Prucalopride5-HT4A and 5-HT4B receptor agonist CAS# 179474-81-8 |
- Piceatannol
Catalog No.:BCN5824
CAS No.:10083-24-6
- R788 disodium
Catalog No.:BCC3695
CAS No.:1025687-58-4
- GS-9973
Catalog No.:BCC5278
CAS No.:1229208-44-9
- R406 (free base)
Catalog No.:BCC2553
CAS No.:841290-80-0
- Fostamatinib (R788)
Catalog No.:BCC5082
CAS No.:901119-35-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 179474-81-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3052762 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H26ClN3O3 | M.Wt | 367.87 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | H2O : 50 mg/mL (135.92 mM; Need ultrasonic) DMSO : ≥ 31 mg/mL (84.27 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
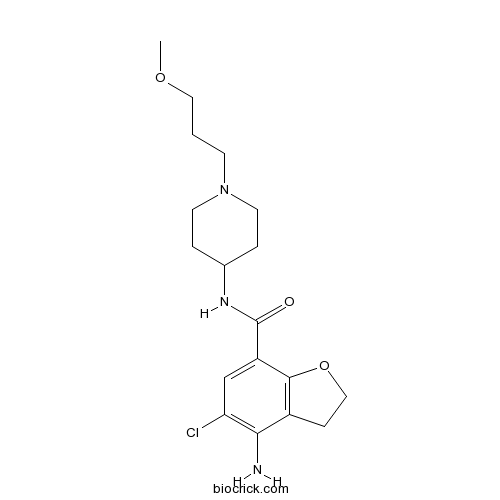
| Chemical Name | 4-amino-5-chloro-N-[1-(3-methoxypropyl)piperidin-4-yl]-2,3-dihydro-1-benzofuran-7-carboxamide | ||
| SMILES | COCCCN1CCC(CC1)NC(=O)C2=CC(=C(C3=C2OCC3)N)Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZPMNHBXQOOVQJL-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H26ClN3O3/c1-24-9-2-6-22-7-3-12(4-8-22)21-18(23)14-11-15(19)16(20)13-5-10-25-17(13)14/h11-12H,2-10,20H2,1H3,(H,21,23) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Prucalopride Dilution Calculator

Prucalopride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7184 mL | 13.5918 mL | 27.1835 mL | 54.367 mL | 67.9588 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5437 mL | 2.7184 mL | 5.4367 mL | 10.8734 mL | 13.5918 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2718 mL | 1.3592 mL | 2.7184 mL | 5.4367 mL | 6.7959 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0544 mL | 0.2718 mL | 0.5437 mL | 1.0873 mL | 1.3592 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0272 mL | 0.1359 mL | 0.2718 mL | 0.5437 mL | 0.6796 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Prucalopride is a selective, high affinity 5-HT receptor agonist for 5-HT4A and 5-HT4B receptor with Ki of 2.5 nM and 8 nM, respectively, exhibits >290-fold selectivity against other 5-HT receptor subtypes. Phase 3.
- Terrestrosin D
Catalog No.:BCN2934
CAS No.:179464-23-4
- Caspofungin Acetate
Catalog No.:BCC4895
CAS No.:179463-17-3
- PD 151746
Catalog No.:BCC5485
CAS No.:179461-52-0
- Leucodin
Catalog No.:BCN7105
CAS No.:17946-87-1
- 2-Methoxyanofinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7632
CAS No.:179457-70-6
- SDZ 220-581 Ammonium salt
Catalog No.:BCC1940
CAS No.:179411-94-0
- SDZ 220-581 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4157
CAS No.:179411-93-9
- AH 11110 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6883
CAS No.:179388-65-9
- Macrocarpal I
Catalog No.:BCN1138
CAS No.:179388-54-6
- Macrocarpal H
Catalog No.:BCN1137
CAS No.:179388-53-5
- Sumanirole maleate
Catalog No.:BCC4112
CAS No.:179386-44-8
- 7-O-Methyleucomol
Catalog No.:BCN6830
CAS No.:17934-15-5
- Prucalopride Succinat
Catalog No.:BCC4708
CAS No.:179474-85-2
- Rutacridone
Catalog No.:BCN7542
CAS No.:17948-33-3
- Venoterpine
Catalog No.:BCN3422
CAS No.:17948-42-4
- 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydronorharman-1-one
Catalog No.:BCN3690
CAS No.:17952-82-8
- PD 150606
Catalog No.:BCC2353
CAS No.:179528-45-1
- Cynaustraline
Catalog No.:BCN2048
CAS No.:17958-37-1
- Cynaustine
Catalog No.:BCN1951
CAS No.:17958-39-3
- Amabiline
Catalog No.:BCN1950
CAS No.:17958-43-9
- Macrocarpal J
Catalog No.:BCN1139
CAS No.:179603-47-5
- N-Benzoyl-leucine
Catalog No.:BCC9092
CAS No.:17966-67-5
- Aflastatin A
Catalog No.:BCN1822
CAS No.:179729-59-0
- 27-Hydroxymangiferolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4689
CAS No.:17983-82-3
Effect of prucalopride on intestinal gas tolerance in patients with functional bowel disorders and constipation.[Pubmed:28090679]
J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Aug;32(8):1457-1462.
BACKGROUND AND AIM: Patients with functional bowel disorders develop gas retention and symptoms in response to intestinal gas loads that are well tolerated by healthy subjects. Stimulation of 5HT-4 receptors in the gut has both prokinetic and antinociceptive effects. The aim of this study is to determine the effect of Prucalopride, a highly selective 5HT-4 agonist, on gas transit and tolerance in women with functional bowel disorders complaining of constipation. METHODS: Twenty-four women with functional bowel disorders complaining of constipation were included in the study. Patients were studied twice on separate days in a cross-over design. On each study day, an intestinal gas challenge test was performed. During the five previous days, Prucalopride (2 mg/day) or placebo was administered. Abdominal symptoms, stool frequency, and stool consistency were recorded during the treatment period on daily questionnaires. RESULTS: During the gas challenge test, Prucalopride did not decrease the volume of gas retained in the subset of patients who had significant gas retention (>/= 200 mL) while on placebo. However, in those patients who had increased symptoms during the gas test (>/= 3 on a 0 to 6 scale) when on placebo, Prucalopride did significantly reduce the perception of symptoms (2.3 +/- 0.5 mean score vs 3.5 +/- 0.3 on placebo; P = 0.045). During the treatment period with Prucalopride, patients exhibited an increase in the total number of bowel movements and decreased stool consistency compared with placebo. CONCLUSION: Prucalopride reduces abdominal symptoms without modifying gas retention when patients with functional bowel disorders are challenged with the gas transit and tolerance test. European Clinical Trials Database (EudraCT2011-006354-86).
Effects of Single-Dose Prucalopride on Intestinal Hypomotility in Horses: Preliminary Observations.[Pubmed:28128322]
Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 27;7:41526.
Abnormalities of gastrointestinal motility are often a challenge in horses; however, the use of prokinetic drugs in such conditions must be firmly established yet. For this reason we carried out a preliminary study on the effects of Prucalopride on intestinal motor activity of horses with gut hypomotility. The effect of Prucalopride per os by oral dose syringe (2 mg/100 kg body weight) was assessed by abdominal ultrasound (evaluating duodenal, cecal, and colonic motor activity) in six horses with gut hypomotility. After administration of Prucalopride, a significant increase of contractile activity was found in the duodenum at 30 minutes (p = 0.0005), 60 minutes (p = 0.01) and 90 minutes (p = 0.01), whereas in the cecum and in the left colon the increase was only present at 60 minutes (p = 0.03, and p = 0.02, respectively). No changes from baseline heart and respiratory rate or behavior side effects were observed after administration of the drug and throughout the observation period. Prucalopride may be a useful adjunct to the therapeutic armamentary for treating hypomotile upper gut conditions of horses. Dosing information is however needed to establish its actual clinical efficacy and its proper effects on the large bowel in these animals.
Prucalopride for the treatment of ileus.[Pubmed:28277883]
Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2017 Apr;26(4):489-493.
INTRODUCTION: Postoperative ileus (POI) is an impairment of coordinated gastrointestinal (GI) motility that develops as a consequence of abdominal surgery and is a major factor contributing to patient morbidity and prolonged hospitalisation. Despite the availability of various options its treatment is still under debate. This review will focus on effect of Prucalopride (5-HT4 receptor agonist) on postoperative ileus based on the existing literature. Areas covered: A literature search of MEDLINE, EMBASE and COCHRANE Library was performed concerning topics related to the treatment of ileus with Prucalopride. The search strategy also included articles relating to other treatments of ileus for comparison with Prucalopride. Expert opinion: Postoperative ileus remains difficult to treat and most strategies encompass preventative measures through enhanced recovery after surgery and laparoscopic approaches. The role of pharmacological intervention is developing with some drugs licensed for use. The evidence for Prucalopride remains unclear although there is randomised controlled trial (RCT) evidence available. Given the potential for reduction in patient morbidity and length of stay the role of Prucalopride in POI should be further investigated with multi-centre RCTs to establish which group of patients will gain the most from this exciting potential treatment.
Promotility Action of the Probiotic Bifidobacterium lactis HN019 Extract Compared with Prucalopride in Isolated Rat Large Intestine.[Pubmed:28184185]
Front Neurosci. 2017 Jan 26;11:20.
Attention is increasingly being focussed on probiotics as potential agents to restore or improve gastrointestinal (GI) transit. Determining mechanism of action would support robust health claims. The probiotic bacterium Bifidobacterium lactis HN019 reduces transit time, but its mechanisms of action and effects on motility patterns are poorly understood. The aim of this study was to investigate changes in GI motility induced by an extract of HN019 on distinct patterns of colonic motility in isolated rat large intestine, compared with a known promotility modulator, Prucalopride. The large intestines from male Sprague Dawley rats (3-6 months) were perfused with Kreb's buffer at 37 degrees C in an oxygenated tissue bath. Isometric force transducers recorded changes in circular muscle activity at four independent locations assessing contractile propagation between the proximal colon and the rectum. HN019 extract was perfused through the tissue bath and differences in tension and frequency quantified relative to pre-treatment controls. Prucalopride (1 muM) increased the frequency of propagating contractions (by 75 +/- 26%) in the majority of preparations studied (10/12), concurrently decreasing the frequency of non-propagating contractions (by 50 +/- 11%). HN019 extract had no effect on contractile activity during exposure (n = 8). However, following wash out, contraction amplitude of propagating contractions increased (by 55 +/- 18%) in the distal colon, while the frequency of non-propagating proximal contractions decreased by 57 +/- 7%. The prokinetic action of Prucalopride increased the frequency of synchronous contractions along the length of colon, likely explaining increased colonic rate of transit in vivo. HN019 extract modified motility patterns in a different manner by promoting propagating contractile amplitude and inhibiting non-propagations, also demonstrating prokinetic activity consistent with the reduction of constipation by B. lactis HN019 in humans.


