PP 2 (AG 1879)Src-family kinases inhibitor CAS# 172889-27-9 |
- PP 1
Catalog No.:BCC3630
CAS No.:172889-26-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 172889-27-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 4878 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C15H16ClN5 | M.Wt | 301.78 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | AGL 1879 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 50 mg/mL (165.69 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
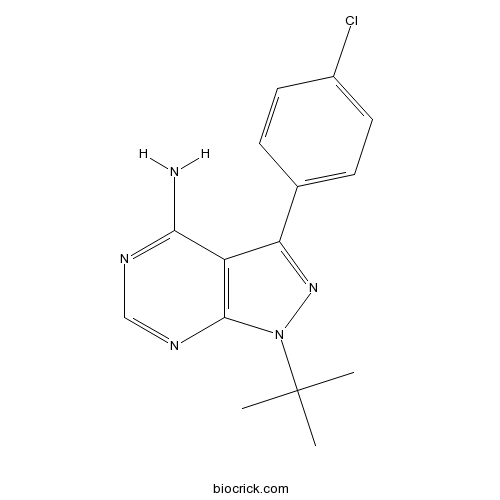
| Chemical Name | 1-tert-butyl-3-(4-chlorophenyl)pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-amine | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)(C)N1C2=C(C(=N1)C3=CC=C(C=C3)Cl)C(=NC=N2)N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | PBBRWFOVCUAONR-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H16ClN5/c1-15(2,3)21-14-11(13(17)18-8-19-14)12(20-21)9-4-6-10(16)7-5-9/h4-8H,1-3H3,(H2,17,18,19) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective inhibitor of Src-family tyrosine kinases. Inhibits p56lck and p59fynT (IC50 values are 4 and 5 nM respectively). Displays > 10000-fold selectivity over ZAP-70 and JAK2. Moderately inhibits CSK (IC50 = 0.73 μM). Negative control PP 3 also available. |

PP 2 (AG 1879) Dilution Calculator

PP 2 (AG 1879) Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.3137 mL | 16.5684 mL | 33.1367 mL | 66.2734 mL | 82.8418 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6627 mL | 3.3137 mL | 6.6273 mL | 13.2547 mL | 16.5684 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3314 mL | 1.6568 mL | 3.3137 mL | 6.6273 mL | 8.2842 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0663 mL | 0.3314 mL | 0.6627 mL | 1.3255 mL | 1.6568 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0331 mL | 0.1657 mL | 0.3314 mL | 0.6627 mL | 0.8284 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
PP2 is a selective inhibitor of Src family with IC50 value of 4 nM and 5 nM for Lck and Fyn, respectively [1].
Src is a tyrosine kinase and contains 9 members: c-Src (this protein), Yes, Fyn, Fgr, Yrk, Lyn, Blk, Hck, and Lck [1].
PP2 is a potent Src family inhibitor that plays an important role in the cancer and is regarded as a promising target for treatment. When tested with human glioma cell line U251 spheroids in 3-D model, PP2 inhibited the cell invasion in a dose-dependent manner (2.5 μM, 10μM). And treated monolayer U251 cells with PP2 (10μM) decreased cell proliferation rate by inhibiting Src [2]. In human T cells, PP2 showed inhibition on anti-CD3-induced tyrosine phosphorylation by inhibiting Lck and Fyn that involved in the early T cell signal transduction [1].
In Sprague-Dawley rat model injected with urethane and after some needed treatment to perform research and record data, pretreatment with PP2 (50M, 10μL it) reversed the reflex potentiation, as well as Src kinase and NR2B phosphorylation by inhibiting Src family [3].
It is also reported that PP2 inhibits ZAP-70, JAK2 and EGF-R with IC50 value of >100 μM, >50 μM, and 480 nM, respectively [1].
References:
[1]. Hanke, J.H., et al., Discovery of a novel, potent, and Src family-selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Study of Lck- and FynT-dependent T cell activation. J Biol Chem, 1996. 271(2): p. 695-701.
[2]. Angers-Loustau, A., et al., SRC regulates actin dynamics and invasion of malignant glial cells in three dimensions. Mol Cancer Res, 2004. 2(11): p. 595-605.
[3]. Wu, H.C., et al., EphrinB2 induces pelvic-urethra reflex potentiation via Src kinase-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of NR2B. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 2011. 300(2): p. F403-11.
- PP 1
Catalog No.:BCC3630
CAS No.:172889-26-8
- H-Aib-OEt.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2670
CAS No.:17288-15-2
- Isocucurbitacin B
Catalog No.:BCN8101
CAS No.:17278-28-3
- Mudanpioside C
Catalog No.:BCN2798
CAS No.:172760-03-1
- Varespladib (LY315920)
Catalog No.:BCC2310
CAS No.:172732-68-2
- Senkyunolide S
Catalog No.:BCC9145
CAS No.:172723-28-3
- Fmoc-β-Homo-Val-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2626
CAS No.:172695-33-9
- Fosaprepitant
Catalog No.:BCC4281
CAS No.:172673-20-0
- Clemastanin A
Catalog No.:BCC8151
CAS No.:172670-47-2
- Eucalyptone
Catalog No.:BCN1111
CAS No.:172617-99-1
- Murrayamine E
Catalog No.:BCN7908
CAS No.:172617-68-4
- Naringin 4'-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN8196
CAS No.:17257-21-5
- LY 272015 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7558
CAS No.:172895-15-7
- LY 266097 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7856
CAS No.:172895-39-5
- Isosinensetin
Catalog No.:BCN2919
CAS No.:17290-70-9
- PB 28 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7411
CAS No.:172907-03-8
- FICZ
Catalog No.:BCC5513
CAS No.:172922-91-7
- Biorobin
Catalog No.:BCN4691
CAS No.:17297-56-2
- BWX 46
Catalog No.:BCC5865
CAS No.:172997-92-1
- Isoanthricin
Catalog No.:BCN3531
CAS No.:17301-70-5
- Poloxime
Catalog No.:BCC5307
CAS No.:17302-61-3
- Goniothalamin
Catalog No.:BCN4690
CAS No.:17303-67-2
- PMPA (NAALADase inhibitor)
Catalog No.:BCC2354
CAS No.:173039-10-6
- Rec 15/2615 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7628
CAS No.:173059-17-1
Heterozygous null bone morphogenetic protein receptor type 2 mutations promote SRC kinase-dependent caveolar trafficking defects and endothelial dysfunction in pulmonary arterial hypertension.[Pubmed:25411245]
J Biol Chem. 2015 Jan 9;290(2):960-71.
Hereditary pulmonary arterial hypertension (HPAH) is a rare, fatal disease of the pulmonary vasculature. The majority of HPAH patients inherit mutations in the bone morphogenetic protein type 2 receptor gene (BMPR2), but how these promote pulmonary vascular disease is unclear. HPAH patients have features of pulmonary endothelial cell (PEC) dysfunction including increased vascular permeability and perivascular inflammation associated with decreased PEC barrier function. Recently, frameshift mutations in the caveolar structural protein gene Caveolin-1 (CAV-1) were identified in two patients with non-BMPR2-associated HPAH. Because caveolae regulate endothelial function and vascular permeability, we hypothesized that defects in caveolar function might be a common mechanism by which BMPR2 mutations promote pulmonary vascular disease. To explore this, we isolated PECs from mice carrying heterozygous null Bmpr2 mutations (Bmpr2(+/-)) similar to those found in the majority of HPAH patients. We show that Bmpr2(+/-) PECs have increased numbers and intracellular localization of caveolae and caveolar structural proteins CAV-1 and Cavin-1 and that these defects are reversed after blocking endocytosis with dynasore. SRC kinase is also constitutively activated in Bmpr2(+/-) PECs, and localization of CAV-1 to the plasma membrane is restored after treating Bmpr2(+/-) PECs with the SRC kinase inhibitor 3-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-amine (PP2). Late outgrowth endothelial progenitor cells isolated from HPAH patients show similar increased activation of SRC kinase. Moreover, Bmpr2(+/-) PECs have impaired endothelial barrier function, and barrier function is restored after treatment with PP2. These data suggest that heterozygous null BMPR2 mutations promote SRC-dependent caveolar trafficking defects in PECs and that this may contribute to pulmonary endothelial barrier dysfunction in HPAH patients.
Shear stress induces cell apoptosis via a c-Src-phospholipase D-mTOR signaling pathway in cultured podocytes.[Pubmed:22472346]
Exp Cell Res. 2012 Jun 10;318(10):1075-85.
The glomerular capillary wall, composed of endothelial cells, the glomerular basement membrane and the podocytes, is continually subjected to hemodynamic force arising from tractional stress due to blood pressure and shear stress due to blood flow. Exposure of glomeruli to abnormal hemodynamic force such as hyperfiltration is associated with glomerular injury and progressive renal disease, and the conversion of mechanical stimuli to chemical signals in the regulation of the process is poorly understood in podocytes. By examining DNA fragmentation, apoptotic nuclear changes and cytochrome c release, we found that shear stress induced cell apoptosis in cultured podocytes. Meanwhile, podocytes exposed to shear stress also stimulated c-Src phosphorylation, phospholipase D (PLD) activation and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling. Using the antibodies against c-Src, PLD(1), and PLD(2) to perform reciprocal co-immunoprecipitations and in vitro PLD activity assay, our data indicated that c-Src interacted with and activated PLD(1) but not PLD(2). The inhibition of shear stress-induced c-Src phosphorylation by PP(2) (a specific inhibitor of c-Src kinase) resulted in reduced PLD activity. Phosphatidic acid, produced by shear stress-induced PLD activation, stimulated mTOR signaling, and caused podocyte hypertrophy and apoptosis.
Zinc induces protein phosphatase 2A inactivation and tau hyperphosphorylation through Src dependent PP2A (tyrosine 307) phosphorylation.[Pubmed:22892311]
Neurobiol Aging. 2013 Mar;34(3):745-56.
The activity of protein phosphatase (PP) 2A is downregulated and promotes the hyperphosphorylation of tau in the brains of Alzheimer's disease (AD), but the mechanism for PP2A inactivation has not been elucidated. We have reported that PP2A phosphorylation at tyrosine 307 (Y307) is involved in PP2A inactivation. Here, we further studied the upstream mechanisms for PP2A phosphorylation and inactivation. We found that zinc, a heavy metal ion that is widely distributed in the normal brain and accumulated in the susceptible regions of AD brain, could induce PP2A inhibition, phosphorylation of PP2A at Y307 and tau hyperphosphorylation both in rat brains and cultured N2a cells, while zinc chelating prevented these changes completely. Upregulation of PP2A chemically or genetically attenuated zinc-induced tau hyperphosphorylation, whereas mutation of Y307 to phenylalanine abolished the zinc-induced tyrosine phosphorylation and inactivation of PP2A. Zinc could activate Src, while PP2, a specific Src family kinases inhibitor, attenuated zinc-induced PP2A phosphorylation and inactivation, indicating that zinc induces PP2A Y307 phosphorylation and inactivation through Src activation. In human tau transgenic mice, zinc chelator rescued PP2A activity, prevented Src activation, and reduced hyperphosphorylated and insoluble tau levels. We concluded that zinc induces PP2A inactivation and tau hyperphosphorylation through Src-dependent pathway, regulation of zinc homeostasis may be a promising therapeutic for AD and the related tauopathies.
Src family kinase inhibitor PP2 accelerates differentiation in human intestinal epithelial cells.[Pubmed:23274493]
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Jan 25;430(4):1195-200.
The proto-oncogene Src is an important protein tyrosine kinase involved in signaling pathways that control cell adhesion, growth, migration and survival. Here, we investigated the involvement of Src family kinases (SFKs) in human intestinal cell differentiation. We first observed that Src activity peaked in early stages of Caco-2/15 cell differentiation. Inhibition of SFKs with PP2, a selective SFK inhibitor, accelerated the overall differentiation program. Interestingly, all polarization and terminal differentiation markers tested, including sucrase-isomaltase, lactase-phlorizin hydrolase and E and Li-cadherins were found to be significantly up-regulated after only 3 days of treatment in the newly differentiating cells. Further investigation of the effects of PP2 revealed a significant up-regulation of the two main intestinal epithelial cell-specific transcription factors Cdx2 and HNF1alpha and a reduction of polycomb PRC2-related epigenetic repressing activity as measured by a decrease in H3K27me3, two events closely related to the control of cell terminal differentiation in the intestine. Taken together, these data suggest that SFKs play a key role in the control of intestinal epithelial cell terminal differentiation.
Pharmacological Inhibition of Focal Adhesion Kinase Attenuates Cardiac Fibrosis in Mice Cardiac Fibroblast and Post-Myocardial-Infarction Models.[Pubmed:26330161]
Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;37(2):515-26.
BACKGROUND: To investigate the role of focal adhesion kinase (FAK)-mediated signaling in hypoxia-induced cardiac fibroblasts (CFs) differentiation and cardiac fibrosis post-myocardial infarction (MI) on a mice model. METHODS: CFs of neonatal C57BL/6 mice were treated under normoxic, hypoxic, or hypoxic+PP2 (known as a Src kinase family inhibitor) conditions. Gene expressions of FAK, alpha-smooth muscle actin (alpha-SMA) and collagen type I alpha 1 (Col1alpha1), or alpha-SMA and vimentin levels were performed by RT-PCR and immunofluorescence staining, respectively. Thirty mice were surgically treated into Sham (n=7) and MI (n=23) groups; and FAK inhibitor PF-562271 was given to six survivor MI mice (as PF group, from 15 survivors). Heart function and collagenous tissues were examined by echocardiography, as well as by Masson's trichrome and Sirius red staining, respectively. Type I collagen, FAK protein, mTOR, ERK1/2, AKT, P70S6K and phospho-FAK levels were also analyzed. RESULTS: FAK inhibition with PP2 significantly decreased CFs differentiation and collagen synthesis under hypoxia treatment. In vivo, PF-562271 treatment resulted in fibrosis attenuation; however, deteriorated heart function of MI mice could not be significantly improved. PF-562271 may affect phospho-mTOR (p<0.05), phospho-ERK1/2 (p<0.01), phospho-AKT (p<0.001) and phospho-P70S6K (p<0.05) to exert its benefits. FAK can be activated either under hypoxia in CFs or MI in a mouse model to promote fibrosis. However, pharmacological inhibition of FAK can attenuate fibrosis response. CONCLUSION: This study provides novel evidence that FAK inhibition may become a promising pharmaceutical strategy to attenuate fibrosis post-MI.
The specificities of protein kinase inhibitors: an update.[Pubmed:12534346]
Biochem J. 2003 Apr 1;371(Pt 1):199-204.
We have previously examined the specificities of 28 commercially available compounds, reported to be relatively selective inhibitors of particular serine/threonine-specific protein kinases [Davies, Reddy, Caivano and Cohen (2000) Biochem. J. 351, 95-105]. In the present study, we have extended this analysis to a further 14 compounds. Of these, indirubin-3'-monoxime, SP 600125, KT 5823 and ML-9 were found to inhibit a number of protein kinases and conclusions drawn from their use in cell-based assays are likely to be erroneous. Kenpaullone, Alsterpaullone, Purvalanol, Roscovitine, pyrazolopyrimidine 1 (PP1), PP2 and ML-7 were more specific, but still inhibited two or more protein kinases with similar potency. Our results suggest that the combined use of Roscovitine and Kenpaullone may be useful for identifying substrates and physiological roles of cyclin-dependent protein kinases, whereas the combined use of Kenpaullone and LiCl may be useful for identifying substrates and physiological roles of glycogen synthase kinase 3. The combined use of SU 6656 and either PP1 or PP2 may be useful for identifying substrates of Src family members. Epigallocatechin 3-gallate, one of the main polyphenolic constituents of tea, inhibited two of the 28 protein kinases in the panel, dual-specificity, tyrosine-phosphorylated and regulated kinase 1A (DYRK1A; IC(50)=0.33 microM) and p38-regulated/activated kinase (PRAK; IC(50)=1.0 microM).
A role for Src kinase in spontaneous epileptiform activity in the CA3 region of the hippocampus.[Pubmed:10890901]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Jul 18;97(15):8653-7.
Members of the Src family of nonreceptor protein tyrosine kinases (PTKs) have been implicated in the regulation of cellular excitability and synaptic plasticity. We have investigated the role of these PTKs in in vitro models of epileptiform activity. Spontaneous epileptiform discharges were induced in vitro in the CA3 region of rat hippocampal slices by superfusion with the potassium channel blocker 4-aminopyridine in Mg(2+)-free medium. In hippocampal slices treated in this fashion, Src kinase activity was increased and the frequency of epileptiform discharges could be greatly reduced by inhibitor of the Src family of PTKs, 4-amino-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-7-(t-butyl)pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine (PP2), but not by the inactive structural analog 4-amino-7-phenylpyrazol[3,4-d]pyrimidine (PP3). 4-Amino-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-7-(t-butyl)pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine also reduced epileptiform activity induced by either 4-aminopyridine or Mg(2+)-free medium alone. These observations demonstrate a role for Src family PTKs in the pathophysiology of epilepsy and suggest potential therapeutic targets for antiepileptic therapy.
Protein kinase inhibitors: the tyrosine-specific protein kinases.[Pubmed:9578319]
Pharmacol Ther. 1998 Feb;77(2):81-114.
Inhibitors for tyrosine-specific protein kinases ultimately may constitute a novel family of medicinally active agents. Unfortunately, the challenges associated with the acquisition of inhibitors for these enzyme targets are unlike any that have ever been encountered in medicinal chemistry. Protein kinases pose a variety of obstacles in regard to inhibitor design, nearly all of which deal with, in one fashion or another, the issue of specificity. The protein kinase family is extraordinarily large, with estimates that the human genome codes for as many as 2000 protein kinases. Furthermore, inhibitors that are directed to the ATP-binding sites of these enzymes must contend with the presence of a large number of other ATP-utilizing proteins and, in addition, must compete with the high intracellular concentrations of ATP. Although specificity ultimately may prove to be less of a concern with peptide-based inhibitors, these agents neither are readily bioavailable nor do they bind with the requisite affinity to the protein-binding domains of protein kinases. In the face of these challenges, an enormous number of inhibitors have been synthesized and evaluated for the tyrosine-specific protein kinases. The advantages and disadvantages associated with inhibitors that are targeted to the ATP-binding site, the protein-binding site, and nonactive site regions required for appropriate subcellular localization are discussed. The handful of tyrosine-specific protein kinases that have been selected as targets to date and their roles in various disease processes are described as well.
Discovery of a novel, potent, and Src family-selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Study of Lck- and FynT-dependent T cell activation.[Pubmed:8557675]
J Biol Chem. 1996 Jan 12;271(2):695-701.
Here, we have studied the activity of a novel protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitor that is selective for the Src family of tyrosine kinases. We have focused our study on the effects of this compound on T cell receptor-induced T cell activation, a process dependent on the activity of the Src kinases Lck and FynT. This compound is a nanomolar inhibitor of Lck and FynT, inhibits anti-CD3-induced protein-tyrosine kinase activity in T cells, demonstrates selectivity for Lck and FynT over ZAP-70, and preferentially inhibits T cell receptor-dependent anti-CD3-induced T cell proliferation over non-T cell receptor-dependent phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate/interleukin-2 (IL-2)-induced T cell proliferation. Interestingly, this compound selectively inhibits the induction of the IL-2 gene, but not the granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor or IL-2 receptor genes. This compound offers a useful new tool for examining the role of the Lck and FynT tyrosine kinases versus ZAP-70 in T cell activation as well as the role of other Src family kinases in receptor function.


