PMPA (NAALADase inhibitor)Glutamate carboxypeptidase 2 inhibitor CAS# 173039-10-6 |
- Carboxypeptidase G2 (CPG2) Inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1452
CAS No.:192203-60-4
- CPA inhibitor
Catalog No.:BCC1500
CAS No.:223532-02-3
- 2-MPPA
Catalog No.:BCC7995
CAS No.:254737-29-6
- ZJ 43
Catalog No.:BCC2355
CAS No.:723331-20-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 173039-10-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 10130754 | Appearance | Powder |
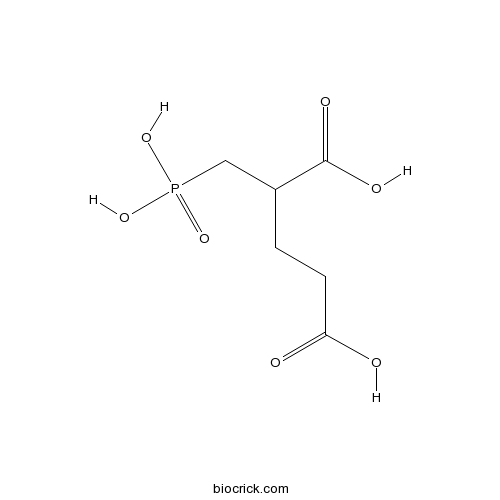
| Formula | C6H11O7P | M.Wt | 226.12 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | 2-(Phosphonomethyl)pentanedioic acid | ||
| Solubility | H2O : ≥ 28 mg/mL (123.83 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-(phosphonomethyl)pentanedioic acid | ||
| SMILES | C(CC(=O)O)C(CP(=O)(O)O)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ISEYJGQFXSTPMQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C6H11O7P/c7-5(8)2-1-4(6(9)10)3-14(11,12)13/h4H,1-3H2,(H,7,8)(H,9,10)(H2,11,12,13) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Highly potent and selective inhibitor of glutamate carboxypeptidase 2 (GCP II/N-acetylated α-linked dipeptidase/NAALADase) with a Ki value of 275 pM. Neuroprotective; protects against glutamate-mediated motor neuron degeneration and reduces volume of injury following middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). |

PMPA (NAALADase inhibitor) Dilution Calculator

PMPA (NAALADase inhibitor) Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.4224 mL | 22.1122 mL | 44.2243 mL | 88.4486 mL | 110.5608 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8845 mL | 4.4224 mL | 8.8449 mL | 17.6897 mL | 22.1122 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4422 mL | 2.2112 mL | 4.4224 mL | 8.8449 mL | 11.0561 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0884 mL | 0.4422 mL | 0.8845 mL | 1.769 mL | 2.2112 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0442 mL | 0.2211 mL | 0.4422 mL | 0.8845 mL | 1.1056 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
PMPA is a selective inhibitor of NAALADase with Ki value of 275 pM [1].
NAALADase also known as GCPII is a zinc metalloenzyme that resides in membranes and involves in the catalyzing process of neuropeptide NAAG to NAA and glutamate. It has been shown that NAALADase has the highest expression in nervous/ prostatic tissues and cancers and NAALADase inhibition produces a variety of effects on providing neuroprotection, detection, imaging and treatment of prostate cancer [2] [3].
PMPA is a potent NAALADase inhibitor and has a more activity than reported NAALADase inhibitor ZJ43. In male C57/Bl mice model, high doses of PMPA inhibited the morphine tolerance development (resembling the effect of 7.5 mg/kg of the NMDA receptor antagonist, memantine) while had no effect on severity of withdrawal; 100 mg/kg PMPA also significantly potentiated morphine withdrawal, but inhibited both acquisition and expression of morphine-induced conditioned place preference which suggested NAALADase involves in phenomena related to opioid addiction [4]. PMPA treatment increased the mice latency to enter the dark box during the training day and at the dose of 150 mg/kg PMPA treatment impaired spontaneous alternation and reduced locomotion in Y-maze task which demonstrated that PMPA affected mice learning and memory tasks through NAALADase inhibition [5].
References:
[1]. Tiffany, C.W., et al., Binding of the glutamate carboxypeptidase II (NAALADase) inhibitor 2-PMPA to rat brain membranes. Eur J Pharmacol, 2001. 427(2): p. 91-6.
[2]. Barinka, C., et al., Glutamate carboxypeptidase II in diagnosis and treatment of neurologic disorders and prostate cancer. Curr Med Chem, 2012. 19(6): p. 856-70.
[3]. Slusher, B.S., et al., Selective inhibition of NAALADase, which converts NAAG to glutamate, reduces ischemic brain injury. Nat Med, 1999. 5(12): p. 1396-402.
[4]. Popik, P., et al., Morphine tolerance and reward but not expression of morphine dependence are inhibited by the selective glutamate carboxypeptidase II (GCP II, NAALADase) inhibitor, 2-PMPA. Neuropsychopharmacology, 2003. 28(3): p. 457-67.
[5]. Lukawski, K., R.M. Kaminski, and S.J. Czuczwar, Effects of selective inhibition of N-acetylated-alpha-linked-acidic dipeptidase (NAALADase) on mice in learning and memory tasks. Eur J Pharmacol, 2008. 579(1-3): p. 202-7.
- Goniothalamin
Catalog No.:BCN4690
CAS No.:17303-67-2
- Poloxime
Catalog No.:BCC5307
CAS No.:17302-61-3
- Isoanthricin
Catalog No.:BCN3531
CAS No.:17301-70-5
- BWX 46
Catalog No.:BCC5865
CAS No.:172997-92-1
- Biorobin
Catalog No.:BCN4691
CAS No.:17297-56-2
- FICZ
Catalog No.:BCC5513
CAS No.:172922-91-7
- PB 28 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7411
CAS No.:172907-03-8
- Isosinensetin
Catalog No.:BCN2919
CAS No.:17290-70-9
- LY 266097 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7856
CAS No.:172895-39-5
- LY 272015 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7558
CAS No.:172895-15-7
- PP 2 (AG 1879)
Catalog No.:BCC3631
CAS No.:172889-27-9
- PP 1
Catalog No.:BCC3630
CAS No.:172889-26-8
- Rec 15/2615 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7628
CAS No.:173059-17-1
- Rhoifolin
Catalog No.:BCN1112
CAS No.:17306-46-6
- Ganoderic acid DM
Catalog No.:BCN1113
CAS No.:173075-45-1
- Centaureidin
Catalog No.:BCN2575
CAS No.:17313-52-9
- SQ 22536
Catalog No.:BCC7065
CAS No.:17318-31-9
- 4-Beta-Hydroxycholesterol
Catalog No.:BCN2752
CAS No.:17320-10-4
- Clomipramine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC5036
CAS No.:17321-77-6
- Broussonetine A
Catalog No.:BCN2515
CAS No.:173220-07-0
- 2,5-Dihydroxy-1-methoxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN7577
CAS No.:173220-32-1
- TC-E 5003
Catalog No.:BCC8008
CAS No.:17328-16-4
- Garciniaxanthone E
Catalog No.:BCN1114
CAS No.:173294-74-1
- Isorhamnetin 3-glucoside-7-rhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN1528
CAS No.:17331-71-4
Neuroprotection produced by the NAALADase inhibitor 2-PMPA in rat cerebellar neurons.[Pubmed:10940354]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2000 Aug 18;402(1-2):31-7.
The present study examined the neuroprotective actions of the N-acetylated-alpha-linked-acidic dipeptidase (NAALADase) inhibitor 2-(phosphonomethyl)pentanedioic acid (2-PMPA) in four in vitro models of neurotoxicity. Using neuron-enriched primary cultures derived from rat embryo (E15) cerebellum, 2-PMPA afforded 100% neuroprotection from injuries induced by hypoxia (EC(50)=8.4 microM). In contrast, against glutamate or N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) injury, 2-PMPA was less potent and its efficacy limited to a maximum of 46% and 16%, respectively. 2-PMPA was not effective against veratridine-induced injury. Also, the less potent analog of 2-PMPA, 2-[phosphonomethyl]succinic acid (2-PMSA), was ineffective. Unlike 2-PMPA, the endogenous NAALADase substrate and mGlu(3) receptor agonist N-acetyl-aspartyl-glutamate (NAAG) was neuroprotective against all four injury mechanisms and compared to 2-PMPA, exhibited a different "phosphate effect" on neuroprotection. These results confirm the superior efficacy of 2-PMPA to protect against injury caused by cellular anoxia, and are discussed relative to upstream modulation of hyperglutamatergic activity vs. downstream modulation of metabotropic receptors as possible targets for ischemia/stroke therapy.
Binding of the glutamate carboxypeptidase II (NAALADase) inhibitor 2-PMPA to rat brain membranes.[Pubmed:11557259]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2001 Sep 14;427(2):91-6.
2-Phosphonomethyl pentanedioic acid (2-PMPA) is a potent and selective inhibitor of glutamate carboxypeptidase II (NAALADase), and has shown robust neuroprotective activity in both in vitro and in vivo models of ischemia. In the brain, glutamate carboxypeptidase II (GCPII) (EC3.4.17.21) hydrolyzes the neuropeptide N-acetylaspartylglutamate (NAAG) to glutamate and N-acetylaspartate. We report the development and characterization of a [(3)H]2-PMPA binding assay. [(3)H]2-PMPA binding was dependent on protein concentration, saturable, and displaceable. The association (k(on)) and dissociation (k(off)) rate constants were 3x10(6) M(-1) s(-1) and 0.01 s(-1), respectively. The dissociation equilibrium constant (K(d)) determined from the ratio of the rate constants (K(d)=k(off)/k(on)) was 1 nM. Scatchard analysis revealed one binding site with K(d)=2 nM and B(max)=0.7 pmol/mg. Binding exhibited similar pharmacological properties to GCPII enzyme activity, including chloride dependency, cobalt stimulation and inhibition by phosphate and quisqualate. The binding of [(3)H]2-PMPA also showed tissue specificity in that tissues previously reported to be devoid of GCPII enzymatic activity were devoid of [(3)H]2-PMPA binding. [(3)H]2-PMPA binding represents an additional probe for the study of GCPII activity, and may be useful as a high throughput screening assay.
Morphine tolerance and reward but not expression of morphine dependence are inhibited by the selective glutamate carboxypeptidase II (GCP II, NAALADase) inhibitor, 2-PMPA.[Pubmed:12629525]
Neuropsychopharmacology. 2003 Mar;28(3):457-67.
Inhibition of glutamate carboxypeptidase II (GCP II; NAALADase) produces a variety of effects on glutamatergic neurotransmission. The aim of this study was to investigate effects of GCP II inhibition with the selective inhibitor, 2-PMPA, on: (a) development of tolerance to the antinociceptive effects, (b) withdrawal, and (c) conditioned reward produced by morphine in C57/Bl mice. The degree of tolerance was assessed using the tail-flick test before and after 6 days of twice daily (b.i.d.) administration of 2-PMPA and 10 mg/kg of morphine. Opioid withdrawal was measured 3 days after twice daily morphine (30 or 10 mg/kg) administration, followed by naloxone challenge. Conditioned morphine reward was investigated using conditioned place preference with a single morphine dose (10 mg/kg). High doses of 2-PMPA inhibited the development of morphine tolerance (resembling the effect of 7.5 mg/kg of the NMDA receptor antagonist, memantine) while not affecting the severity of withdrawal. A high dose of 2-PMPA (100 mg/kg) also significantly potentiated morphine withdrawal, but inhibited both acquisition and expression of morphine-induced conditioned place preference. Memantine inhibited the intensity of morphine withdrawal as well as acquisition and expression of morphine-induced conditioned place preference. In addition, 2-PMPA did not affect learning or memory retrieval in a simple two-trial test, nor did it produce withdrawal symptoms in morphine-dependent, placebo-challenged mice. Results suggest involvement of GCP II (NAALADase) in phenomena related to opioid addiction.


