PD 150606Non-peptide calpain inhibitor CAS# 179528-45-1 |
- Calpain Inhibitor I, ALLN
Catalog No.:BCC1233
CAS No.:110044-82-1
- Calpeptin
Catalog No.:BCC2351
CAS No.:117591-20-5
- Acetyl-Calpastatin (184-210) (human)
Catalog No.:BCC2350
CAS No.:123714-50-1
- Calpain Inhibitor II, ALLM
Catalog No.:BCC1234
CAS No.:136632-32-1
- MDL 28170
Catalog No.:BCC2352
CAS No.:88191-84-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 179528-45-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9839500 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C9H7IO2S | M.Wt | 306.12 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 28 mg/mL (91.47 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
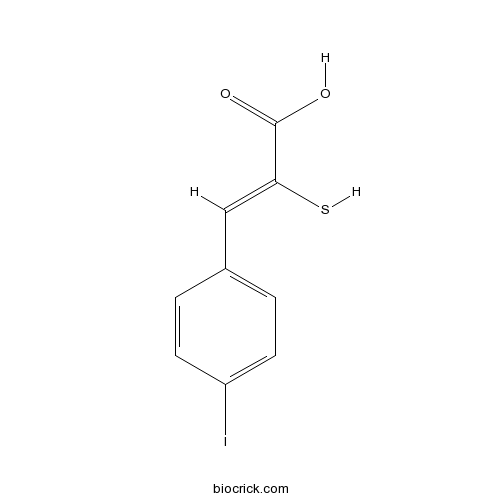
| Chemical Name | (Z)-3-(4-iodophenyl)-2-sulfanylprop-2-enoic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CC=C1C=C(C(=O)O)S)I | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DJCVSFWGKYHMKH-YVMONPNESA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C9H7IO2S/c10-7-3-1-6(2-4-7)5-8(13)9(11)12/h1-5,13H,(H,11,12)/b8-5- | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective, cell-permeable non-peptide calpain inhibitor (Ki values for ν and m-calpains are 0.21 and 0.37 μM respectively). Targets the calcium binding sites of calpain. Demonstrates high specificity for calpains relative to other proteases, and is a non-competitive inhibitor with respect to the substrate. |

PD 150606 Dilution Calculator

PD 150606 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.2667 mL | 16.3335 mL | 32.6669 mL | 65.3339 mL | 81.6673 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6533 mL | 3.2667 mL | 6.5334 mL | 13.0668 mL | 16.3335 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3267 mL | 1.6333 mL | 3.2667 mL | 6.5334 mL | 8.1667 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0653 mL | 0.3267 mL | 0.6533 mL | 1.3067 mL | 1.6333 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0327 mL | 0.1633 mL | 0.3267 mL | 0.6533 mL | 0.8167 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
PD 150606 is a specific inhibitor of calpain with Ki value of 0.21 μM and 0.37 μM for mu- and m- calpains, respectively [1].
Calpain is an enzyme and plays an important role in a variety of physiological processes, including signaling, cytoskeletal remodeling, regulation of gene expression, apoptosis and cell cycle progression. It has been shown that calpain involves in many pathologies, like muscular dystrophies, cancer, diabetes, Alzheimer's disease and multiple sclerosis [2] [3].
PD 150606 is a potent calpain inhibitor and has similar activity as calpain inhibitor-III. When tested with A2058, A375 and HS578T cell lines infected with ΔPK(resulted the failure of cells growth in 3D culture), administration of PD 150606 in a concentration of 100 μM restored 3D growth in soft sugar culture by inhibiting calpain [2].
Treated pathogen-free adult C57BL/6 mice with PD 150606 (3 mg/kg, i.p) before LPS injection to establish sepsis mouse model that had lower myocardial calpain activity, the result showed that PD 150606 prevented the degradation of myocardial Hsp90/p-Akt protein induced by LPS and inhibited myocardial caspase-3 activation and apoptosis [3].
References:
[1]. Wang, K.K., et al., An alpha-mercaptoacrylic acid derivative is a selective nonpeptide cell-permeable calpain inhibitor and is neuroprotective. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1996. 93(13): p. 6687-92.
[2]. Colunga, A., et al., Calpain-dependent clearance of the autophagy protein p62/SQSTM1 is a contributor to DeltaPK oncolytic activity in melanoma. Gene Ther, 2014. 21(4): p. 371-8.
[3]. Li, X., et al., The role of the Hsp90/Akt pathway in myocardial calpain-induced caspase-3 activation and apoptosis during sepsis. BMC Cardiovasc Disord, 2013. 13: p. 8.
- 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydronorharman-1-one
Catalog No.:BCN3690
CAS No.:17952-82-8
- Venoterpine
Catalog No.:BCN3422
CAS No.:17948-42-4
- Rutacridone
Catalog No.:BCN7542
CAS No.:17948-33-3
- Prucalopride Succinat
Catalog No.:BCC4708
CAS No.:179474-85-2
- Prucalopride
Catalog No.:BCC5055
CAS No.:179474-81-8
- Terrestrosin D
Catalog No.:BCN2934
CAS No.:179464-23-4
- Caspofungin Acetate
Catalog No.:BCC4895
CAS No.:179463-17-3
- PD 151746
Catalog No.:BCC5485
CAS No.:179461-52-0
- Leucodin
Catalog No.:BCN7105
CAS No.:17946-87-1
- 2-Methoxyanofinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7632
CAS No.:179457-70-6
- SDZ 220-581 Ammonium salt
Catalog No.:BCC1940
CAS No.:179411-94-0
- SDZ 220-581 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4157
CAS No.:179411-93-9
- Cynaustraline
Catalog No.:BCN2048
CAS No.:17958-37-1
- Cynaustine
Catalog No.:BCN1951
CAS No.:17958-39-3
- Amabiline
Catalog No.:BCN1950
CAS No.:17958-43-9
- Macrocarpal J
Catalog No.:BCN1139
CAS No.:179603-47-5
- N-Benzoyl-leucine
Catalog No.:BCC9092
CAS No.:17966-67-5
- Aflastatin A
Catalog No.:BCN1822
CAS No.:179729-59-0
- 27-Hydroxymangiferolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4689
CAS No.:17983-82-3
- 3-oxo-Olean-12-en-28-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3171
CAS No.:17990-42-0
- 7-Chlorokynurenic acid
Catalog No.:BCC6577
CAS No.:18000-24-3
- Ketohakonanol
Catalog No.:BCN7427
CAS No.:18004-20-1
- SDZ NKT 343
Catalog No.:BCC7349
CAS No.:180046-99-5
- Voafinidine
Catalog No.:BCN6738
CAS No.:180059-77-2
Sn- and Pd-Free Synthesis of D-pi-A Organic Sensitizers for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells by Cu-Catalyzed Direct Arylation.[Pubmed:28371473]
ChemSusChem. 2017 May 22;10(10):2284-2290.
The development of nanoparticle-polymer-hybrid-based heterogeneous catalysts with high reactivity and good recyclability is highly desired for their applications in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries. Herein, we have developed a novel synthetic strategy by choosing a predesigned metal-anchored building block for in situ generation of metal (Pd) nanoparticles in the stable, porous, and crystalline covalent organic framework (COF), without using conventional reducing agents. In situ generation of Pd nanoparticles in the COF skeleton is explicitly confirmed from PXRD, XPS, TEM images, and (15)N NMR spectral analysis. This hybrid material is found to be an excellent reusable heterogeneous catalyst for the synthesis of biologically and pharmaceutically important 2-substituted benzofurans from 2-bromophenols and terminal alkynes via a tandem process with the turnover number up to 1101. The heterogeneity of the catalytic process is unambiguously verified by a mercury poisoning experiment and leaching test. This hybrid material shows superior catalytic performance compared to commercially available homogeneous as well as heterogeneous Pd catalysts. Tumor expression of the immune co-signaling molecule CD274/PD-L1 was originally described as impeding antitumor immunity by direct engagement of its receptor, PDCD1/PD-1, on antitumor T cells. Melanoma-intrinsic PDCD1 was recently shown to promote tumor growth and MTOR signals in cooperation with tumor CD274, and sarcoma-intrinsic CD274 signaling promotes glucose metabolism to impede antitumor immunity. Our recent report shows that tumor cell-intrinsic CD274 promotes MTORC1 signaling in mouse melanoma and mouse and human ovarian cancer, inhibits autophagy and sensitizes some tumors to clinically available pharmacological autophagy inhibitors and confers resistance to MTOR inhibitors. Tumor CD274 could be a biomarker of autophagy or MTOR inhibitor response in selected tumors, and these inhibitors could improve anti-CD274 or anti-PDCD1 cancer immunotherapy. As we found that distinct tumor types exhibit this CD274-driven phenotype, it could be widely applicable. The role of Ca++ in cell death is controversial. Extracellular Ca++ influx and calpain activation occurred during the late phase of renal proximal tubule cell injury produced by the mitochondrial inhibitor antimycin A. Chelation of intracellular Ca++, extracellular Ca++, the calcium channel blocker nifedipine, calpain inhibitor 1 and the dissimilar calpain inhibitor PD150606 blocked antimycin A-induced influx of extracellular Ca++ and cell death. The calcium channel blocker verapamil was ineffective. Calpain inhibitor 1 and PD150606 were cytoprotective also against tetrafluoroethyl-L-cysteine-, bromohydroquinone-, oxidant (t-butylhydroperoxide)- and calcium ionophore (ionomycin)-induced cell death. Extracellular Ca++ influx was associated with the translocation of calpain activity from the cytosol to the membrane and was prevented by calpain inhibitor 1, PD150606 and nifedipine. Finally, nifedipine, calpain inhibitor 1, PD150606 and the Cl- channel inhibitors [5-nitro-2-(3-phenylpropylamino)-benzoate, niflumic acid, diphenylamine-2-carboxylate, and indanyloxyacetic acid] blocked the increase in Cl- influx that occurs during the late phase of cell injury and triggers terminal cell swelling and death. These data suggest that Ca++ and calpains play a common and critical role in renal proximal tubule cell death produced by diverse agents. In addition, calpain activation appears to play a dual role during the late phase of cell injury. Initial calpain activation elicits extracellular Ca++ influx through a nifedipine-sensitive pathway, resulting in calpain translocation to the membrane and in turn Cl- influx. Overactivation of calcium-activated neutral protease (calpain) has been implicated in the pathophysiology of several degenerative conditions, including stroke, myocardial ischemia, neuromuscular degeneration, and cataract formation. Alpha-mercaptoacrylate derivatives (exemplified by PD150606), with potent and selective inhibitory actions against calpain, have been identified. PD150606 exhibits the following characteristics: (i) Ki values for mu- and m-calpains of 0.21 microM and 0.37 microM, respectively, (ii) high specificity for calpains relative to other proteases, (iii) uncompetitive inhibition with respect to substrate, and (iv) it does not shield calpain against inactivation by the active-site inhibitor trans-(epoxysuccinyl)-L-leucyl-amido-3-methylbutane, suggesting a nonactive site action for PD150606. The recombinant calcium-binding domain from each of the large or small subunits of mu-calpain was found to interact with PD150606. In low micromolar range, PD15O6O6 inhibited calpain activity in two intact cell systems. The neuroprotective effects of this class of compound were also demonstrated by the ability of PD150606 to attenuate hypoxic/hypoglycemic injury to cerebrocortical neurons in culture and excitotoxic injury to Purkinje cells in cerebellar slices.Predesigned Metal-Anchored Building Block for In Situ Generation of Pd Nanoparticles in Porous Covalent Organic Framework: Application in Heterogeneous Tandem Catalysis.[Pubmed:28368103]
ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017 Apr 19;9(15):13785-13792.
Tumor cell-intrinsic CD274/PD-L1: A novel metabolic balancing act with clinical potential.[Pubmed:28368722]
Autophagy. 2017 May 4;13(5):987-988.
Calpains mediate calcium and chloride influx during the late phase of cell injury.[Pubmed:9399991]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997 Dec;283(3):1177-84.
An alpha-mercaptoacrylic acid derivative is a selective nonpeptide cell-permeable calpain inhibitor and is neuroprotective.[Pubmed:8692879]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jun 25;93(13):6687-92.


