ONO-AE3-208EP4 receptor inhibitor,high affinity and selective CAS# 402473-54-5 |
- MK-2894
Catalog No.:BCC1757
CAS No.:1006036-87-8
- MK-2894 sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC1758
CAS No.:1006036-88-9
- Metformin HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4799
CAS No.:1115-70-4
- Resveratrol
Catalog No.:BCN5607
CAS No.:501-36-0
- 4'-Demethylepipodophyllotoxin
Catalog No.:BCN5918
CAS No.:6559-91-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 402473-54-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 10111831 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C24H21FN2O3 | M.Wt | 404.43 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | AE 3-208 | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO and to 10 mM in 1.1eq. NaOH with gentle warming | ||
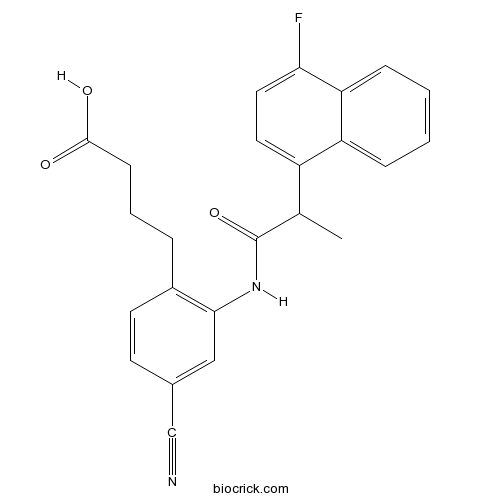
| Chemical Name | 4-[4-cyano-2-[2-(4-fluoronaphthalen-1-yl)propanoylamino]phenyl]butanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(C1=CC=C(C2=CC=CC=C21)F)C(=O)NC3=C(C=CC(=C3)C#N)CCCC(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MTDIMKNAJUQTIO-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C24H21FN2O3/c1-15(18-11-12-21(25)20-7-3-2-6-19(18)20)24(30)27-22-13-16(14-26)9-10-17(22)5-4-8-23(28)29/h2-3,6-7,9-13,15H,4-5,8H2,1H3,(H,27,30)(H,28,29) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | High affinity and selective EP4 receptor antagonist (Ki values are 1.3, 30, 790 and 2400 nM for EP4, EP3, FP and TP receptors respectively). Displays no affinity for EP1, EP2, DP or IP receptors (Ki >10 μM). Inhibits PGE2-induced IL-8 production in colonic epithelial caco-2 cells and attenuates PGE2 inhibition of natural killer T cell activation. Suppresses recovery from experimentally-induced colitis and stimulates CD4+ T cell proliferation in C57BL/6 mice. Also reduces metastasis of mammary tumor cells in a murine model of breast cancer. Orally active. |

ONO-AE3-208 Dilution Calculator

ONO-AE3-208 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4726 mL | 12.3631 mL | 24.7262 mL | 49.4523 mL | 61.8154 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4945 mL | 2.4726 mL | 4.9452 mL | 9.8905 mL | 12.3631 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2473 mL | 1.2363 mL | 2.4726 mL | 4.9452 mL | 6.1815 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0495 mL | 0.2473 mL | 0.4945 mL | 0.989 mL | 1.2363 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0247 mL | 0.1236 mL | 0.2473 mL | 0.4945 mL | 0.6182 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
ONO-AE3-208 is an inhibitor of EP4 [1].
EP4 is one of the prostaglandin E2 receptors and is associated with inflammatory disease and cancer such as prostate cancer. As an antagonist of EP4, ONO-AE3-208 is expected to be a potential therapy for prostate cancer. In vitro assays show that ONO-AE3-208 can suppress the migration and invasion of prostate cancer cells. 10μM of ONO-AE3-208 decreases wound healing proportion of PC3 and LNCaP cell lines in wound-healing assay. And in Transwell Invasion assay, ONO-AE3-208 inhibits cell invasion even at concentration of 0.1μM. ONO-AE3-208 is also reported to suppress bone metastasis in vivo [1].
Since activation of E2 can increase the expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) and release inflammatory cytokines, and then exacerbates abdominal aortic aneurism (AAA) formation, ONO-AE3-208 is also used in the studies of AAA formation. It has been proved that ONO-AE3-208 can cause the elastic fiber degradation and inhibit AAA formation in vivo in a dose-dependent manner [2].
References:
[1] Song Xu, Zhengyu Zhang, Osamu Ogawa,Takeshi Yoshikawa, Hiromasa Sakamoto, Noboru Shibasaki, akayuki Goto, Liming Wang, Naoki Terada. An EP4 antagonist ONO-AE3-208 suppresses cell invasion, migration and metastasis of prostate cancer. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014, April.
[2] Utako Yokoyama, Ryo Ishiwata, Mei-Hua Jin, Yuko Kato, Orie Suzuki, Huiling Jin, Yasuhiro Ichikawa, Syun Kumagaya, Yuzo Katayama, Takayuki Fujita, Satoshi Okumura, Motohiko Sato, Yukihiko Sugimoto, Hiroki Aoki, Shinichi Suzuki, Munetaka Masuda, Susumu Minamisawa, Yoshihiro Ishikawa. Inhibition of EP4 Signaling Attenuates Aortic Aneurysm Formation. Plos One. 2012, May. 7, 5, e36724.
- Glycitin
Catalog No.:BCN5895
CAS No.:40246-10-4
- 5-O-Feruloylquinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3788
CAS No.:40242-06-6
- H-Hyp-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3248
CAS No.:40216-83-9
- H-Orn-OMe.2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3001
CAS No.:40216-82-8
- Fmoc-β-Homo-Gln(Trt)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2647
CAS No.:401915-55-7
- Fmoc-β-homo-Arg(Pbf)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2649
CAS No.:401915-53-5
- Andarine
Catalog No.:BCC1168
CAS No.:401900-40-1
- SKA 31
Catalog No.:BCC7743
CAS No.:40172-65-4
- Boc-N-Me-Phe.DCHA
Catalog No.:BCC3348
CAS No.:40163-88-0
- Erucifoline
Catalog No.:BCN2081
CAS No.:40158-95-0
- H-Arg-pNA.2HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2858
CAS No.:40127-11-5
- Ceftaroline fosamil
Catalog No.:BCC5266
CAS No.:400827-46-5
- Acetylcimigenol 3-O-alpha-L-arabinopyranside
Catalog No.:BCN1447
CAS No.:402513-88-6
- DMeOB
Catalog No.:BCC7213
CAS No.:40252-74-2
- NSC 693868
Catalog No.:BCC7208
CAS No.:40254-90-8
- Firategrast
Catalog No.:BCC1575
CAS No.:402567-16-2
- Deacetylcinobufagin
Catalog No.:BCN2720
CAS No.:4026-95-3
- SB 399885 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7595
CAS No.:402713-81-9
- 7-Methoxyneochamaejasmine A
Catalog No.:BCN3134
CAS No.:402828-38-0
- DR 4485 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7990
CAS No.:402942-53-4
- Telaprevir (VX-950)
Catalog No.:BCC2107
CAS No.:402957-28-2
- MDL 12330A hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7066
CAS No.:40297-09-4
- Cassyfiline
Catalog No.:BCN4763
CAS No.:4030-51-7
- p-Menth-1-ene-3,6-diol
Catalog No.:BCN5454
CAS No.:4031-55-4
[Inhibitory effect of ONO-AE3-208 on the formation of bone metastasis of prostate cancer in mice].[Pubmed:25195362]
Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2014 Aug;20(8):684-9.
OBJECTIVE: To examine the effect of ONO-AE3-208, an EP4 antagonist, on the formation of bone metastasis from prostate cancer in mice. METHODS: Thirty-four 6-week old nude mice were divided into an experimental and a control group of equal number to be treated by intraperitoneal injection of ONO-AE3-208 and double distilled water, respectively. Then PC3/LUC cells were constructed by stably transfecting luciferin to prostate cancer PC3 cells and inoculated into the left ventricle of the mice to establish an animal model of systemic bone metastasis. The time of metastasis formation, photon tumor burdens, and changes of the survival curves after modeling were compared between the two groups of mice. RESULTS: At 30 days after modeling, bioluminescence imaging analysis showed that the photon tumor burdens were significantly increased in a time-dependent manner in the control group in comparison with those in the experimental group (P < 0.01). The rate of metastasis formation was significantly higher in the former than in the latter (93.3% vs 33.3%, P < 0.001). The median time of metastasis formation was 29 d (95% CI 26.547 - 35.262) in the experimental animals as compared with 21 d (95% CI 17.213 -24.787) in the controls (P < 0.001). CONCLUSION: EP4 antagonist ONO-AE3-208 can inhibit the formation of bone metastasis from prostate cancer in mice.
An EP4 antagonist ONO-AE3-208 suppresses cell invasion, migration, and metastasis of prostate cancer.[Pubmed:24744183]
Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014 Sep;70(1):521-7.
EP4 is one of the prostaglandin E2 receptors, which is the most common prostanoid and is associated with inflammatory disease and cancer. We previously reported that over-expression of EP4 was one of the mechanisms responsible for progression to castration-resistant prostate cancer, and an EP4 antagonist ONO-AE3-208 in vivo suppressed the castration-resistant progression regulating the activation of androgen receptor. The aim of this study was to analyze the association of EP4 with prostate cancer metastasis and the efficacy of ONO-AE3-208 for suppressing the metastasis. The expression levels of EP4 mRNA were evaluated in prostate cancer cell lines, LNCaP, and PC3. EP4 over-expressing LNCaP was established, and their cell invasiveness was compared with the control LNCaP (LNCaP/mock). The in vitro cell proliferation, invasion, and migration of these cells were examined under different concentrations of ONO-AE3-208. An in vivo bone metastatic mouse model was constructed by inoculating luciferase expressing PC3 cells into left ventricle of nude mice. Their bone metastasis was observed by bioluminescent imaging with or without ONO-AE3-208 administration. The EP4 mRNA expression levels were higher in PC3 than in LNCaP, and EP4 over-expression of LNCaP cells enhanced their cell invasiveness. The in vitro cell invasion and migration were suppressed by ONO-AE3-208 in a dose-dependent manner without affecting cell proliferation. The in vivo bone metastasis of PC3 was also suppressed by ONO-AE3-208 treatment. EP4 expression levels were correlated with prostate cancer cell invasiveness and EP4 specific antagonist ONO-AE3-208 suppressed cell invasion, migration, and bone metastasis, indicating that it is a potential novel therapeutic modality for the treatment of metastatic prostate cancer.
Exosome-like nanoparticles from intestinal mucosal cells carry prostaglandin E2 and suppress activation of liver NKT cells.[Pubmed:23467936]
J Immunol. 2013 Apr 1;190(7):3579-89.
Regulation and induction of anergy in NKT cells of the liver can inhibit autoimmune and antitumor responses by mechanisms that are poorly understood. We investigated the effects of PGE2, delivered by intestinal, mucus-derived, exosome-like nanoparticles (IDENs), on NKT cells in mice. In this study, we demonstrate that IDENs migrate to the liver where they induce NKT cell anergy. These effects were mediated by an IDENs' PGE2. Blocking PGE2 synthesis attenuated IDENs inhibition of induction of IFN-gamma and IL-4 by alpha-galactosylceramide (alpha-GalCer)-stimulated liver NKT cells in a PGE2 E-type prostanoid 2/E-type prostanoid 4 receptor-mediated manner. Proinflammatory conditions enhanced the migration of IDENs to the liver where alpha-GalCer and PGE2 induced NKT anergy in response to subsequent alpha-GalCer stimulation. These findings demonstrate that IDENs carrying PGE2 can be transferred from the intestine to the liver, where they act as immune modulators, inducing an anergic-like state of NKT cells. These reagents might be developed as therapeutics for autoimmune liver diseases.
Prostaglandin E(2) couples through EP(4) prostanoid receptors to induce IL-8 production in human colonic epithelial cell lines.[Pubmed:19175605]
Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Feb;156(3):475-85.
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Prostaglandin (PG) E(2) and interleukin (IL)-8 are simultaneously increased during the inflammation that characterizes numerous pathologies such as inflammatory bowel disease. IL-8 is a potent neutrophil chemo-attractant and activator, and can initiate and/or exacerbate tissue injury. PGE(2) signals principally through prostanoid receptors of the EP(2) and/or EP(4) subtypes to promote cAMP-dependent cellular functions. The aim of this study was to identify the role of the EP(2) and EP(4) receptor subtype(s) on two human colonic epithelial cell lines (Caco-2 and T84), in regulating PGE(2)-induced IL-8 production. EXPERIMENTAL APPROACH: To identify the causative receptor, we knocked-down and over-expressed EP(2) and EP(4) receptor subtypes in colonic epithelial cells and studied the effect of several selective EP(2)/EP(4) receptor agonists and antagonists. The inductions of IL-8 and EP receptor mRNA and protein expression were determined by real-time PCR and western blot analysis. The affinity of PGE(2) and Bmax values for the EP(2) and EP(4) receptor on colonic epithelial cells were determined by radioligand-binding assays with [(3)H]PGE(2). KEY RESULTS: PGE(2) had the highest affinity for the EP(4) receptor subtype and promoted a robust stimulation of cAMP-dependent IL-8 synthesis. This effect was mimicked by a selective EP(4) receptor agonist, ONO-AE1-329, and abolished by silencing the EP(4) receptor gene by using siRNA techniques, a selective EP(4) receptor antagonist (ONO-AE3-208) and a selective inhibitor (Rp-cAMP) of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. CONCLUSIONS AND IMPLICATIONS: These findings suggest that initiation and progression of colonic inflammation induced by IL-8 could be mediated, at least in part, by PGE(2) acting via the EP(4) receptor subtype.
Prostaglandin E receptor EP4 antagonism inhibits breast cancer metastasis.[Pubmed:16540639]
Cancer Res. 2006 Mar 15;66(6):2923-7.
Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression in epithelial tumors is frequently associated with a poor prognosis. In a murine model of metastatic breast cancer, we showed that COX-2 inhibition is associated with decreased metastatic capacity. The COX-2 product, prostaglandin E(2) (PGE(2)), acts through a family of G protein-coupled receptors designated EP1-4 that mediate intracellular signaling by multiple pathways. We characterized EP receptor expression on three murine mammary tumor cell lines and show that all four EP isoforms were detected in each cell. Stimulation of cells with either PGE(2) or the selective EP4/EP2 agonist PGE(1)-OH resulted in increased intracellular cyclic AMP and this response was inhibited with either EP2 or EP4 antagonists. Nothing is known about the function of EP receptors in tumor metastasis. We tested the hypothesis that the prevention of EP receptor signaling would, like inhibition of PGE(2) synthesis, inhibit tumor metastasis. Our results show for the first time that antagonism of the EP4 receptor with either AH23848 or ONO-AE3-208 reduced metastasis as compared with vehicle-treated controls. The therapeutic effect was comparable to that observed with the dual COX-1/COX-2 inhibitor indomethacin. EP3 antagonism had no effect on tumor metastasis. Mammary tumor cells migrated in vitro in response to PGE(2) and this chemotactic response was blocked by EP receptor antagonists. Likewise, the proliferation of tumor cells was also directly inhibited by antagonists of either EP4 or EP1/EP2. These studies support the hypothesis that EP receptor antagonists may be an alternative approach to the use of COX inhibitors to prevent tumor metastasis.
The prostaglandin receptor EP4 suppresses colitis, mucosal damage and CD4 cell activation in the gut.[Pubmed:11927615]
J Clin Invest. 2002 Apr;109(7):883-93.
We used mice deficient in each of the eight types and subtypes of prostanoid receptors and examined the roles of prostanoids in dextran sodium sulfate-induced (DSS-induced) colitis. Among the prostanoid receptor-deficient mice, only EP4-deficient mice and not mice deficient in either DP, EP1, EP2, EP3, FP, IP, or TP developed severe colitis with 3% DSS treatment, which induced only marginal colitis in wild-type mice. This phenotype was mimicked in wild-type mice by administration of an EP4-selective antagonist (AE3-208). The EP4 deficiency impaired mucosal barrier function and induced epithelial loss, crypt damage, and aggregation of neutrophils and lymphocytes in the colon. Conversely, administration of an EP4-selective agonist (AE1-734) to wild-type mice ameliorated severe colitis normally induced with 7% DSS, while that of AE3-208 suppressed recovery from colitis and induced significant proliferation of CD4+ T cells. In vitro AE3-208 enhanced and AE1-734 suppressed the proliferation and Th1 cytokine production of lamina propria mononuclear cells from the colon. DNA microarray analysis revealed elevated expression of genes associated with immune response and reduced expression of genes with mucosal repair and remodeling in the colon of EP4-deficient mice. We conclude that EP4 maintains intestinal homeostasis by keeping mucosal integrity and downregulating immune response.


