FICZHigh affinity aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) agonist CAS# 172922-91-7 |
- Pioglitazone HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2278
CAS No.:112529-15-4
- Rosiglitazone
Catalog No.:BCC2264
CAS No.:122320-73-4
- T0070907
Catalog No.:BCC2261
CAS No.:313516-66-4
- GW0742
Catalog No.:BCC2267
CAS No.:317318-84-6
- Clofibric Acid
Catalog No.:BCC4652
CAS No.:882-09-7
- Troglitazone
Catalog No.:BCC2016
CAS No.:97322-87-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 172922-91-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 1863 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C19H12N2O | M.Wt | 284.31 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 10 mg/mL (35.17 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) | ||
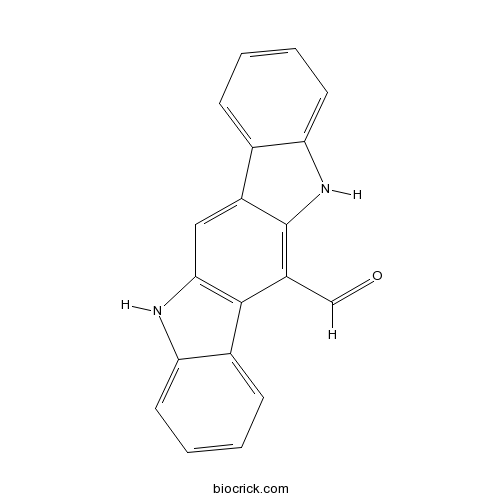
| Chemical Name | 5,11-dihydroindolo[3,2-b]carbazole-12-carbaldehyde | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C2C(=C1)C3=CC4=C(C5=CC=CC=C5N4)C(=C3N2)C=O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZUDXFBWDXVNRKF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H12N2O/c22-10-14-18-12-6-2-4-8-16(12)20-17(18)9-13-11-5-1-3-7-15(11)21-19(13)14/h1-10,20-21H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | High affinity aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) agonist (Kd = 70 p M). Proposed to be an endogenous AhR ligand. Induces transient expression of cytochrome P450-1A1 (CYP1A1) in vitro. |

FICZ Dilution Calculator

FICZ Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5173 mL | 17.5864 mL | 35.1729 mL | 70.3457 mL | 87.9322 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.7035 mL | 3.5173 mL | 7.0346 mL | 14.0691 mL | 17.5864 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3517 mL | 1.7586 mL | 3.5173 mL | 7.0346 mL | 8.7932 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0703 mL | 0.3517 mL | 0.7035 mL | 1.4069 mL | 1.7586 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0352 mL | 0.1759 mL | 0.3517 mL | 0.7035 mL | 0.8793 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- PB 28 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7411
CAS No.:172907-03-8
- Isosinensetin
Catalog No.:BCN2919
CAS No.:17290-70-9
- LY 266097 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7856
CAS No.:172895-39-5
- LY 272015 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7558
CAS No.:172895-15-7
- PP 2 (AG 1879)
Catalog No.:BCC3631
CAS No.:172889-27-9
- PP 1
Catalog No.:BCC3630
CAS No.:172889-26-8
- H-Aib-OEt.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2670
CAS No.:17288-15-2
- Isocucurbitacin B
Catalog No.:BCN8101
CAS No.:17278-28-3
- Mudanpioside C
Catalog No.:BCN2798
CAS No.:172760-03-1
- Varespladib (LY315920)
Catalog No.:BCC2310
CAS No.:172732-68-2
- Senkyunolide S
Catalog No.:BCC9145
CAS No.:172723-28-3
- Fmoc-β-Homo-Val-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2626
CAS No.:172695-33-9
- Biorobin
Catalog No.:BCN4691
CAS No.:17297-56-2
- BWX 46
Catalog No.:BCC5865
CAS No.:172997-92-1
- Isoanthricin
Catalog No.:BCN3531
CAS No.:17301-70-5
- Poloxime
Catalog No.:BCC5307
CAS No.:17302-61-3
- Goniothalamin
Catalog No.:BCN4690
CAS No.:17303-67-2
- PMPA (NAALADase inhibitor)
Catalog No.:BCC2354
CAS No.:173039-10-6
- Rec 15/2615 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7628
CAS No.:173059-17-1
- Rhoifolin
Catalog No.:BCN1112
CAS No.:17306-46-6
- Ganoderic acid DM
Catalog No.:BCN1113
CAS No.:173075-45-1
- Centaureidin
Catalog No.:BCN2575
CAS No.:17313-52-9
- SQ 22536
Catalog No.:BCC7065
CAS No.:17318-31-9
- 4-Beta-Hydroxycholesterol
Catalog No.:BCN2752
CAS No.:17320-10-4
Evidence for New Light-Independent Pathways for Generation of the Endogenous Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Agonist FICZ.[Pubmed:26686552]
Chem Res Toxicol. 2016 Jan 19;29(1):75-86.
Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), a conserved transcription factor best known as a target for highly toxic halogenated substances such as dioxin, under normal xenobiotic-free conditions is of considerable scientific interest. We have demonstrated previously that a photoproduct of tryptophan, 6-formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole (FICZ), fulfills the criteria for an endogenous ligand for this receptor and proposed that this compound is the enigmatic mediator of the physiological functions of AhR. Here, we describe novel light-independent pathways by which FICZ can be formed. The oxidant H2O2 was shown to convert tryptophan to FICZ on its own in the absence of light. The enzymatic deamination of tryptamine yielded indole-3-acetaldehyde (I3A), which then rearranged to FICZ and its oxidation product, indolo[3,2-b]carbazole-6-carboxylic acid (CICZ). Indole-3-pyruvate (I3P) also produced I3A, FICZ, and CICZ. Malassezia yeast species, which constitute a part of the normal skin microbiota, produce a number of AhR activators from tryptophan. We identified both FICZ and CICZ among those products. Formation of FICZ from tryptophan or I3P produces a complex mixture of indole derivatives, some of which are CYP1A1 inhibitors. These can hinder the cellular clearance of FICZ and thereby increase its power as an AhR agonist. We present a general molecular mechanism involving dehydrogenations and oxidative coupling for the formation of FICZ in which I3A is the important precursor. In conclusion, our results suggest that FICZ is likely to be formed systemically.
The highly bioactive molecule and signal substance 6-formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole (FICZ) plays bi-functional roles in cell growth and apoptosis in vitro.[Pubmed:28289825]
Arch Toxicol. 2017 Oct;91(10):3365-3372.
The maintenance of cellular homeostasis is a complex process that is governed by the receipt of prototypical growth and death signals. The endogenous functions of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) in cellular homeostasis are not well understood. We aimed to establish whether the disturbance of endogenously activated AHR can influence cell growth, and if so, what mechanism(s) are involved. Cell growth was measured in mouse hepatoma Hepa-1 wild-type and cytochrome P4501A1 (CYP1A1)-deficient c37 cells. In other sets of experiments, HepG2 cells were exposed to different doses of FICZ (0.01nM-1 microM) alone or in combination with 50 nM of the CYP1A1 inhibitor 3'methoxy-4'nitro-flavone (MNF). CYP1A1 enzyme activity, cell viability, oxidative stress, and several endpoints of apoptosis were measured. FICZ treatment at a high concentration or in combination with MNF induced sustained CYP1A1 activity and led to oxidative stress and activation of apoptosis via a mitochondrial-dependent pathway. In comparison with the wild-type Hepa-1 cells, c37 cells lacking CYP1A1 activity proliferated faster in normal medium which contains trace levels of FICZ. Besides, in HepG2 cells, FICZ stimulated cell growth at low concentrations but inhibited cell growth at high concentrations. Based on these findings, we propose that CYP1A1 inhibitors, by increasing the levels of the endogenous ligand FICZ, change the cell growth kinetics and trigger cell death and apoptosis through a mitochondrial-dependent pathway. Since AHR controls multiple cellular functions, a wide range of toxicity can be expected by disturbing its endogenous functions.
Biological effects of 6-formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole (FICZ) in vivo are enhanced by loss of CYP1A function in an Ahr2-dependent manner.[Pubmed:27112072]
Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Jun 15;110-111:117-29.
6-Formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole (FICZ) is a potent aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) agonist that is efficiently metabolized by AHR-regulated cytochrome P4501 enzymes. FICZ is a proposed physiological AHR ligand that induces its own degradation as part of a regulatory negative feedback loop. In vitro studies in cells show that CYP1 inhibition in the presence of FICZ results in enhanced AHR activation, suggesting that FICZ accumulates in the cell when its metabolism is blocked. We used zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos to investigate the in vivo effects of FICZ when CYP1A is knocked down or inhibited. Embryos were injected with morpholino antisense oligonucleotides targeting CYP1A (CYP1A-MO), Ahr2, or a combination of both. FICZ exposure of non-injected embryos or embryos injected with control morpholino had little effect. In CYP1A-MO-injected embryos, however, FICZ dramatically increased mortality, incidence and severity of pericardial edema and circulation failure, reduced hatching frequency, blocked swim bladder inflation, and strongly potentiated expression of Ahr2-regulated genes. These effects were substantially reduced in embryos with a combined knockdown of Ahr2 and CYP1A, indicating that the toxicity was mediated at least partly by Ahr2. Co-exposure to the CYP1 inhibitor alpha-naphthoflavone (alphaNF) and FICZ had similar effects as the combination of CYP1A-MO and FICZ. HPLC analysis of FICZ-exposed embryos showed increased levels of FICZ after concomitant CYP1A-MO injection or alphaNF co-exposure. Together, these results show that a functioning CYP1/AHR feedback loop is crucial for regulation of AHR signaling by a potential physiological ligand in vivo and further highlights the role of CYP1 enzymes in regulating biological effects of FICZ.
Time-dependent transcriptomic and biochemical responses of 6-formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole (FICZ) and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) are explained by AHR activation time.[Pubmed:27301797]
Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 Sep 1;115:134-43.
6-Formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole (FICZ) and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) are ligands of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) and bind to the AHR with high affinity. Until recently, TCDD was considered to be the most potent AHR agonist, but several recent studies indicate that FICZ binds with greater affinity to the AHR than TCDD. To advance our understanding of the similarities and differences of the effects of FICZ and TCDD exposure in chicken embryo hepatocyte (CEH) cultures, we compared relative expression changes of 27 dioxin-responsive genes by the use of a chicken PCR array, porphyrin accumulation and ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase (EROD) activity at different time points. In addition, an egg injection study was performed to assess the effects of FICZ on the developing chicken embryo. The results of the current study showed: (1) mean EROD-derived relative potency values for FICZ compared to TCDD changed as a function of time (i.e. 9, 0.004, 0.0008 and 0.00008 at 3, 8, 24, and 48h, respectively) in CEH cultures; (2) FICZ exposure did not result in porphyrin accumulation in CEH cultures; (3) concordance between gene expression profiles for FICZ and TCDD was time- and concentration-dependent, and (4) no mortality or morphological abnormalities were observed in chicken embryos injected with 0.87ng FICZ/g egg into the air cell. The results presented herein suggest that while FICZ and TCDD share similar molecular targets, transient versus sustained AHR activation by FICZ and TCDD result in differential transcriptomic responses. Moreover, rapid metabolism of FICZ in hepatocytes resulted in a significant decrease in the induction of EROD activity.
AhR sensing of bacterial pigments regulates antibacterial defence.[Pubmed:25119038]
Nature. 2014 Aug 28;512(7515):387-92.
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) is a highly conserved ligand-dependent transcription factor that senses environmental toxins and endogenous ligands, thereby inducing detoxifying enzymes and modulating immune cell differentiation and responses. We hypothesized that AhR evolved to sense not only environmental pollutants but also microbial insults. We characterized bacterial pigmented virulence factors, namely the phenazines from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and the naphthoquinone phthiocol from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, as ligands of AhR. Upon ligand binding, AhR activation leads to virulence factor degradation and regulated cytokine and chemokine production. The relevance of AhR to host defence is underlined by heightened susceptibility of AhR-deficient mice to both P. aeruginosa and M. tuberculosis. Thus, we demonstrate that AhR senses distinct bacterial virulence factors and controls antibacterial responses, supporting a previously unidentified role for AhR as an intracellular pattern recognition receptor, and identify bacterial pigments as a new class of pathogen-associated molecular patterns.
The suggested physiologic aryl hydrocarbon receptor activator and cytochrome P4501 substrate 6-formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole is present in humans.[Pubmed:19054769]
J Biol Chem. 2009 Jan 30;284(5):2690-6.
Dioxins and other polycyclic aromatic compounds formed during the combustion of waste and fossil fuels represent a risk to human health, as well as to the well being of our environment. Compounds of this nature exert carcinogenic and endocrine-disrupting effects in experimental animals by binding to the orphan aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR). Understanding the mechanism of action of these pollutants, as well as the physiological role(s) of the AhR, requires identification of the endogenous ligand(s) of this receptor. We reported earlier that activation of AhR by ultraviolet radiation is mediated by the chromophoric amino acid tryptophan (Trp), and we suggested that a new class of compounds derived from Trp, in particular 6-formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole (FICZ), acts as natural high affinity ligands for this receptor. Here we describe seven new FICZ-derived indolo[3,2-b]carbazole-6-carboxylic acid metabolites and two sulfoconjugates, and we demonstrate the following. (i) FICZ is formed efficiently by photolysis of Trp upon exposure to visible light. (ii) FICZ is an exceptionally good substrate for cytochromes P450 (CYP) 1A1, 1A2, and 1B1, and its hydroxylated metabolites are remarkably good substrates for the sulfotransferases (SULTs) 1A1, 1A2, 1B1, and 1E1. Finally, (iii) sulfoconjugates of phenolic metabolites of FICZ are present in human urine. Our findings indicate that formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazols are the most potent naturally occurring activators of the AhR signaling pathway and may be the key substrates of the CYP1 and SULT1 families of enzymes. These conclusions contradict the widespread view that xenobiotic compounds are the major AhR ligands and CYP1 substrates.
Structure elucidation of two tryptophan-derived, high affinity Ah receptor ligands.[Pubmed:8807817]
Chem Biol. 1995 Dec;2(12):841-5.
BACKGROUND: Environmental contaminants, such as 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) and other structurally related 'environmental hormones', exert their harmful biological effects through the Ah receptor signaling pathway. Several naturally occurring substances also bind to this receptor, but its natural role is still obscure. Tryptophan derivatives of the indolo[3,2-b]carbazole type, earlier suggested by us to be endogenous ligands for the receptor, should be a powerful tool in understanding receptor function. We therefore set out to determine their identity. RESULTS: The two tryptophan-derived Ah receptor ligands have been chemically analyzed and characterized by means of mass spectrometry, 1H NMR and 13C NMR. UV, infra-red and fluorescence spectra were also recorded. All data are in accordance with the two compounds being closely related indolo[3,2-b]carbazole derivatives. Evidence is presented that compound A (MW = 312) is the symmetrical 6,12-diformylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole, and compound B (MW = 284) is the monosubstituted 6-formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole. CONCLUSIONS: The elucidation of the structures of the two high affinity Ah receptor ligands 6,12-diformylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole and 6-formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole provides the necessary basis for further mechanistic studies of this important group of compounds, and will help in determining the natural role of the Ah receptor.


