OcinaplonGABAA modulator; anxiolytic CAS# 96604-21-6 |
- GW4064
Catalog No.:BCC4500
CAS No.:278779-30-9
- Chenodeoxycholic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2620
CAS No.:474-25-9
- XL335
Catalog No.:BCC4501
CAS No.:629664-81-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 96604-21-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 216456 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C17H11N5O | M.Wt | 301.3 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in 2eq.HCl and to 10 mM in DMSO | ||
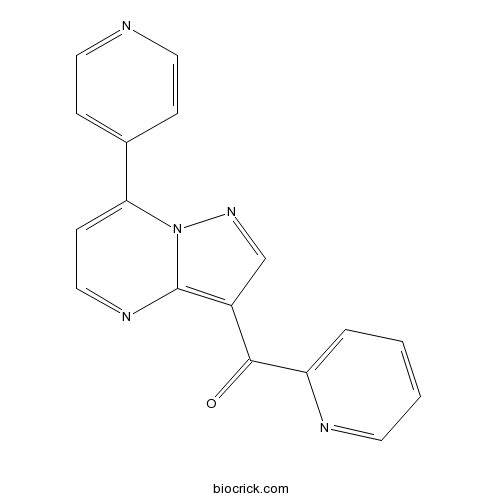
| Chemical Name | pyridin-2-yl-(7-pyridin-4-ylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)methanone | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=NC(=C1)C(=O)C2=C3N=CC=C(N3N=C2)C4=CC=NC=C4 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | OQJFBUOFGHPMSR-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C17H11N5O/c23-16(14-3-1-2-7-19-14)13-11-21-22-15(6-10-20-17(13)22)12-4-8-18-9-5-12/h1-11H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Modulator of GABAA receptors. Displays modest selectivity for GABAA α1 receptors; displays partial agonist activity at α2-, α3- and α5-containing receptors. Exhibits anxiolytic activity. |

Ocinaplon Dilution Calculator

Ocinaplon Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.319 mL | 16.5948 mL | 33.1895 mL | 66.379 mL | 82.9738 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6638 mL | 3.319 mL | 6.6379 mL | 13.2758 mL | 16.5948 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3319 mL | 1.6595 mL | 3.319 mL | 6.6379 mL | 8.2974 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0664 mL | 0.3319 mL | 0.6638 mL | 1.3276 mL | 1.6595 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0332 mL | 0.1659 mL | 0.3319 mL | 0.6638 mL | 0.8297 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 3beta-Hydroxylanosta-8,24-diene-21-al
Catalog No.:BCN3329
CAS No.:96574-03-7
- Salvianolic acid A
Catalog No.:BCN5951
CAS No.:96574-01-5
- Szechenyine
Catalog No.:BCN2601
CAS No.:96562-88-8
- 3,3'-[Iminobis(methylene)]bis-2(3H)furanone
Catalog No.:BCN1295
CAS No.:96562-86-6
- Methyl gypsogenin 3-O-beta-D-glucuronopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1296
CAS No.:96553-02-5
- 5,7-Dihydroxy-2-isopropylchromone
Catalog No.:BCN4514
CAS No.:96552-59-9
- Cudraxanthone D
Catalog No.:BCN4513
CAS No.:96552-41-9
- Nifuroxazide
Catalog No.:BCC4686
CAS No.:965-52-6
- Goniodiol 7-acetate
Catalog No.:BCN4793
CAS No.:96422-53-6
- Goniodiol
Catalog No.:BCN3958
CAS No.:96422-52-5
- Amygdaloside
Catalog No.:BCC8231
CAS No.:96420-61-0
- Goniotriol
Catalog No.:BCN4745
CAS No.:96405-62-8
- Decuroside I
Catalog No.:BCN3909
CAS No.:96638-79-8
- Viscidulin III tetraacetate
Catalog No.:BCN4515
CAS No.:96684-81-0
- Rabdoserrin A
Catalog No.:BCN8041
CAS No.:96685-01-7
- [D-Arg1,D-Phe5,D-Trp7,9,Leu11]-Substance P
Catalog No.:BCC7211
CAS No.:96736-12-8
- Chlorisondamine diiodide
Catalog No.:BCC6885
CAS No.:96750-66-2
- (±)-McN 5652
Catalog No.:BCC7267
CAS No.:96795-89-0
- Chlorovaltrate K
Catalog No.:BCN7126
CAS No.:96801-92-2
- Orlistat
Catalog No.:BCC3830
CAS No.:96829-58-2
- Przewaquinone C
Catalog No.:BCN3003
CAS No.:96839-29-1
- Indatraline hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7123
CAS No.:96850-13-4
- 8beta-Tigloyloxycostunolide
Catalog No.:BCN7115
CAS No.:96850-21-4
- Maoecrystal B
Catalog No.:BCN4516
CAS No.:96850-29-2
Pharmacological Properties of DOV 315,090, an ocinaplon metabolite.[Pubmed:18554397]
BMC Pharmacol. 2008 Jun 13;8:11.
BACKGROUND: Compounds targeting the benzodiazepine binding site of the GABAA-R are widely prescribed for the treatment of anxiety disorders, epilepsy, and insomnia as well as for pre-anesthetic sedation and muscle relaxation. It has been hypothesized that these various pharmacological effects are mediated by different GABAA-R subtypes. If this hypothesis is correct, then it may be possible to develop compounds targeting particular GABAA-R subtypes as, for example, selective anxiolytics with a diminished side effect profile. The pyrazolo[1,5-a]-pyrimidine Ocinaplon is anxioselective in both preclinical studies and in patients with generalized anxiety disorder, but does not exhibit the selectivity between alpha1/alpha2-containing receptors for an anxioselective that is predicted by studies using transgenic mice. RESULTS: We hypothesized that the pharmacological properties of Ocinaplon in vivo might be influenced by an active biotransformation product with greater selectivity for the alpha2 subunit relative to alpha1. One hour after administration of Ocinaplon, the plasma concentration of its primary biotransformation product, DOV 315,090, is 38% of the parent compound. The pharmacological properties of DOV 315,090 were assessed using radioligand binding studies and two-electrode voltage clamp electrophysiology. We report that DOV 315,090 possesses modulatory activity at GABAA-Rs, but that its selectivity profile is similar to that of Ocinaplon. CONCLUSION: These findings imply that DOV 315,090 could contribute to the action of Ocinaplon in vivo, but that the anxioselective properties of Ocinaplon cannot be readily explained by a subtype selective effect/action of DOV 315,090. Further inquiry is required to identify the extent to which different subtypes are involved in the anxiolytic and other pharmacological effects of GABAA-R modulators.
A multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized study of efficacy and safety of ocinaplon (DOV 273,547) in generalized anxiety disorder.[Pubmed:20041911]
CNS Neurosci Ther. 2010 Apr;16(2):63-75.
Preclinical studies demonstrated that Ocinaplon, a positive allosteric modulator of GABA(A) receptors, possesses anxiolytic-like actions at doses devoid of the side effects typically associated with benzodiazepines. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of Ocinaplon in a multicenter, double-blind proof-of-concept trial of male and female outpatients who met DSM-IV criteria for GAD with no coexisting depression, and had a baseline score of > or =20 on the Hamilton Scale for Anxiety (HAM-A). Patients with <20% reduction in HAM-A to placebo in a single-blind 7-day run-in period were randomly assigned to treatment with Ocinaplon 90 mg t.i.d. (n = 31) or placebo for 28 days (n = 29). Ocinaplon was more effective than placebo in reducing HAM-A scores (P= 0.009). Patients assigned to Ocinaplon exhibited a mean improvement of 14.2 points (SE = 2.6) on the total score of the HAM-A scale at the conclusion of the trial, while patients assigned to placebo obtained a mean improvement of 6.3 points (SE = 2.0). A significant (P= 0.023) difference in improvement between Ocinaplon and placebo was observed beginning at and continuing from 1-week after the initiation of dosing. The proportion of patients with treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAE) was not statistically significant between Ocinaplon and placebo. One serious adverse event (SAE) occurred in the Ocinaplon group that was considered possibly related to study medication (icterus following transaminase elevations). The patient had preexisting medical conditions that may have contributed to this SAE. A full recovery was observed with no residual effects. The overall safety profile revealed no patterns of TEAEs, including those effects typically associated with other anxiolytic and/or benzodiazepine compounds, such as sedation. Ocinaplon appears to be a well-tolerated and effective treatment for GAD. It produces a rapid onset of anxiolytic action absent the side effects (e.g., dizziness, sedation) typically reported following anxiolytic doses of benzodiazepines.
Discriminative stimulus properties of GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators TPA023, ocinaplon and NG2-73 in rats trained to discriminate chlordiazepoxide or zolpidem.[Pubmed:21762686]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Oct 1;668(1-2):190-3.
There is increased understanding that distinct GABA(A) receptor subtypes mediate different effects of classical benzodiazepines. Here, we aimed to define the contributions of alpha(1)-containing subtypes of the subtype-selective GABA(A) receptor positive allosteric modulators TPA023, Ocinaplon, and NG2-73 using drug discrimination. We characterized these compounds with defined subunit preferences in rats that were trained to discriminate either the non-selective benzodiazepine chlordiazepoxide (CDP, 5.0 mg/kg) or the alpha(1)-selective drug zolpidem (1.5 mg/kg). In short, CDP but not zolpidem generalized to the CDP cue. In contrast, zolpidem-trained rats showed opposite effects and generalized to zolpidem but not to CDP, while the response rate reducing effects of both ligands were comparable. Moreover, TPA023, lacking efficacy at the GABA(A) receptor alpha(1) subunit, occasioned dose-dependent CDP-appropriate responding but generalized only to around 10% to zolpidem. Both Ocinaplon and NG2-73 completely generalized to both the CDP and zolpidem cue. Overall, our data confirm and extend the previous findings in rats that compounds that lack efficacy at alpha(1)-containing GABA(A) receptors generalize to CDP, whereas the opposite holds true for alpha(1)-preferential compounds, which generalize to the alpha(1)-selective positive allosteric modulator zolpidem. Also, our data support the hypothesis that subtle in vitro differences in alpha subunit efficacy and/or affinity may eventually have large consequences in vivo. Together, our data demonstrate a reliable in vivo method to determine the contribution of the subtype-selective mechanism(s) of action for novel and subtype-selective GABA(A) receptor positive allosteric modulators, suggesting that a complex activation of multiple alpha subunits accounts for drug discrimination between non-selective and selective GABA(A) receptor ligands.
Comparative cue generalization profiles of L-838, 417, SL651498, zolpidem, CL218,872, ocinaplon, bretazenil, zopiclone, and various benzodiazepines in chlordiazepoxide and zolpidem drug discrimination.[Pubmed:16339395]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Mar;316(3):1291-9.
The zolpidem discriminative cue is mediated by GABA(A)-alpha1 receptors, whereas the chlordiazepoxide cue may be mediated via non-alpha1 GABA(A) receptors because compounds with selective affinity for GABA(A)-alpha1 receptors fully generalize to the former cue. We predicted that L-838,417 [7-tert-butyl-3-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-6-(2-methyl-2H-1,2,4-triazol-3-ylmethoxy)-1, 2,4-triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazine], a partial agonist at non-alpha1 GABA(A) receptors and an antagonist at GABA(A)-alpha1 receptors, would generalize to the chlordiazepoxide but not the zolpidem-discriminative cue. SL651498 [6-fluoro-9-methyl-2-phenyl-4-(pyrrolidin-1-yl-carbonyl)-2,9-dihydro-1H-pyridol[3 ,4-b]indol-1-one] is a full agonist at GABA(A)-alpha2 receptors, with lower efficacy at GABA(A)-alpha3 receptors and least efficacy at GABA(A)-alpha1 and GABA(A)-alpha5 receptors. Because SL651498 has efficacy at GABA(A)-alpha1 receptors, we anticipated that it would generalize to both discriminative cues. Rats were trained to discriminate either zolpidem (3 mg/kg) or chlordiazepoxide (5 mg/kg) from vehicle using a two-lever operant procedure. The generalization profiles of L-838,417 and SL651498 were compared with nonselective full agonists, GABA(A)-alpha1-selective ligands zolpidem and CL218,872 [3-methyl-6-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1,2,4-triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazine], the nonselective partial agonist bretazenil, and the novel anxioselective drug Ocinaplon. A nonselective partial agonist was included because L-838,417 and SL651498 are partial agonists at some GABA(A) receptors, and this property may influence their generalization profiles. All nonselective full agonists and Ocinaplon fully generalized to both cues. CL218,872 and zolpidem generalized to zolpidem only, whereas L-838,417 fully generalized to chlordiazepoxide only. SL651498 fully generalized to chlordiazepoxide and occasioned significant zolpidem-appropriate responding. Bretazenil was similar to SL651498. In conclusion, at this training dose, the chlordiazepoxide-discriminative stimulus is mediated primarily via non-alpha1 GABA(A) receptors and the generalization profiles of the ligands tested seem to correspond with their in vitro profiles at GABA(A) receptor subtypes.
GABAA receptors as targets for novel anxiolytic drugs.[Pubmed:17071543]
World J Biol Psychiatry. 2006;7(4):231-7.
Anxiety disorders are highly prevalent and disabling disorders which are commonly treated with pharmacotherapy and/or psychotherapy. While benzodiazepines are of great value for the treatment of acute anxiety states, their long-term use is hampered by their well-known side effect profile. Meanwhile, antidepressants represent first line treatment options for anxiety disorders. However, their slow onset of action is a disadvantage for their use in these disorders. Therefore, there is need for novel anxiolytics with a rapid onset of action and a favourable side effect profile. Currently, there is a renaissance of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA) receptors as targets for the development of novel anxiolytic drugs. While compounds structurally related to GABA, e.g., pregabalin, have already entered large scale clinical development, GABA transporter inhibitors, subtype specific benzodiazepines and GABAA receptor modulating neuroactive steroids are promising new candidates. However, their clinical efficacy has still to be shown in clinical trials.
Selective anxiolysis produced by ocinaplon, a GABA(A) receptor modulator.[Pubmed:15870187]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 May 17;102(20):7380-5.
Benzodiazepines remain widely used for the treatment of anxiety disorders despite prominent, often limiting side effects including sedation, muscle relaxation, and ataxia. A compound producing a robust anxiolytic action comparable to benzodiazepines, but lacking these limiting side effects at therapeutic doses (an anxioselective agent), would represent an important advance in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder, and perhaps other anxiety disorders. Here we report that the pyrazolo[1,5-a]-pyrimidine, Ocinaplon, exhibits an anxioselective profile in both preclinical procedures and in patients with generalized anxiety disorder, the most common of the anxiety disorders. In rats, Ocinaplon produces significant muscle relaxation, ataxia, and sedation only at doses >25-fold higher than the minimum effective dose (3.1 mg/kg) in the Vogel "conflict" test. This anticonflict effect is blocked by flumazenil (Ro 15-1788), indicating that like benzodiazepines, Ocinaplon produces an anxiolytic action through allosteric modulation of GABA(A) receptors. Nonetheless, in eight recombinant GABA(A) receptor isoforms expressed in Xenopus oocytes, the potency and efficacy of Ocinaplon to potentiate GABA responses varied with subunit composition not only in an absolute sense, but also relative to the prototypical benzodiazepine, diazepam. In a double blind, placebo controlled clinical trial, a 2-week regimen of Ocinaplon (total daily dose of 180-240 mg) produced statistically significant reductions in the Hamilton rating scale for anxiety scores. In this study, the incidence of benzodiazepine-like side effects (e.g., sedation, dizziness) in Ocinaplon-treated patients did not differ from placebo. These findings indicate that Ocinaplon represents a unique approach both for the treatment and understanding of anxiety disorders.


