulsion. The oil showed the presence of octanoic acid, n-tetradecane, methyl 11-(2-cyclopenten-1-yl) undecanoate (methyl hydnocarpate), 13-(2-cyclopenten-1-yl) Tridecanoic acid (methyl chaulmoograte), and 10,13-eicosadienoic acid. The amount of caffeic acid was 0.0636 mg/g, which was higher than the amount of gallic acid (0.0076 mg/g) in the samples. The formulated nanohydrogel showed an average droplet size of 103.6 nm with a surface charge of -17.6 mV. The minimal inhibitory bactericidal, and fungicidal concentrations of nanohydrogel against pathogenic bacteria and fungi were ranging from 0.78 to 1.56 mul/mL with 70.29-83.62 % antibiofilm activity. Also, nanohydrogel showed a significantly (p < 0.05) higher killing rate for Escherichia coli (7.89 log CFU/mL) than Staphylococcus aureus (7.81 log CFU/mL) with comparable anti-inflammatory activity than commercial standard (49.28-84.56 %). Therefore, it can be concluded that being hydrophobic, and having the capability of target-specific drug absorption as well as biocompatibility nanohydrogels can be utilized to cure various pathogenic microbial infections.
Untargeted metabolomics and lipidomics to assess plasma metabolite changes in dairy goats with subclinical hyperketonemia.[Pubmed:37028962]
J Dairy Sci. 2023 May;106(5):3692-3705.
Subclinical hyperketonemia (SCHK) is the major metabolic disease observed during the transition period in dairy goats, and is characterized by high plasma levels of nonesterified fatty acids (NEFA) and beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB). However, no prior study has comprehensively assessed metabolomic profiles of dairy goats with SCHK. Plasma samples were collected within 1 h after kidding from SCHK goats (BHB concentration >0.8 mM, n = 7) and clinically healthy goats (BHB concentration <0.8 mM, n = 7) with similar body condition score (2.75 +/- 0.15, mean +/- standard error of the mean) and parity (primiparous). A combination of targeted and untargeted mass spectrometric approaches was employed for analyzing the various changes in the plasma lipidome and metabolome. Statistical analyses were performed using the GraphPad Prism 8.0, SIMCA-P software (version 14.1), and R packages (version 4.1.3). Plasma aminotransferase, nonesterified fatty acids, and BHB concentrations were greater in the SCHK group, but plasma glucose concentrations were lower. A total of 156 metabolites and 466 lipids were identified. The analysis of untargeted metabolomics data by principal component analysis and orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis revealed a separation between SCHK and clinically healthy goats. According to the screening criteria (unpaired t-test, P < 0.05), 30 differentially altered metabolites and 115 differentially altered lipids were detected. Pathway enrichment analysis identified citrate cycle, alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism, glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism, and phenylalanine metabolism as significantly altered pathways. A greater concentration of plasma isocitric acid and cis-aconitic acid levels was observed in SCHK goats. In addition, AA such as lysine and isoleucine were greater, whereas alanine and phenylacetylglycine were lower in SCHK dairy goats. Dairy goats with SCHK also exhibited greater oleic acid, acylcarnitine, and phosphatidylcholine and lower choline and sphingomyelins. Acylcarnitines, oleic acid, and Tridecanoic acid displayed positive correlations with several lipid species. Alanine, hippuric acid, and histidinyl-phenylalanine were negatively correlated with several lipids. Overall, altered metabolites in SCHK dairy goats indicated a more severe degree of negative energy balance. Data also indicated an imbalance in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, lipid metabolism, and AA metabolism. The findings provide a more comprehensive understanding of the pathogenesis of SCHK in dairy goats.
Unveiling Chemical, Antioxidant and Antibacterial Properties of Fagonia indica Grown in the Hail Mountains, Saudi Arabia.[Pubmed:36987042]
Plants (Basel). 2023 Mar 17;12(6):1354.
The Aja and Salma mountains in the Hail region are home to a variety of indigenous wild plants, some of which are used in Bedouin folk medicine to treat various ailments. The purpose of the current study was to unveil the chemical, antioxidant and antibacterial properties of Fagonia indica (Showeka) grown widely in these mountains, as data on the biological activities of this plant in this remote area are scarce. XRF spectrometry indicated the presence of some essential elements, which were in the order of Ca > S > K > AL > CL > Si > P > Fe > Mg > Na > Ti > Sr > Zn > Mn. Qualitative chemical screening revealed the presence of saponins, terpenes, flavonoids, tannins, phenols and cardiac glycosides in the methanolic extract (80% v/v). GC-MS showed the presence of 2-chloropropanoic acid 18.5%, tetrahydro-2-methylfuran 20.1%, Tridecanoic acid 12-methyl-, methyl ester 2.2%, hexadecanoic acid, methyl ester 8.6%, methyl 3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl) propionate 13.4%, methyl linoleate 7.0%, petroselinic acid methyl ester 15%, erucylamide 6.7% and diosgenin 8.5%. Total phenols, total tannins, flavonoids, DPPH, reducing power, -carotene and ABTS IC(50) (mg/mL) scavenging activity were used to measure the antioxidant capabilities of Fagonia indica, which exhibited prominent antioxidant properties at low concentrations when compared to ascorbic acid, butylate hydroxytoluene and beta-carotene. The antibacterial investigation revealed significant inhibitory effects against Bacillus subtilis MTCC121 and Pseudomona aeruginosa MTCC 741 with inhibition zones of 15.00 +/- 1.5 and 12.0 +/- 1.0 mm, respectively. The MIC (minimum inhibitory concentration) and MBC (minimum bactericidal concentration) ranged between 125 to 500 mug/mL. The MBC/MIC ratio indicated possible bactericidal efficacy against Bacillus subtilis and bacteriostatic activity against Pseudomona aeruginosa. The study also showed that this plant has anti-biofilm formation activity.


