(±)-McN 56525-HT uptake inhibitor CAS# 96795-89-0 |
- Alvespimycin
Catalog No.:BCC1346
CAS No.:467214-20-6
- 17-AAG (KOS953)
Catalog No.:BCC2121
CAS No.:75747-14-7
- Retaspimycin
Catalog No.:BCC1889
CAS No.:857402-23-4
- PU-H71
Catalog No.:BCC1872
CAS No.:873436-91-0
- 17-AAG Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1297
CAS No.:911710-03-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 96795-89-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6336338 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C19H21NS | M.Wt | 295.44 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | McN 5652-Z | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 50 mM in 1eq. HCl and to 75 mM in DMSO | ||
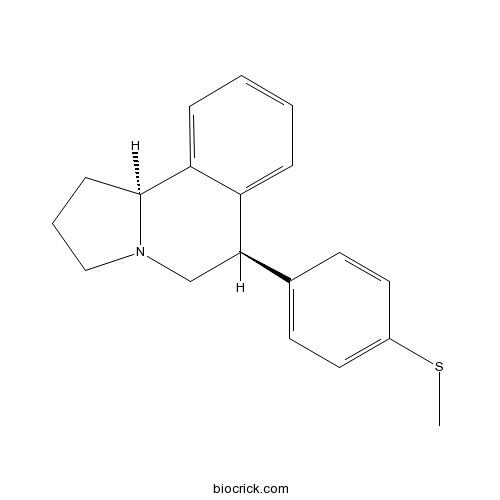
| Chemical Name | (6R,10bS)-6-(4-methylsulfanylphenyl)-1,2,3,5,6,10b-hexahydropyrrolo[2,1-a]isoquinoline | ||
| SMILES | CSC1=CC=C(C=C1)C2CN3CCCC3C4=CC=CC=C24 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | YVKDUIAAPBKHMJ-MOPGFXCFSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H21NS/c1-21-15-10-8-14(9-11-15)18-13-20-12-4-7-19(20)17-6-3-2-5-16(17)18/h2-3,5-6,8-11,18-19H,4,7,12-13H2,1H3/t18-,19+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent, high affinity serotonin re-uptake inhibitor; selective in vivo. Displays moderate selectivity over noradrenalin and dopamine re-uptake in vitro (Ki values are 0.68, 2.9 and 36.8 nM for inhibition of serotonin, noradrenalin and dopamine uptake respectively in rat brain synaptosomes). Potently potentiates 5-HT-induced effects in vivo following oral administration. Biological activity resides predominantly in the (+)-enantiomer. |

(±)-McN 5652 Dilution Calculator

(±)-McN 5652 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.3848 mL | 16.9239 mL | 33.8478 mL | 67.6956 mL | 84.6196 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.677 mL | 3.3848 mL | 6.7696 mL | 13.5391 mL | 16.9239 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3385 mL | 1.6924 mL | 3.3848 mL | 6.7696 mL | 8.462 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0677 mL | 0.3385 mL | 0.677 mL | 1.3539 mL | 1.6924 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0338 mL | 0.1692 mL | 0.3385 mL | 0.677 mL | 0.8462 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
(±)-McN 5652 is a highly potent inhibitor of serotonin (5-HT, 5-hydroxytryptamine) uptake with a Ki value of approximately 0.6 nM in rat brain synaptosomes in vitro and an ED50 value of approximately 2 mg/kg p.o. ex vivo [1].
5-HT is a monoaminergic neurotransmitter to modulate numerous sensory, behavioural processes and motor in the mammalian nervous system [2]. There are at least three main groups of 5-HT receptor: 5-HT1, 5-HT2, and 5-HT3. Each group is not only structurally but also operationally distinct. Each receptor group has its own distinct transduction system. 5-HT4 is the more recently identified receptor. It almost represents a fourth 5-HT receptor class [3].
Receptor binding experiments indicated that McN-5652 has a weak affinity for serotonin 5-HT2 receptor (apparent Ki approximately 200 nM) and a very low affinity for serotonin 5-HT1 receptor [1].
In vivo, McN-5652 was required in low doses to potentiate the serotonin syndrome in rats. For this serotonin syndrome, the ED50 value was 1.5 mg/kg 2 hr after p.o. dosing. To potentiate head twitches which were induced by L-5-hydroxytryptophan (L-5HTP) in mice, the ED50 value is just 0.4 mg/kg 2 hr after p.o. dosing. That means McN-5652 is of high potency as a serotonin uptake inhibitor [1].
References:
[1]. Shank RP, Vaught JL, Pelley KA, et al. McN-5652: a highly potent inhibitor of serotonin uptake. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 1988, 247(3):1032-8.
[2]. Tecott LH, Sun LM, Akana SF, et al. Eating disorder and epilepsy in mice lacking 5-HT2c serotonin receptors. Nature, 1995, 374(6522):542-6.
[3]. Hoyer D, Clarke DE, Fozard JR, et al. International Union of Pharmacology classification of receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine (Serotonin). Pharmacol Rev, 1994, 46(2):157-203.
- Chlorisondamine diiodide
Catalog No.:BCC6885
CAS No.:96750-66-2
- [D-Arg1,D-Phe5,D-Trp7,9,Leu11]-Substance P
Catalog No.:BCC7211
CAS No.:96736-12-8
- Rabdoserrin A
Catalog No.:BCN8041
CAS No.:96685-01-7
- Viscidulin III tetraacetate
Catalog No.:BCN4515
CAS No.:96684-81-0
- Decuroside I
Catalog No.:BCN3909
CAS No.:96638-79-8
- Ocinaplon
Catalog No.:BCC6167
CAS No.:96604-21-6
- 3beta-Hydroxylanosta-8,24-diene-21-al
Catalog No.:BCN3329
CAS No.:96574-03-7
- Salvianolic acid A
Catalog No.:BCN5951
CAS No.:96574-01-5
- Szechenyine
Catalog No.:BCN2601
CAS No.:96562-88-8
- 3,3'-[Iminobis(methylene)]bis-2(3H)furanone
Catalog No.:BCN1295
CAS No.:96562-86-6
- Methyl gypsogenin 3-O-beta-D-glucuronopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCN1296
CAS No.:96553-02-5
- 5,7-Dihydroxy-2-isopropylchromone
Catalog No.:BCN4514
CAS No.:96552-59-9
- Chlorovaltrate K
Catalog No.:BCN7126
CAS No.:96801-92-2
- Orlistat
Catalog No.:BCC3830
CAS No.:96829-58-2
- Przewaquinone C
Catalog No.:BCN3003
CAS No.:96839-29-1
- Indatraline hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7123
CAS No.:96850-13-4
- 8beta-Tigloyloxycostunolide
Catalog No.:BCN7115
CAS No.:96850-21-4
- Maoecrystal B
Catalog No.:BCN4516
CAS No.:96850-29-2
- Maoecrystal A
Catalog No.:BCN5407
CAS No.:96850-30-5
- XCC
Catalog No.:BCC7890
CAS No.:96865-83-7
- XAC
Catalog No.:BCC7600
CAS No.:96865-92-8
- VIP (guinea pig)
Catalog No.:BCC5725
CAS No.:96886-24-7
- Nyasol
Catalog No.:BCN7579
CAS No.:96895-25-9
- 1,2-Bis(4'-methyl-2,2'-bipyridin-4-yl)ethane
Catalog No.:BCC8414
CAS No.:96897-04-0
Structural studies on McN-5652-X, a high-affinity ligand for the serotonin transporter in mammalian brain.[Pubmed:12735993]
Bioorg Med Chem. 2003 May 29;11(11):2463-70.
McN-5652-X, (+)-1, is a potent, selective inhibitor of serotonin reuptake in mammalian brain. When radiolabeled with (11)C, it has served as a positron-emission tomography (PET) radiotracer for in vivo imaging of central serotonin transporters. We have determined the solid-state structures of (+)-1.HClO(4) and (+)-1.(+)-(2R,3R)-tartrate by single-crystal X-ray diffraction, thereby confirming the trans relative configuration (Chemical Abstracts Service rules of nomenclature) and the 6S,10bR absolute configuration for (+)-1. Results from a vibrational circular dichroism (VCD) study on (+)-1 in CDCl(3) are consistent with the 6S,10bR absolute configuration.
Serotonin transporters in obsessive-compulsive disorder: a positron emission tomography study with [(11)C]McN 5652.[Pubmed:14675806]
Biol Psychiatry. 2003 Dec 15;54(12):1414-21.
BACKGROUND: Serotonergic abnormalities have been hypothesized to contribute to obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). This study examined whether brain serotonin transporter (SERT) availability is altered in OCD using positron emission tomography (PET) and the SERT PET radiotracer [(11)C]McN 5652. METHODS: Eleven OCD subjects, free of psychiatric medications and comorbid depression, and 11 matched healthy control subjects underwent PET scans following injection of [(11)C]McN 5652 and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans. Total distribution volumes (V(T)) were derived by kinetic analysis (one tissue compartment model) using the arterial input function. Two measures of SERT availability were computed: binding potential (BP) and specific to nonspecific partition coefficient (V(3)"). Groups were compared using region of interest (ROI) analysis and voxelwise analysis of spatially normalized parametric maps; ROIs were selected based on their relatively high SERT density and included subcortical (dorsal caudate, dorsal putamen, ventral striatum, midbrain, thalamus) and limbic (hippocampus, amygdala, anterior cingulate cortex) regions. RESULTS: No significant group differences were observed in [(11)C]McN 5652 BP or V(3)" in the ROIs. No significant group differences were detected in the voxelwise analysis of BP or V(3)" maps. CONCLUSIONS: OCD without comorbid depression, may not be associated with major changes in SERT availability in subcortical and limbic regions.
Brain serotonin transporter distribution in subjects with impulsive aggressivity: a positron emission study with [11C]McN 5652.[Pubmed:15863793]
Am J Psychiatry. 2005 May;162(5):915-23.
OBJECTIVE: The serotonin system is believed to play a role in modulating impulsivity and violence. Previous imaging studies have implicated the anterior cingulate and orbitofrontal cortex in impulsive aggression. This study evaluated regional serotonin transporter distribution in the brain of individuals with impulsive aggression by using positron emission tomography (PET) with the serotonin transporter PET radiotracer [(11)C]McN 5652. METHOD: Ten individuals with impulsive aggression and 10 age- and sex-matched healthy comparison subjects underwent [(11)C]McN 5652 PET. All individuals were medication free at the time of scanning. Regional total distribution volumes were derived by using a one-tissue compartment kinetic model with arterial input function. Outcome measures of serotonin transporter availability included the binding potential and the specific-to-nonspecific partition coefficient (V(3)''). RESULTS: Serotonin transporter availability was significantly reduced in the anterior cingulate cortex of individuals with impulsive aggression compared with healthy subjects, as noted by differences in both binding potential (mean=3.1 ml/g [SD=1.9] versus 5.0 ml/g [SD=2.0], respectively) and V(3)'' (mean=0.15 [SD=0.09] versus 0.26 [SD=0.09]). In other regions examined, serotonin transporter density was nonsignificantly lower in individuals with impulsive aggression compared with healthy subjects. CONCLUSIONS: Pathological impulsive aggressivity might be associated with lower serotonergic innervation in the anterior cingulate cortex, a region that plays an important role in affective regulation.
Comparative evaluation of serotonin transporter radioligands 11C-DASB and 11C-McN 5652 in healthy humans.[Pubmed:15073266]
J Nucl Med. 2004 Apr;45(4):682-94.
UNLABELLED: Alterations of serotonin transporters (SERT) are implicated in a large number of psychiatric conditions. (11)C-(+)-6beta-(4-Methylthiophenyl)-1,2,3,5,6alpha,10beta-hexahydropyrrolo[2,1-a ]isoquinoline ((11)C-McN 5652) was the first PET radiotracer successfully developed as a SERT imaging agent. Recently, (11)C-3-amino-4-(2-dimethylaminomethylphenylthio)benzonitrile ((11)C-DASB) was introduced as an alternative to (11)C-McN 5652. Comparative evaluation of (11)C-DASB and (11)C-McN 5652 in baboons indicates that (11)C-DASB is associated with (a) lower nonspecific binding in the brain, (b) higher plasma free fraction, and (c) faster plasma clearance and brain uptake kinetics, enabling measurement of SERT parameters in a shorter scanning time. The purpose of this study was to compare these 2 agents in healthy humans. METHODS: Six healthy volunteers underwent 2 PET scans on the same day, one with (11)C-DASB and one with (11)C-McN 5652, in counterbalanced order. Regional distribution volumes (V(T)) were derived for 16 brain regions by kinetic analysis using the arterial input function. RESULTS: Both (11)C-DASB and (11)C-McN 5652 displayed similar patterns of accumulation: highest levels in the midbrain, thalamus and striatum; intermediate in the limbic regions; low in the neocortex; and lowest in the cerebellum. (11)C-DASB cerebellar V(T) (10.1 +/- 2.0 mL g(-1)) was lower than that of (11)C-McN 5652 (20.8 +/- 3.6 mL g(-1)), indicating lower nonspecific binding. As a result, regional specific-to-nonspecific equilibrium partition coefficients (V(3)") of (11)C-DASB were higher compared with those of (11)C-McN 5652 (for example, midbrain V(3)" of (11)C-DASB and (11)C-McN 5652 were 2.04 +/- 0.44 and 1.20 +/- 0.34, respectively). The plasma free fraction was 8.9% +/- 1.6% for (11)C-DASB and was not measurable for (11)C-McN 5652. In contrast to the situation observed in baboons, plasma clearances of both compounds were similar in humans, and the minimal scanning times required to derive time-invariant distribution volumes in all regions were comparable for both tracers (95 min). CONCLUSION: With the exception of the scanning time, predictions from baboon studies were confirmed in humans. The higher specific-to-nonspecific ratios of (11)C-DASB are a critical advantage. This property will be especially important for the measurement of SERT in regions with moderate density, such as the limbic regions, where alterations of serotonin transmission might be associated with anxiety and depression.
Effects of pyrroloisoquinoline enantiomers ((+)- and (-)-McN-5652-Z) on behavioral and pharmacological serotonergic mechanisms in rats.[Pubmed:1831423]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Apr 10;196(1):85-92.
A behavioral syndrome consisting of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)-dependent behaviors (e.g. forepaw treading, retropulsion and splayed hindlimbs) as well as hyperthermia occurred after bilateral injection of the (6S, 10bR)-(+)-enantiomer of McN-5652-Z into the cerebral ventricles in pargyline-treated rats. Both the behavioral syndrome and hyperthermia produced by (+)-McN-5652-Z were counteracted by parachlorophenylalanine or ketanserin. The (6R, 10bS)-(-)-enantiomer of McN-5652-Z influenced neither behavior nor body temperature. The enantiomers of McN-5652-Z differed also in their ability to inhibit ex vivo binding of paroxetine in rat frontal cortex and hypothalamus, in vitro uptake of 5-HT in rat blood platelets, and 5-HT-induced contraction of rat vascular smooth muscle, with (+)-McN-5652-Z being most active. No difference was observed between the effects of (+)- and (-)-McN-5652-Z on 5-HT metabolism by rat brain monoamine oxidase. Molecular models of N-protonated enantiomers having a cis B,C-ring juncture and a B-ring chair conformation were differentiated using a hypothetical model of the 5-HT uptake area. The findings indicate that the enantiomers of McN-5652-Z are useful tools for studying the stereoselectivity of behavioral and pharmacological effects exerted by serotonergic neurotransmission.
Pyrroloisoquinoline antidepressants. 3. A focus on serotonin.[Pubmed:2213832]
J Med Chem. 1990 Oct;33(10):2793-7.
A collection of hexahydropyrroloisoquinoline derivatives (1-22), which represent a class of compounds that inhibit the neuronal uptake of dopamine (DA), norepinephrine (NE), and serotonin (5-HT), was investigated in vivo for serotonin-potentiating properties in the mouse head-twitch and rat serotonin syndrome assays. The p-methylthio compound 3b (McN-5652-Z) was found to possess exceptional activity in these assays, and the activity was attributable almost exclusively to the (+)-6S,10bR enantiomer. Ten closely related analogues were synthesized, tested, and compared among themselves and with some previously prepared compounds, both in vivo and in vitro. Several trans diastereomers exhibited strong inhibition of 5-HT uptake and substantial potentiation of 5-HT, while the cis diastereomers (3a, 4a, and 10a) tested were virtually devoid of such activity. Although 3b was only moderately selective in inhibiting the uptake of 5-HT vs NE, its 10-substituted analogues 4b, 7b-9b had improved 5-HT selectivity relative to NE, to the extent of 20-25 times (150-200 times relative to DA). Of these more selective compounds (in vitro), only 4b and 7b had substantial activity in vivo. Sulfoxide 11b appeared to function as a prodrug of 3b in vivo.
McN-5652: a highly potent inhibitor of serotonin uptake.[Pubmed:2905001]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Dec;247(3):1032-8.
McN-5652 is one of a series of substituted pyrrolo-isoquinolines that, as a group, potently inhibit the uptake of one or more of the monoamines, norepinephrine, serotonin and dopamine. McN-5652 is characterized by exceptionally high potency as an inhibitor of the uptake of serotonin by rat brain synaptosomes in vitro (Ki approximately 0.6 nM) and ex vivo (ED50 approximately 2 mg/kg p.o.). The high potency of McN-5652 as a serotonin uptake inhibitor in vivo is indicated further by the low doses required to potentiate L-5-hydroxytryptophan-induced head twitches in mice (ED50 = 0.4 mg/kg 2 hr after p.o. dosing) and the serotonin syndrome in rats (ED50 = 1.5 mg/kg 2 hr after p.o. dosing). McN-5652 also potently inhibited the synaptosomal uptake of norepinephrine (Ki approximately 3 nM) and was a moderately potent inhibitor of the synaptosomal uptake of dopamine (Ki approximately 40 nM). McN-5652 inhibited tetrabenazine-induced ptosis in rats and mice but was much less effective in blocking the sedation caused by tetrabenazine. In rats, McN-5652 did not induce the stereotyped behavior often caused by dopamine agonists and inhibitors of dopamine uptake. Receptor binding experiments indicated that McN-5652 has a weak affinity for serotonin 5-HT2 and alpha-1 adrenergic receptors (apparent Ki approximately 200 nM) and a very low affinity for dopamine D1 and D2 receptors, serotonin 5-HT1, alpha-2 adrenergic, muscarinic and gamma-aminobutyric acid-A receptors. Experiments using the guinea pig ileum indicate that McN-5652 is a weak, noncompetitive antagonist of histamine.


