Fostamatinib (R788)Spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) inhibitor CAS# 901119-35-5 |
- Saquinavir
Catalog No.:BCC1921
CAS No.:127779-20-8
- Saquinavir mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC1922
CAS No.:149845-06-7
- Nelfinavir Mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC1794
CAS No.:159989-65-8
- Lopinavir
Catalog No.:BCC3621
CAS No.:192725-17-0
- Darunavir
Catalog No.:BCC3623
CAS No.:206361-99-1
- BMS-626529
Catalog No.:BCC1427
CAS No.:701213-36-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 901119-35-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11671467 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C23H26FN6O9P | M.Wt | 580.46 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Fostamatinib | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 62.5 mg/mL (107.67 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
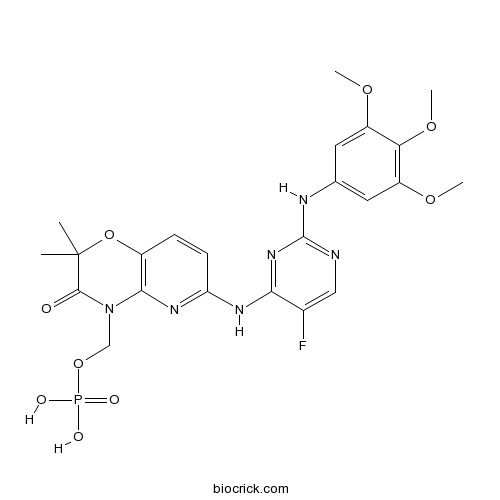
| Chemical Name | [6-[[5-fluoro-2-(3,4,5-trimethoxyanilino)pyrimidin-4-yl]amino]-2,2-dimethyl-3-oxopyrido[3,2-b][1,4]oxazin-4-yl]methyl dihydrogen phosphate | ||
| SMILES | CC1(C(=O)N(C2=C(O1)C=CC(=N2)NC3=NC(=NC=C3F)NC4=CC(=C(C(=C4)OC)OC)OC)COP(=O)(O)O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GKDRMWXFWHEQQT-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C23H26FN6O9P/c1-23(2)21(31)30(11-38-40(32,33)34)20-14(39-23)6-7-17(28-20)27-19-13(24)10-25-22(29-19)26-12-8-15(35-3)18(37-5)16(9-12)36-4/h6-10H,11H2,1-5H3,(H2,32,33,34)(H2,25,26,27,28,29) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | R788 (Fostamatinib), a prodrug of the active metabolite R406, is a potent Syk inhibitor with IC50 of 41 nM.
IC50 Value: 41 nM [1]
Target: Syk
in vitro: R788 is a methylene phosphate prodrug of R406, which can be rapidly converted to R406 in vivo. R406 (in vitro active form of R788) selectively inhibits Syk-dependent signaling with EC50 values ranging from 33 nM to 171 nM, more potently than Syk-independent pathways in different cells [1]. R406 inhibits cellular proliferation of a variety of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) cell lines with EC50 values ranging from 0.8 μM to 8.1 μM [2]. R406 treatment reduces basal phosphorylation of BLNK, Akt, glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3), forkhead box O (FOXO) and ERK not only in cells with high (TCL-002) but also in cells with low levels of phosphorylated Syk (TCL1-551). In addition, R406 completely inhibits the anti-IgM induced Bcr signal in TCL1 leukemias. Despite the higher levels of constitutively active Syk in TCL1 leukemias, R406 is not selectively cytotoxic to the leukemic cells [3].
in vivo: R788 effectively inhibits BCR signaling in vivo, resulting in reduced proliferation and survival of the malignant B cells and significantly prolonged survival of the treated animals [3]. References: | |||||

Fostamatinib (R788) Dilution Calculator

Fostamatinib (R788) Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7228 mL | 8.6139 mL | 17.2277 mL | 34.4554 mL | 43.0693 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3446 mL | 1.7228 mL | 3.4455 mL | 6.8911 mL | 8.6139 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1723 mL | 0.8614 mL | 1.7228 mL | 3.4455 mL | 4.3069 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0345 mL | 0.1723 mL | 0.3446 mL | 0.6891 mL | 0.8614 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0172 mL | 0.0861 mL | 0.1723 mL | 0.3446 mL | 0.4307 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Fostamatinib is a small molecule inhibitor of spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) with IC50 value of 41nM [1].
Fostamatinib is an orally bioavailable prodrug of R406. It is developed for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. The effective metabolite of fostamatinib, R406, is an ATP-competitive inhibitor of Syk with Ki value of 30nM. R406 also inhibits the activity of other kinases including Flt3, Lyn (IC50=63nM) and Lck (IC50=37nM). It is found that R406 inhibits both BCR and FcR mediated responses in vitro. Besides that, R406 also shows effects in other cells types and signalling pathways. In the in vivo assay, fostamatinib shows to be highly active to inhibit FcR-mediated signaling in various animal models of allergy, autoimmunity and inflammation. Moreover, fostamatinib also exerts efficacy in SLE animal models. Treatment of fostamatinib suppresses the established renal and skin disease and reduces lymphadenopathy in the MRL/lpr strain [1].
References:
[1] McAdoo S P, Tam F W K. Fostamatinib disodium. Drugs of the future, 2011, 36(4): 273.
- TAME
Catalog No.:BCC4367
CAS No.:901-47-3
- Rebamipide
Catalog No.:BCC4836
CAS No.:90098-04-7
- AVX 13616
Catalog No.:BCC5407
CAS No.:900814-48-4
- Chondroitin sulfate
Catalog No.:BCN1312
CAS No.:9007-28-7
- 5-O-beta-D-Glucopyranosylmyricanol
Catalog No.:BCN8044
CAS No.:90052-02-1
- AS-252424
Catalog No.:BCC4988
CAS No.:900515-16-4
- PF-3274167
Catalog No.:BCC6451
CAS No.:900510-03-4
- Inulin
Catalog No.:BCC4789
CAS No.:9005-80-5
- Ylangenyl acetate
Catalog No.:BCN6704
CAS No.:90039-63-7
- Detomidine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4346
CAS No.:90038-01-0
- PFI 4
Catalog No.:BCC6484
CAS No.:900305-37-5
- Agar (bacteriological)
Catalog No.:BCC1208
CAS No.:9002-18-0
- GSK 5959
Catalog No.:BCC5597
CAS No.:901245-65-6
- Gossypolone
Catalog No.:BCC1375
CAS No.:4547-72-2
- AT7519 Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1376
CAS No.:902135-91-5
- NVP-LCQ195
Catalog No.:BCC1816
CAS No.:902156-99-4
- UBP 310
Catalog No.:BCC6052
CAS No.:902464-46-4
- FPA 124
Catalog No.:BCC7518
CAS No.:902779-59-3
- 10-Deacetyl-7-xylosyl paclitaxel
Catalog No.:BCN2947
CAS No.:90332-63-1
- 7-Xylosyl-10-deacetyltaxol B
Catalog No.:BCN7667
CAS No.:90332-64-2
- 7-Xylosyl-10-deacetyltaxol C
Catalog No.:BCN7663
CAS No.:90332-65-3
- 7-Xylosyltaxol
Catalog No.:BCN5341
CAS No.:90332-66-4
- Shizukolidol
Catalog No.:BCN4444
CAS No.:90332-92-6
- Seneciphyllinine
Catalog No.:BCN2132
CAS No.:90341-45-0
Effects of fostamatinib (R788), an oral spleen tyrosine kinase inhibitor, on health-related quality of life in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: analyses of patient-reported outcomes from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.[Pubmed:23378467]
J Rheumatol. 2013 Apr;40(4):369-78.
OBJECTIVE: To assess the influence of fostamatinib on patient-reported outcomes (PRO) in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to methotrexate (MTX). METHODS: Patients taking background MTX (N = 457) were enrolled in a phase II clinical trial (NCT00665925) and randomized equally to placebo, fostamatinib 100 mg twice daily (bid), or fostamatinib 150 mg once daily (qd) for 24 weeks. Self-administered PRO measures included pain, patient's global assessment (PtGA) of disease activity, physical function, health-related quality of life (HRQOL), and fatigue. Mean change from baseline and a responder analysis of the proportion of patients achieving a minimal clinically important difference were determined. RESULTS: At Week 24, there were statistically significant improvements in pain, PtGA, physical function, fatigue, and the physical component summary of the Medical Outcomes Study Short Form-36 (SF-36) for fostamatinib 100 mg bid compared with placebo. Mean (standard error) changes from baseline in the fostamatinib 100 mg bid group versus the placebo group were -31.3 (2.45) versus -17.8 (2.45), p < 0.001 for pain; -29.1 (2.26) versus -16.7 (2.42), p < 0.001 for PtGA; -0.647 (0.064) versus -0.343 (0.062), p < 0.001 for physical function; 7.40 (1.00) versus 4.50 (0.94), p < 0.05 for fatigue; 8.52 (0.77) versus 4.90 (0.78), p < 0.01 for SF-36 physical component score; and 3.99 (0.93) versus 3.71 (0.99), p = 0.83 for SF-36 mental component score. Patients receiving fostamatinib 150 mg qd showed improvements in some PRO, including physical function. CONCLUSION: Patients treated with fostamatinib 100 mg bid showed significant improvements in HRQOL outcomes.
The Syk inhibitor fostamatinib disodium (R788) inhibits tumor growth in the Emu- TCL1 transgenic mouse model of CLL by blocking antigen-dependent B-cell receptor signaling.[Pubmed:20716772]
Blood. 2010 Dec 2;116(23):4894-905.
Inhibition of antigen-dependent B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling is considered a promising therapeutic approach in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), but experimental in vivo evidence to support this view is still lacking. We have now investigated whether inhibition of BCR signaling with the selective Syk inhibitor fostamatinib disodium (R788) will affect the growth of the leukemias that develop in the Emu-TCL1 transgenic mouse model of CLL. Similarly to human CLL, these leukemias express stereotyped BCRs that react with autoantigens exposed on the surface of senescent or apoptotic cells, suggesting that they are antigen driven. We show that R788 effectively inhibits BCR signaling in vivo, resulting in reduced proliferation and survival of the malignant B cells and significantly prolonged survival of the treated animals. The growth-inhibitory effect of R788 occurs despite the relatively modest cytotoxic effect in vitro and is independent of basal Syk activity, suggesting that R788 functions primarily by inhibiting antigen-dependent BCR signals. Importantly, the effect of R788 was found to be selective for the malignant clones, as no disturbance in the production of normal B lymphocytes was observed. Collectively, these data provide further rationale for clinical trials with R788 in CLL and establish the BCR-signaling pathway as an important therapeutic target in this disease.


